| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
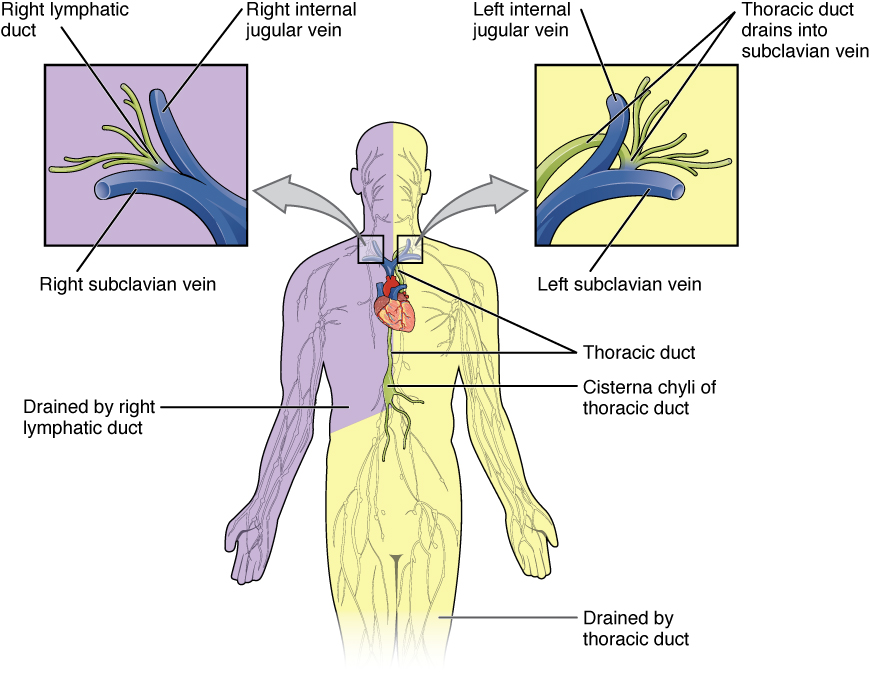
The overall drainage system of the body is asymmetrical (see [link] ). The right lymphatic duct receives lymph from only the upper right side of the body. The lymph from the rest of the body enters the bloodstream through the thoracic duct via all the remaining lymphatic trunks. In general, lymphatic vessels of the subcutaneous tissues of the skin, that is, the superficial lymphatics, follow the same routes as veins, whereas the deep lymphatic vessels of the viscera generally follow the paths of arteries.
The immune system is a collection of barriers, cells, and soluble proteins that interact and communicate with each other in extraordinarily complex ways. The modern model of immune function is organized into three phases based on the timing of their effects. The three temporal phases consist of the following:
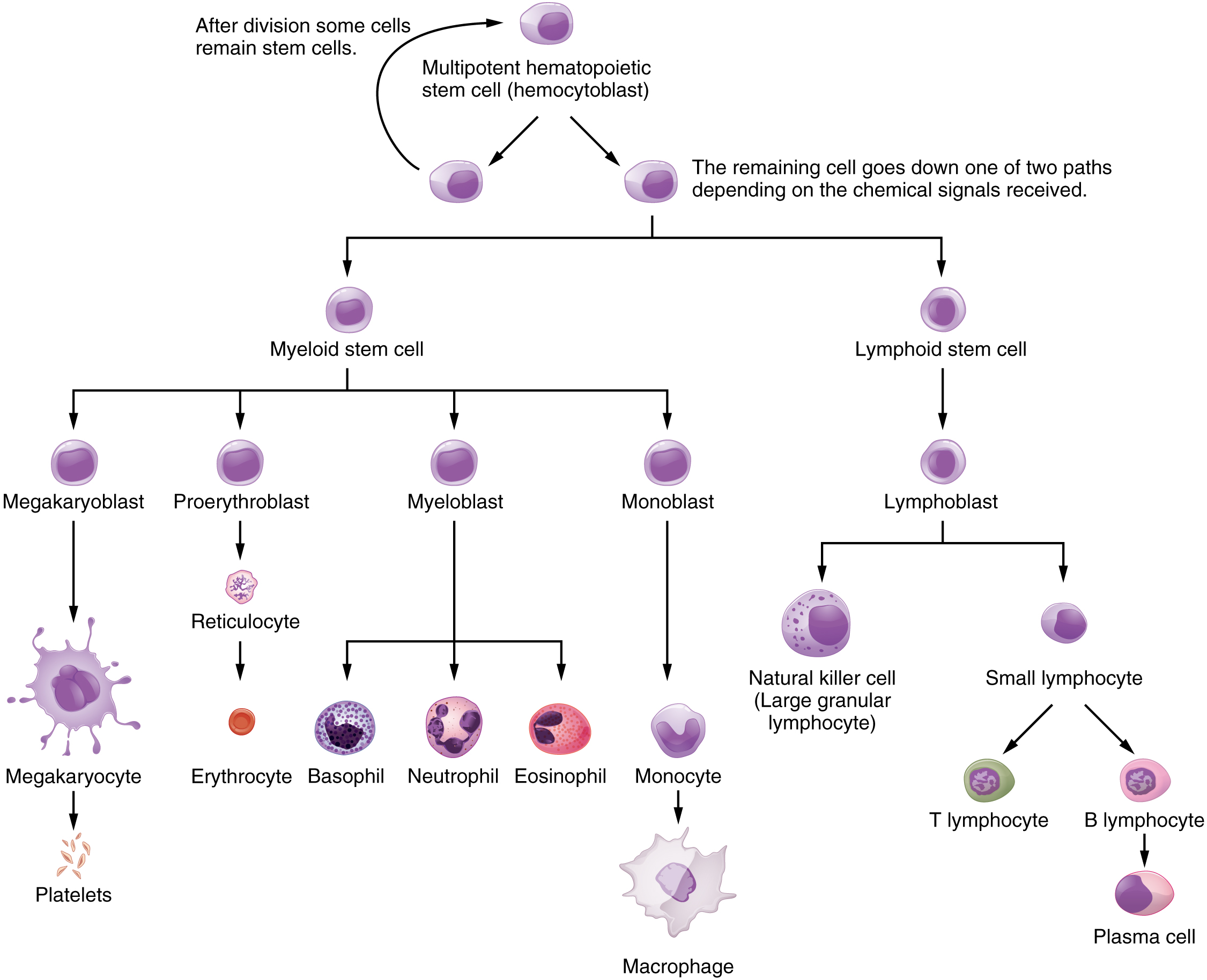
The cells of the blood, including all those involved in the immune response, arise in the bone marrow via various differentiation pathways from hematopoietic stem cells ( [link] ). In contrast with embryonic stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells are present throughout adulthood and allow for the continuous differentiation of blood cells to replace those lost to age or function. These cells can be divided into three classes based on function:
As stated above, lymphocytes are the primary cells of adaptive immune responses ( [link] ). The two basic types of lymphocytes, B cells and T cells, are identical morphologically with a large central nucleus surrounded by a thin layer of cytoplasm. They are distinguished from each other by their surface protein markers as well as by the molecules they secrete. While B cells mature in red bone marrow and T cells mature in the thymus, they both initially develop from bone marrow. T cells migrate from bone marrow to the thymus gland where they further mature. B cells and T cells are found in many parts of the body, circulating in the bloodstream and lymph, and residing in secondary lymphoid organs, including the spleen and lymph nodes, which will be described later in this section. The human body contains approximately 10 12 lymphocytes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?