| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
View the University of Michigan WebScope at (External Link) to explore the tissue sample in greater detail. If you zoom on the cells at the outermost layer of this section of skin, what do you notice about the cells?
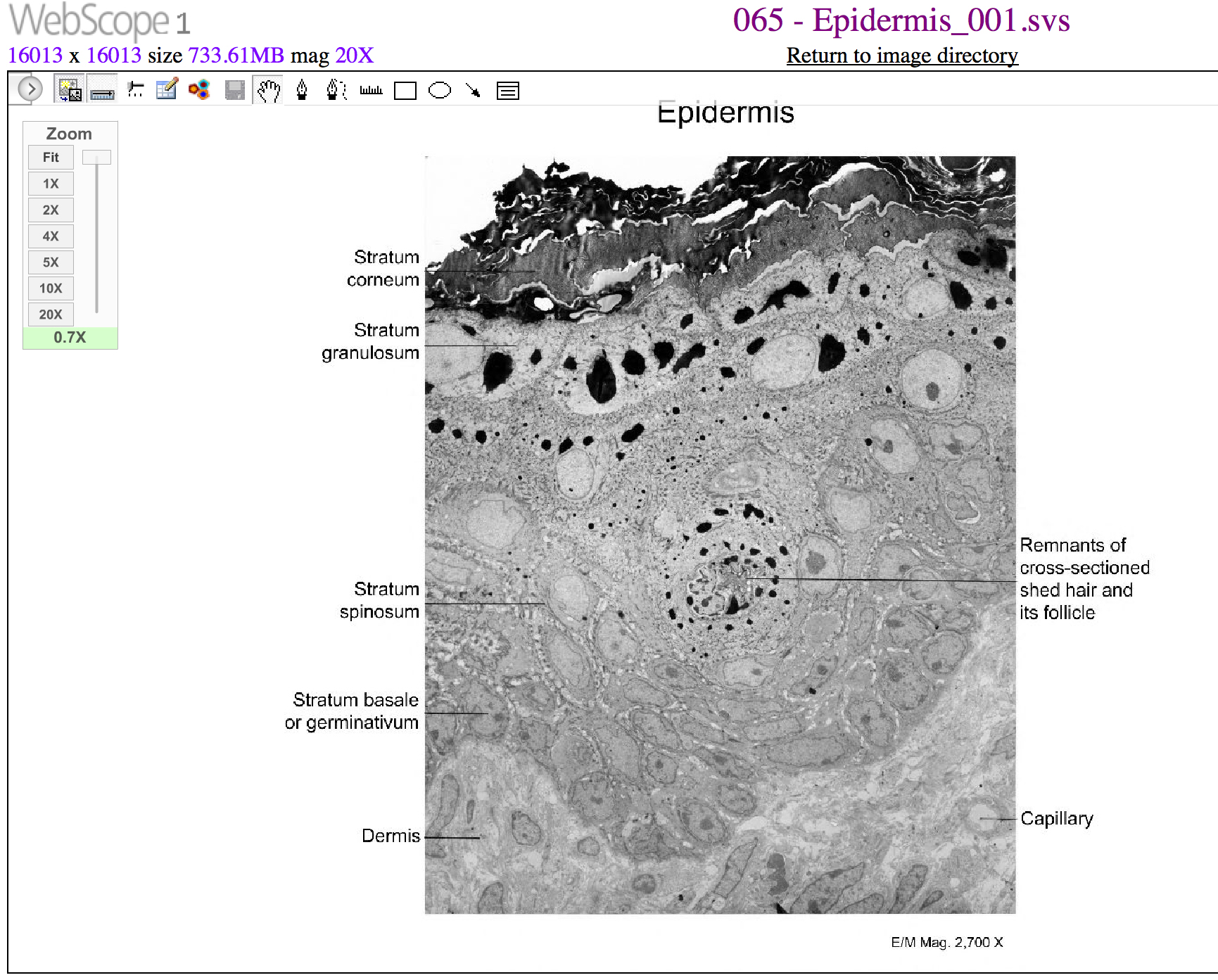
The keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum begin the synthesis of keratin and release a water-repelling glycolipid that helps prevent water loss from the body, making the skin relatively waterproof. As new keratinocytes are produced atop the stratum basale, the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum are pushed into the stratum granulosum.
The stratum granulosum has a grainy appearance due to further changes to the keratinocytes as they are pushed from the stratum spinosum. The cells (three to five layers deep) become flatter, their cell membranes thicken, and they generate large amounts of the proteins keratin, which is fibrous, and keratohyalin , which accumulates as lamellar granules within the cells (see [link] ). These two proteins make up the bulk of the keratinocyte mass in the stratum granulosum and give the layer its grainy appearance. The nuclei and other cell organelles disintegrate as the cells die, leaving behind the keratin, keratohyalin, and cell membranes that will form the stratum lucidum, the stratum corneum, and the accessory structures of hair and nails.
The stratum lucidum is a smooth, seemingly translucent layer of the epidermis located just above the stratum granulosum and below the stratum corneum. This thin layer of cells is found only in the thick skin of the palms, soles, and digits. The keratinocytes that compose the stratum lucidum are dead and flattened (see [link] ). These cells are densely packed with eleiden , a clear protein rich in lipids, derived from keratohyalin, which gives these cells their transparent (i.e., lucid) appearance and provides a barrier to water.
The stratum corneum is the most superficial layer of the epidermis and is the layer exposed to the outside environment (see [link] ). The increased keratinization (also called cornification) of the cells in this layer gives it its name. There are usually 15 to 30 layers of cells in the stratum corneum. This dry, dead layer helps prevent the penetration of microbes and the dehydration of underlying tissues, and provides a mechanical protection against abrasion for the more delicate, underlying layers. Cells in this layer are shed periodically and are replaced by cells pushed up from the stratum granulosum (or stratum lucidum in the case of the palms and soles of feet). The entire layer is replaced during a period of about 4 weeks. Cosmetic procedures, such as microdermabrasion, help remove some of the dry, upper layer and aim to keep the skin looking “fresh” and healthy.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?