| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
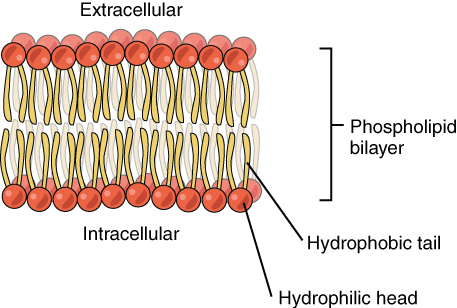
The lipid bilayer forms the basis of the cell membrane, but it is peppered throughout with various proteins. Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein ( [link] ). As its name suggests, an integral protein is a protein that is embedded in the membrane. A channel protein is an example of an integral protein that selectively allows particular materials, such as certain ions, to pass into or out of the cell.
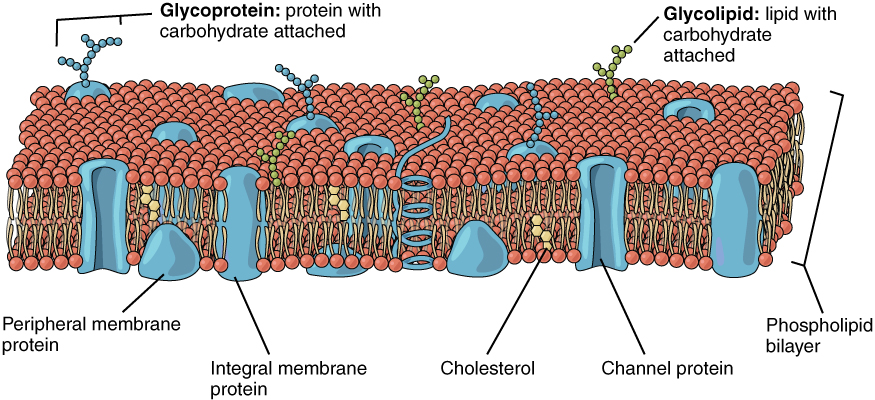
Another important group of integral proteins are cell recognition proteins, which serve to mark a cell’s identity so that it can be recognized by other cells. A receptor is a type of recognition protein that can selectively bind a specific molecule outside the cell, and this binding induces a chemical reaction within the cell. A ligand is the specific molecule that binds to and activates a receptor. Some integral proteins serve dual roles as both a receptor and an ion channel. One example of a receptor-ligand interaction is the receptors on nerve cells that bind neurotransmitters, such as dopamine. When a dopamine molecule binds to a dopamine receptor protein, a channel within the transmembrane protein opens to allow certain ions to flow into the cell.
Some integral membrane proteins are glycoproteins. A glycoprotein is a protein that has carbohydrate molecules attached, which extend into the extracellular matrix. The attached carbohydrate tags on glycoproteins aid in cell recognition. The carbohydrates that extend from membrane proteins and even from some membrane lipids collectively form the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx is a fuzzy-appearing coating around the cell formed from glycoproteins and other carbohydrates attached to the cell membrane. The glycocalyx can have various roles. For example, it may have molecules that allow the cell to bind to another cell, it may contain receptors for hormones, or it might have enzymes to break down nutrients. The glycocalyces found in a person’s body are products of that person’s genetic makeup. They give each of the individual’s trillions of cells the “identity” of belonging in the person’s body. This identity is the primary way that a person’s immune defense cells “know” not to attack the person’s own body cells, but it also is the reason organs donated by another person might be rejected.
Peripheral proteins are typically found on the inner or outer surface of the lipid bilayer but can also be attached to the internal or external surface of an integral protein. These proteins typically perform a specific function for the cell. Some peripheral proteins on the surface of intestinal cells, for example, act as digestive enzymes to break down nutrients to sizes that can pass through the cells and into the bloodstream.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?