| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A major distinction between the lymphatic and cardiovascular systems in humans is that lymph is not actively pumped by the heart, but is forced through the vessels by the movements of the body, the contraction of skeletal muscles during body movements, and breathing. One-way valves (semi-lunar valves) in lymphatic vessels keep the lymph moving toward the heart. Lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck.
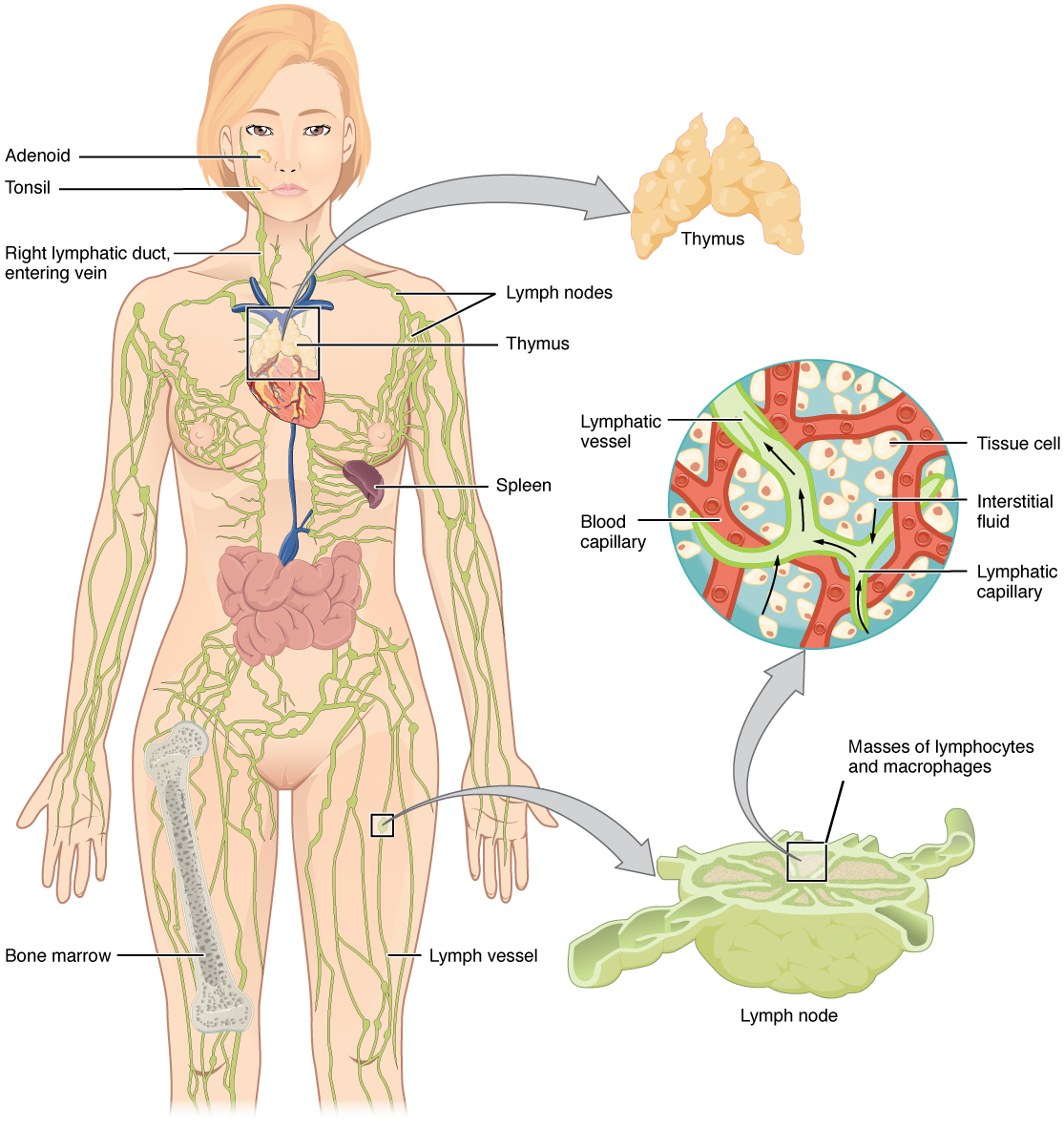
Lymphatic capillaries , also called the terminal lymphatics, are vessels where interstitial fluid enters the lymphatic system to become lymph fluid. Located in almost every tissue in the body, these vessels are interlaced among the arterioles and venules of the circulatory system in the soft connective tissues of the body ( [link] ). Exceptions are the central nervous system, bone marrow, bones, teeth, and the cornea of the eye, which do not contain lymph vessels.
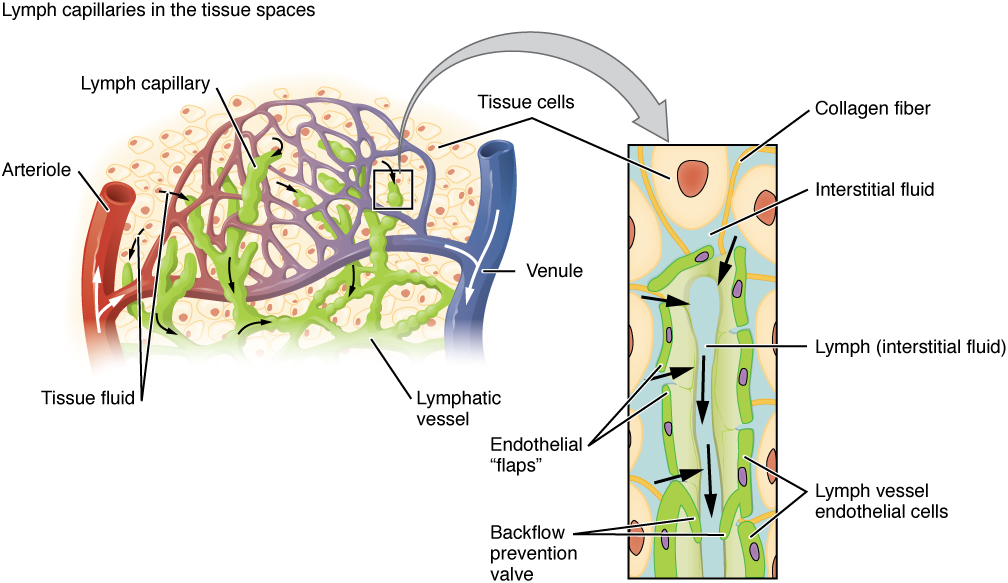
Lymphatic capillaries are formed by a one cell-thick layer of endothelial cells and represent the open end of the system, allowing interstitial fluid to flow into them via overlapping cells (see [link] ). When interstitial pressure is low, the endothelial flaps close to prevent “backflow.” As interstitial pressure increases, the spaces between the cells open up, allowing the fluid to enter. Entry of fluid into lymphatic capillaries is also enabled by the collagen filaments that anchor the capillaries to surrounding structures. As interstitial pressure increases, the filaments pull on the endothelial cell flaps, opening up them even further to allow easy entry of fluid.
In the small intestine, lymphatic capillaries called lacteals are critical for the transport of dietary lipids and lipid-soluble vitamins to the bloodstream. In the small intestine, dietary triglycerides combine with other lipids and proteins, and enter the lacteals to form a milky fluid called chyle . The chyle then travels through the lymphatic system, eventually entering the liver and then the bloodstream.
The lymphatic capillaries empty into larger lymphatic vessels, which are similar to veins in terms of their three-tunic structure and the presence of valves. These one-way valves are located fairly close to one another, and each one causes a bulge in the lymphatic vessel, giving the vessels a beaded appearance (see [link] ).
The superficial and deep lymphatics eventually merge to form larger lymphatic vessels known as lymphatic trunks . On the right side of the body, the right sides of the head, thorax, and right upper limb drain lymph fluid into the right subclavian vein via the right lymphatic duct ( [link] ). On the left side of the body, the remaining portions of the body drain into the larger thoracic duct, which drains into the left subclavian vein. The thoracic duct itself begins just beneath the diaphragm in the cisterna chyli , a sac-like chamber that receives lymph from the lower abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs by way of the left and right lumbar trunks and the intestinal trunk.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?