| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Propagation of an action potential along the sarcolemma is the excitation portion of excitation-contraction coupling. Recall that this excitation actually triggers the release of calcium ions (Ca ++ ) from its storage in the cell’s SR. For the action potential to reach the membrane of the SR, there are periodic invaginations in the sarcolemma, called T-tubules (“T” stands for “transverse”). You will recall that the diameter of a muscle fiber can be up to 100 μ m, so these T-tubules ensure that the membrane can get close to the SR in the sarcoplasm. The arrangement of a T-tubule with the membranes of SR on either side is called a triad ( [link] ). The triad surrounds the cylindrical structure called a myofibril , which contains actin and myosin.
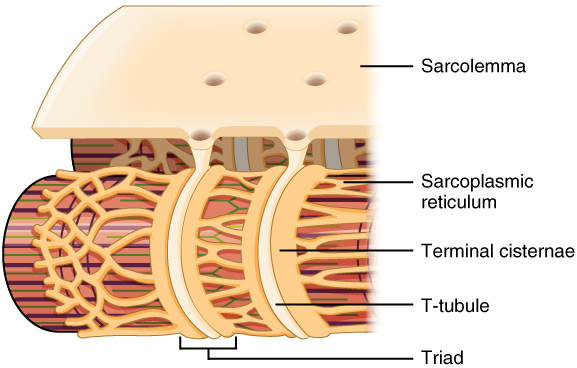
The T-tubules carry the action potential into the interior of the cell, which triggers the opening of calcium channels in the membrane of the adjacent SR, causing Ca ++ to diffuse out of the SR and into the sarcoplasm. It is the arrival of Ca ++ in the sarcoplasm that initiates contraction of the muscle fiber by its contractile units, or sarcomeres.
Skeletal muscles contain connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. There are three layers of connective tissue: epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat.
Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a form of endoplasmic reticulum. Muscle fibers are composed of myofibrils. The striations are created by the organization of actin and myosin resulting in the banding pattern of myofibrils.
Watch this video to learn more about macro- and microstructures of skeletal muscles. (a) What are the names of the “junction points” between sarcomeres? (b) What are the names of the “subunits” within the myofibrils that run the length of skeletal muscle fibers? (c) What is the “double strand of pearls” described in the video? (d) What gives a skeletal muscle fiber its striated appearance?
(a) Z-lines. (b) Sarcomeres. (c) This is the arrangement of the actin and myosin filaments in a sarcomere. (d) The alternating strands of actin and myosin filaments.
Every skeletal muscle fiber is supplied by a motor neuron at the NMJ. Watch this video to learn more about what happens at the neuromuscular junction. (a) What is the definition of a motor unit? (b) What is the structural and functional difference between a large motor unit and a small motor unit? Can you give an example of each? (c) Why is the neurotransmitter acetylcholine degraded after binding to its receptor?
(a) It is the number of skeletal muscle fibers supplied by a single motor neuron. (b) A large motor unit has one neuron supplying many skeletal muscle fibers for gross movements, like the Temporalis muscle, where 1000 fibers are supplied by one neuron. A small motor has one neuron supplying few skeletal muscle fibers for very fine movements, like the extraocular eye muscles, where six fibers are supplied by one neuron. (c) To avoid prolongation of muscle contraction.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?