| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although smooth muscle contraction relies on the presence of Ca ++ ions, smooth muscle fibers have a much smaller diameter than skeletal muscle cells. T-tubules are not required to reach the interior of the cell and therefore not necessary to transmit an action potential deep into the fiber. Smooth muscle fibers have a limited calcium-storing SR but have calcium channels in the sarcolemma (similar to cardiac muscle fibers) that open during the action potential along the sarcolemma. The influx of extracellular Ca ++ ions, which diffuse into the sarcoplasm to reach the calmodulin, accounts for most of the Ca ++ that triggers contraction of a smooth muscle cell.
Muscle contraction continues until ATP-dependent calcium pumps actively transport Ca ++ ions back into the SR and out of the cell. However, a low concentration of calcium remains in the sarcoplasm to maintain muscle tone. This remaining calcium keeps the muscle slightly contracted, which is important in certain tracts and around blood vessels.
Because most smooth muscles must function for long periods without rest, their power output is relatively low, but contractions can continue without using large amounts of energy. Some smooth muscle can also maintain contractions even as Ca ++ is removed and myosin kinase is inactivated/dephosphorylated. This can happen as a subset of cross-bridges between myosin heads and actin, called latch-bridges , keep the thick and thin filaments linked together for a prolonged period, and without the need for ATP. This allows for the maintaining of muscle “tone” in smooth muscle that lines arterioles and other visceral organs with very little energy expenditure.
Smooth muscle is not under voluntary control; thus, it is called involuntary muscle. The triggers for smooth muscle contraction include hormones, neural stimulation by the ANS, and local factors. In certain locations, such as the walls of visceral organs, stretching the muscle can trigger its contraction (the stretch-relaxation response).
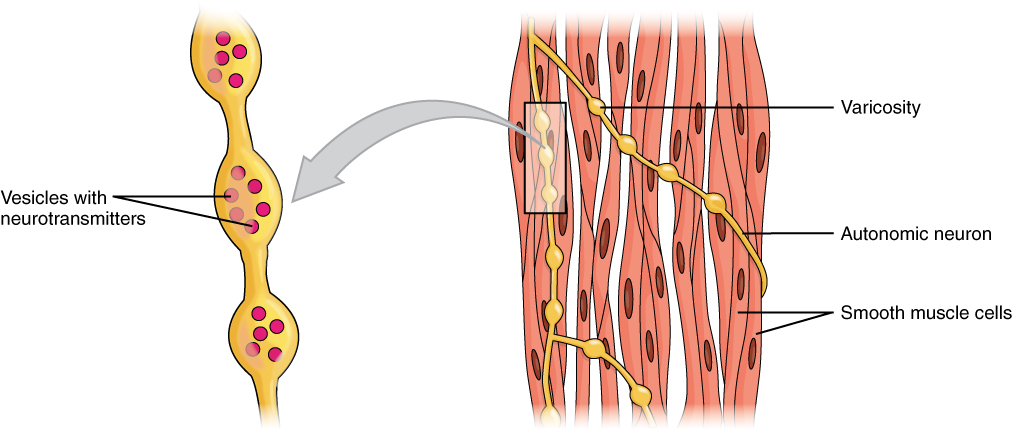
Axons of neurons in the ANS do not form the highly organized NMJs with smooth muscle, as seen between motor neurons and skeletal muscle fibers. Instead, there is a series of neurotransmitter-filled bulges called varicosities as an axon courses through smooth muscle, loosely forming motor units ( [link] ). A varicosity releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Also, visceral muscle in the walls of the hollow organs (except the heart) contains pacesetter cells. A pacesetter cell can spontaneously trigger action potentials and contractions in the muscle.
Smooth muscle is organized in two ways: as single-unit smooth muscle, which is much more common; and as multiunit smooth muscle. The two types have different locations in the body and have different characteristics. Single-unit muscle has its muscle fibers joined by gap junctions so that the muscle contracts as a single unit. This type of smooth muscle is found in the walls of all visceral organs except the heart (which has cardiac muscle in its walls), and so it is commonly called visceral muscle . Because the muscle fibers are not constrained by the organization and stretchability limits of sarcomeres, visceral smooth muscle has a stress-relaxation response . This means that as the muscle of a hollow organ is stretched when it fills, the mechanical stress of the stretching will trigger contraction, but this is immediately followed by relaxation so that the organ does not empty its contents prematurely. This is important for hollow organs, such as the stomach or urinary bladder, which continuously expand as they fill. The smooth muscle around these organs also can maintain a muscle tone when the organ empties and shrinks, a feature that prevents “flabbiness” in the empty organ. In general, visceral smooth muscle produces slow, steady contractions that allow substances, such as food in the digestive tract, to move through the body.
Multiunit smooth muscle cells rarely possess gap junctions, and thus are not electrically coupled. As a result, contraction does not spread from one cell to the next, but is instead confined to the cell that was originally stimulated. Stimuli for multiunit smooth muscles come from autonomic nerves or hormones but not from stretching. This type of tissue is found around large blood vessels, in the respiratory airways, and in the eyes.
Similar to skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle can undergo hypertrophy to increase in size. Unlike other muscle, smooth muscle can also divide to produce more cells, a process called hyperplasia . This can most evidently be observed in the uterus at puberty, which responds to increased estrogen levels by producing more uterine smooth muscle fibers, and greatly increases the size of the myometrium.
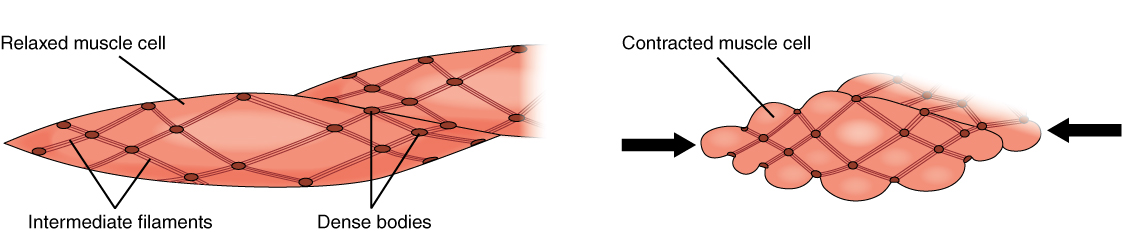
Smooth muscle is found throughout the body around various organs and tracts. Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus, and are spindle-shaped. Smooth muscle cells can undergo hyperplasia, mitotically dividing to produce new cells. The smooth cells are nonstriated, but their sarcoplasm is filled with actin and myosin, along with dense bodies in the sarcolemma to anchor the thin filaments and a network of intermediate filaments involved in pulling the sarcolemma toward the fiber’s middle, shortening it in the process. Ca ++ ions trigger contraction when they are released from SR and enter through opened voltage-gated calcium channels. Smooth muscle contraction is initiated when the Ca ++ binds to intracellular calmodulin, which then activates an enzyme called myosin kinase that phosphorylates myosin heads so they can form the cross-bridges with actin and then pull on the thin filaments. Smooth muscle can be stimulated by pacesetter cells, by the autonomic nervous system, by hormones, spontaneously, or by stretching. The fibers in some smooth muscle have latch-bridges, cross-bridges that cycle slowly without the need for ATP; these muscles can maintain low-level contractions for long periods. Single-unit smooth muscle tissue contains gap junctions to synchronize membrane depolarization and contractions so that the muscle contracts as a single unit. Single-unit smooth muscle in the walls of the viscera, called visceral muscle, has a stress-relaxation response that permits muscle to stretch, contract, and relax as the organ expands. Multiunit smooth muscle cells do not possess gap junctions, and contraction does not spread from one cell to the next.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?