| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
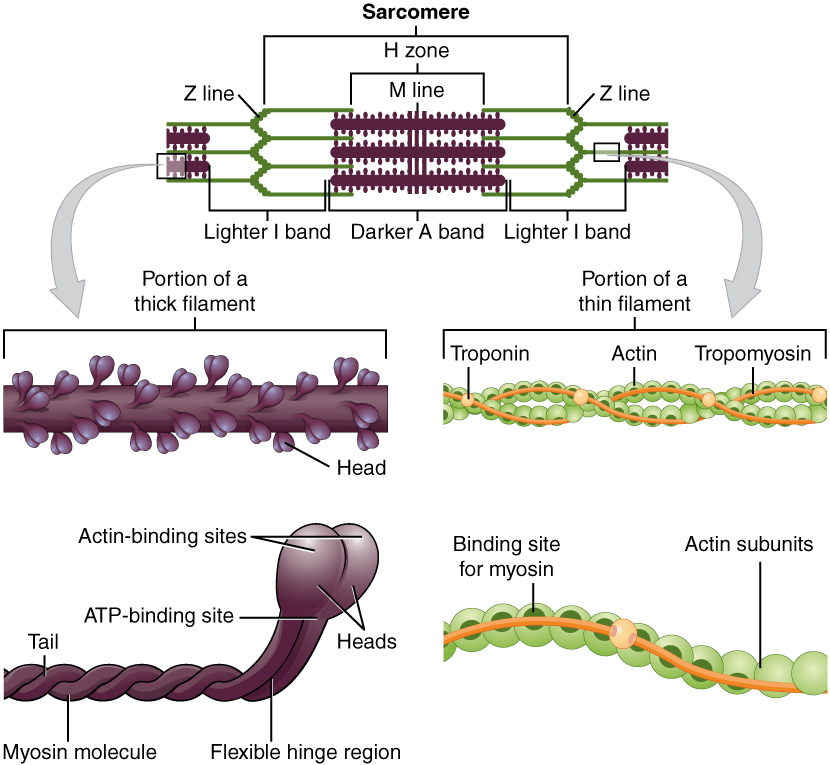
The sarcomere is the functional unit of the muscle fiber. The sarcomere itself is bundled within the myofibril that runs the entire length of the muscle fiber and attaches to the sarcolemma at its end. As myofibrils contract, the entire muscle cell contracts. Because myofibrils are only approximately 1.2 μ m in diameter, hundreds to thousands (each with thousands of sarcomeres) can be found inside one muscle fiber. Each sarcomere is approximately 2 μ m in length with a three-dimensional cylinder-like arrangement and is bordered by structures called Z-discs (also called Z-lines, because pictures are two-dimensional), to which the actin myofilaments are anchored ( [link] ). Because the actin and its troponin-tropomyosin complex (projecting from the Z-discs toward the center of the sarcomere) form strands that are thinner than the myosin, it is called the thin filament of the sarcomere. Likewise, because the myosin strands and their multiple heads (projecting from the center of the sarcomere, toward but not all to way to, the Z-discs) have more mass and are thicker, they are called the thick filament of the sarcomere.
Another specialization of the skeletal muscle is the site where a motor neuron’s terminal meets the muscle fiber—called the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) . This is where the muscle fiber first responds to signaling by the motor neuron. Every skeletal muscle fiber in every skeletal muscle is innervated by a motor neuron at the NMJ. Excitation signals from the neuron are the only way to functionally activate the fiber to contract.
Every skeletal muscle fiber is supplied by a motor neuron at the NMJ. Watch this video to learn more about what happens at the NMJ. (a) What is the definition of a motor unit? (b) What is the structural and functional difference between a large motor unit and a small motor unit? (c) Can you give an example of each? (d) Why is the neurotransmitter acetylcholine degraded after binding to its receptor?
All living cells have membrane potentials, or electrical gradients across their membranes. The inside of the membrane is usually around -60 to -90 mV, relative to the outside. This is referred to as a cell’s membrane potential. Neurons and muscle cells can use their membrane potentials to generate electrical signals. They do this by controlling the movement of charged particles, called ions, across their membranes to create electrical currents. This is achieved by opening and closing specialized proteins in the membrane called ion channels. Although the currents generated by ions moving through these channel proteins are very small, they form the basis of both neural signaling and muscle contraction.
Both neurons and skeletal muscle cells are electrically excitable, meaning that they are able to generate action potentials. An action potential is a special type of electrical signal that can travel along a cell membrane as a wave. This allows a signal to be transmitted quickly and faithfully over long distances.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?