| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inside the nuclear envelope is a gel-like nucleoplasm with solutes that include the building blocks of nucleic acids. There also can be a dark-staining mass often visible under a simple light microscope, called a nucleolus (plural = nucleoli). The nucleolus is a region of the nucleus that is responsible for manufacturing the RNA necessary for construction of ribosomes. Once synthesized, newly made ribosomal subunits exit the cell’s nucleus through the nuclear pores.
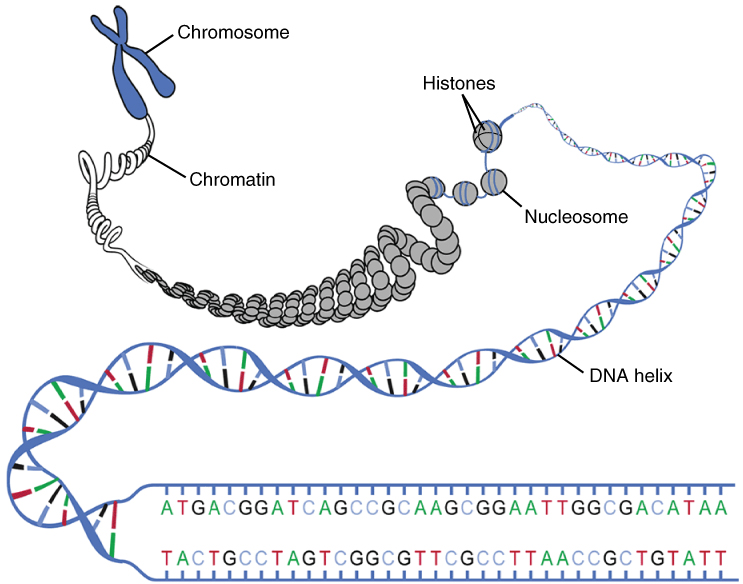
The genetic instructions that are used to build and maintain an organism are arranged in an orderly manner in strands of DNA. Within the nucleus are threads of chromatin composed of DNA and associated proteins ( [link] ). Along the chromatin threads, the DNA is wrapped around a set of histone proteins. A nucleosome is a single, wrapped DNA-histone complex. Multiple nucleosomes along the entire molecule of DNA appear like a beaded necklace, in which the string is the DNA and the beads are the associated histones. When a cell is in the process of division, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, so that the DNA can be safely transported to the “daughter cells.” The chromosome is composed of DNA and proteins; it is the condensed form of chromatin. It is estimated that humans have almost 22,000 genes distributed on 46 chromosomes.
In order for an organism to grow, develop, and maintain its health, cells must reproduce themselves by dividing to produce two new daughter cells, each with the full complement of DNA as found in the original cell. Billions of new cells are produced in an adult human every day. Only very few cell types in the body do not divide, including nerve cells, skeletal muscle fibers, and cardiac muscle cells. The division time of different cell types varies. Epithelial cells of the skin and gastrointestinal lining, for instance, divide very frequently to replace those that are constantly being rubbed off of the surface by friction.
A DNA molecule is made of two strands that “complement” each other in the sense that the molecules that compose the strands fit together and bind to each other, creating a double-stranded molecule that looks much like a long, twisted ladder. Each side rail of the DNA ladder is composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups ( [link] ). The two sides of the ladder are not identical, but are complementary. These two backbones are bonded to each other across pairs of protruding bases, each bonded pair forming one “rung,” or cross member. The four DNA bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). Because of their shape and charge, the two bases that compose a pair always bond together. Adenine always binds with thymine, and cytosine always binds with guanine. The particular sequence of bases along the DNA molecule determines the genetic code. Therefore, if the two complementary strands of DNA were pulled apart, you could infer the order of the bases in one strand from the bases in the other, complementary strand. For example, if one strand has a region with the sequence AGTGCCT, then the sequence of the complementary strand would be TCACGGA.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?