| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
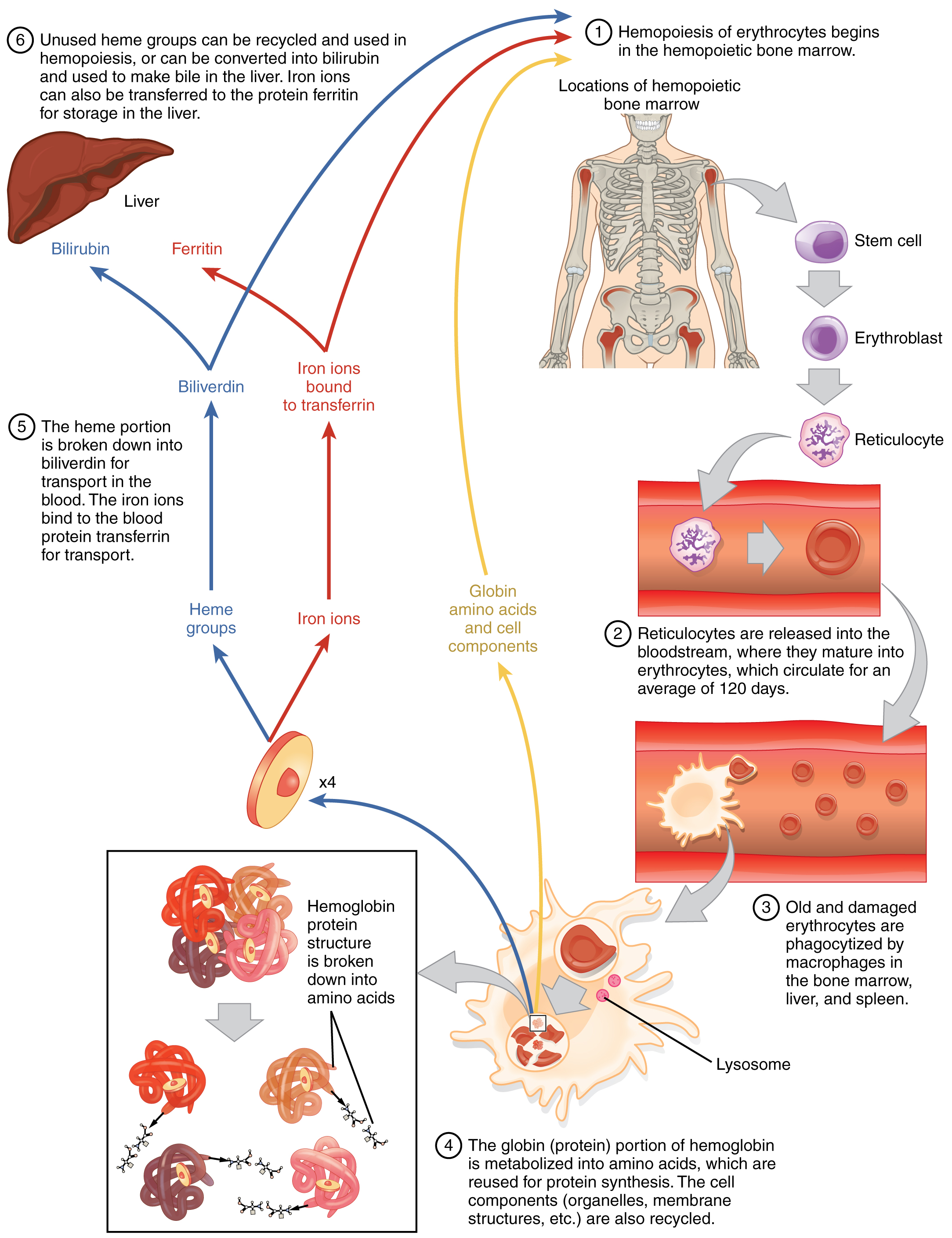
Erythrocytes live up to 120 days in the circulation, after which the worn-out cells are removed by a type of myeloid phagocytic cell called a macrophage , located primarily within the bone marrow, liver, and spleen. The components of the degraded erythrocytes’ hemoglobin are further processed as follows:
The breakdown pigments formed from the destruction of hemoglobin can be seen in a variety of situations. At the site of an injury, biliverdin from damaged RBCs produces some of the dramatic colors associated with bruising. With a failing liver, bilirubin cannot be removed effectively from circulation and causes the body to assume a yellowish tinge associated with jaundice. Stercobilins within the feces produce the typical brown color associated with this waste. And the yellow of urine is associated with the urobilins.
The erythrocyte lifecycle is summarized in [link] .
The size, shape, and number of erythrocytes, and the number of hemoglobin molecules can have a major impact on a person’s health. When the number of RBCs or hemoglobin is deficient, the general condition is called anemia . There are more than 400 types of anemia and more than 3.5 million Americans suffer from this condition. Anemia can be broken down into three major groups: those caused by blood loss, those caused by faulty or decreased RBC production, and those caused by excessive destruction of RBCs. Clinicians often use two groupings in diagnosis: The kinetic approach focuses on evaluating the production, destruction, and removal of RBCs, whereas the morphological approach examines the RBCs themselves, paying particular emphasis to their size. A common test is the mean corpuscle volume (MCV), which measures size. Normal-sized cells are referred to as normocytic, smaller-than-normal cells are referred to as microcytic, and larger-than-normal cells are referred to as macrocytic. Reticulocyte counts are also important and may reveal inadequate production of RBCs. The effects of the various anemias are widespread, because reduced numbers of RBCs or hemoglobin will result in lower levels of oxygen being delivered to body tissues. Since oxygen is required for tissue functioning, anemia produces fatigue, lethargy, and an increased risk for infection. An oxygen deficit in the brain impairs the ability to think clearly, and may prompt headaches and irritability. Lack of oxygen leaves the patient short of breath, even as the heart and lungs work harder in response to the deficit.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?