| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
DNA replication is the copying of DNA that occurs before cell division can take place. After a great deal of debate and experimentation, the general method of DNA replication was deduced in 1958 by two scientists in California, Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. This method is illustrated in [link] and described below.
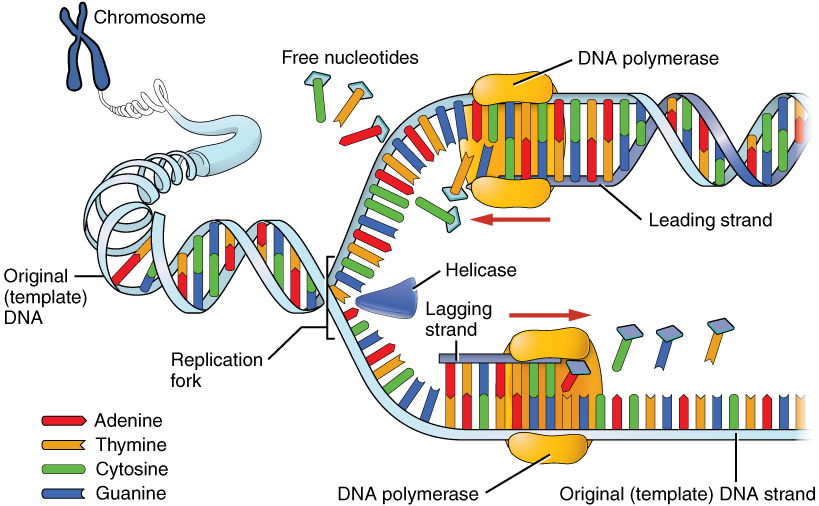
Stage 1: Initiation. The two complementary strands are separated, much like unzipping a zipper. Special enzymes, including helicase , untwist and separate the two strands of DNA.
Stage 2: Elongation. Each strand becomes a template along which a new complementary strand is built. DNA polymerase brings in the correct bases to complement the template strand, synthesizing a new strand base by base. A DNA polymerase is an enzyme that adds free nucleotides to the end of a chain of DNA, making a new double strand. This growing strand continues to be built until it has fully complemented the template strand.
Stage 3: Termination. Once the two original strands are bound to their own, finished, complementary strands, DNA replication is stopped and the two new identical DNA molecules are complete.
Each new DNA molecule contains one strand from the original molecule and one newly synthesized strand. The term for this mode of replication is “semiconservative,” because half of the original DNA molecule is conserved in each new DNA molecule. This process continues until the cell’s entire genome , the entire complement of an organism’s DNA, is replicated. As you might imagine, it is very important that DNA replication take place precisely so that new cells in the body contain the exact same genetic material as their parent cells. Mistakes made during DNA replication, such as the accidental addition of an inappropriate nucleotide, have the potential to render a gene dysfunctional or useless. Fortunately, there are mechanisms in place to minimize such mistakes. A DNA proofreading process enlists the help of special enzymes that scan the newly synthesized molecule for mistakes and corrects them. Once the process of DNA replication is complete, the cell is ready to divide. You will explore the process of cell division later in the chapter.
Watch this video to learn about DNA replication. DNA replication proceeds simultaneously at several sites on the same molecule. What separates the base pair at the start of DNA replication?
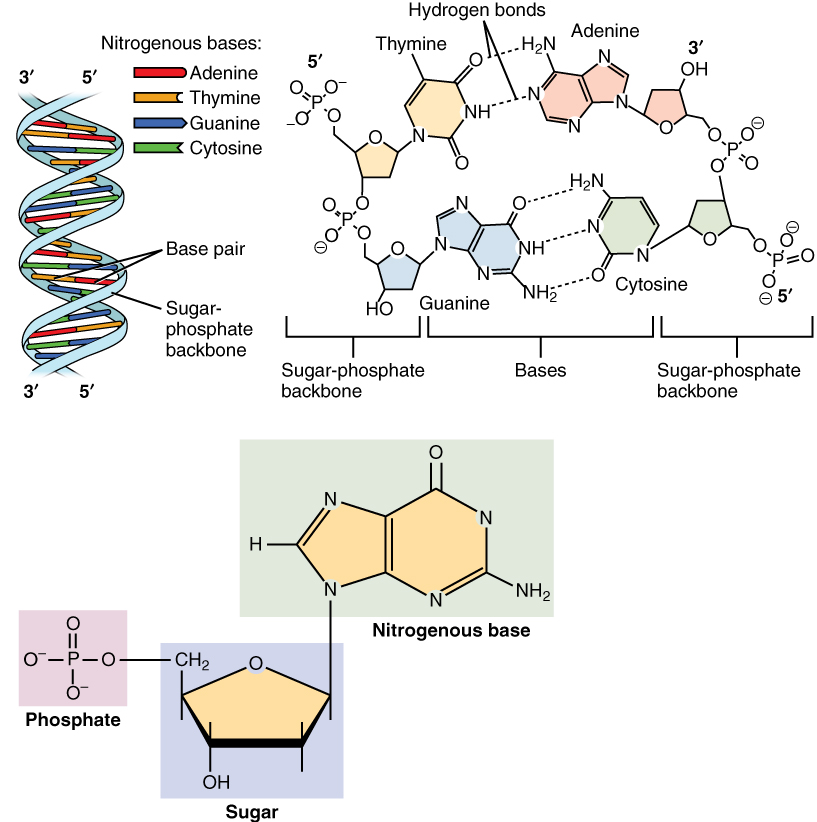
The nucleus is the command center of the cell, containing the genetic instructions for all of the materials a cell will make (and thus all of its functions it can perform). The nucleus is encased within a membrane of two interconnected lipid bilayers, side-by-side. This nuclear envelope is studded with protein-lined pores that allow materials to be trafficked into and out of the nucleus. The nucleus contains one or more nucleoli, which serve as sites for ribosome synthesis. The nucleus houses the genetic material of the cell: DNA. DNA is normally found as a loosely contained structure called chromatin within the nucleus, where it is wound up and associated with a variety of histone proteins. When a cell is about to divide, the chromatin coils tightly and condenses to form chromosomes.
There is a pool of cells constantly dividing within your body. The result is billions of new cells being created each day. Before any cell is ready to divide, it must replicate its DNA so that each new daughter cell will receive an exact copy of the organism’s genome. A variety of enzymes are enlisted during DNA replication. These enzymes unwind the DNA molecule, separate the two strands, and assist with the building of complementary strands along each parent strand. The original DNA strands serve as templates from which the nucleotide sequence of the new strands are determined and synthesized. When replication is completed, two identical DNA molecules exist. Each one contains one original strand and one newly synthesized complementary strand.
Watch this video to learn about DNA replication. DNA replication proceeds simultaneously at several sites on the same molecule. What separates the base pair at the start of DNA replication?
an enzyme

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?