| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
The skeletal system forms the rigid internal framework of the body. It consists of the bones, cartilages, and ligaments. Bones support the weight of the body, allow for body movements, and protect internal organs. Cartilage provides flexible strength and support for body structures such as the thoracic cage, the external ear, and the trachea and larynx. At joints of the body, cartilage can also unite adjacent bones or provide cushioning between them. Ligaments are the strong connective tissue bands that hold the bones at a moveable joint together and serve to prevent excessive movements of the joint that would result in injury. Providing movement of the skeleton are the muscles of the body, which are firmly attached to the skeleton via connective tissue structures called tendons. As muscles contract, they pull on the bones to produce movements of the body. Thus, without a skeleton, you would not be able to stand, run, or even feed yourself!
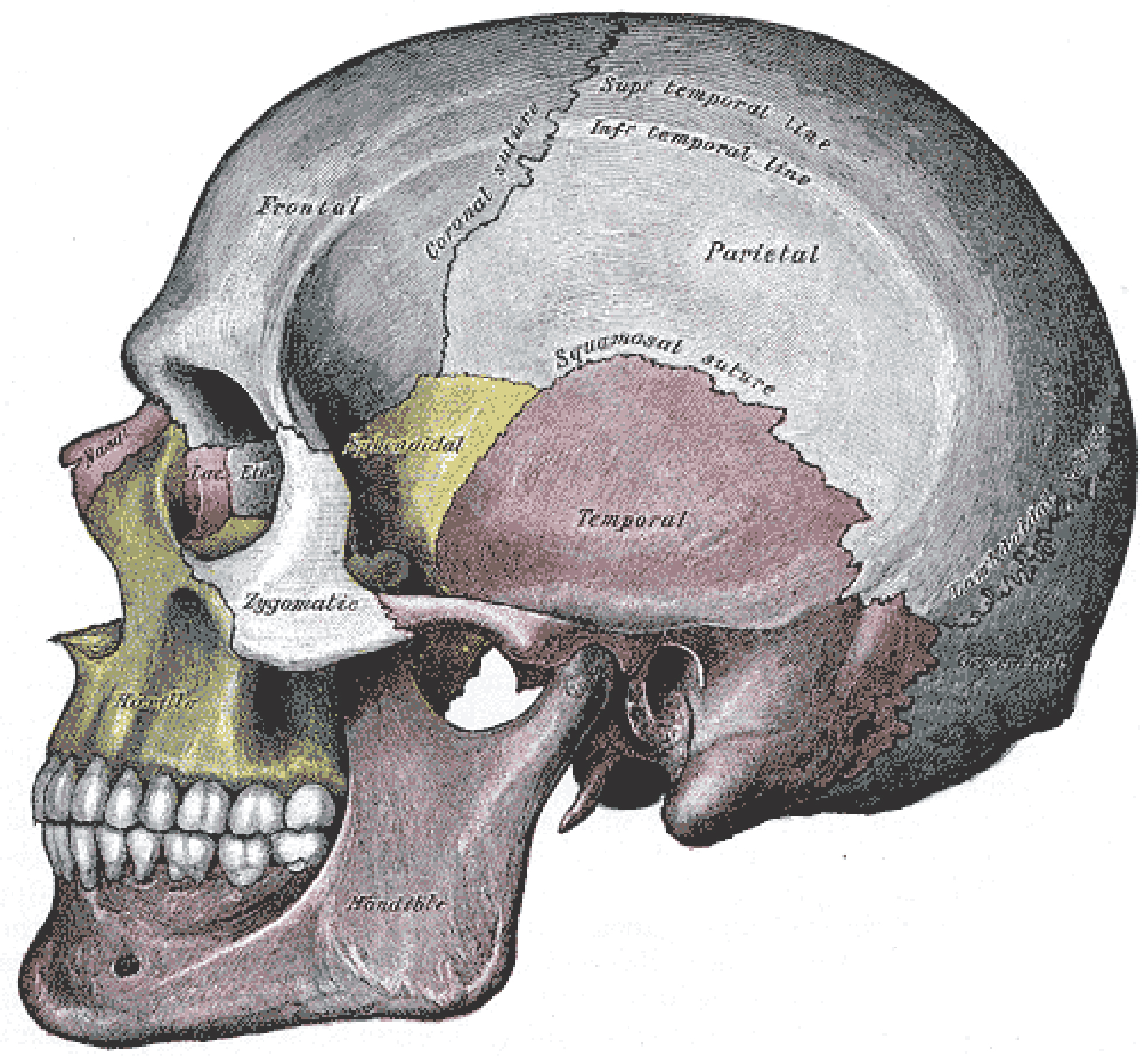
Each bone of the body serves a particular function, and therefore bones vary in size, shape, and strength based on these functions. For example, the bones of the lower back and lower limb are thick and strong to support your body weight. Similarly, the size of a bony landmark that serves as a muscle attachment site on an individual bone is related to the strength of this muscle. Muscles can apply very strong pulling forces to the bones of the skeleton. To resist these forces, bones have enlarged bony landmarks at sites where powerful muscles attach. This means that not only the size of a bone, but also its shape, is related to its function. For this reason, the identification of bony landmarks is important during your study of the skeletal system.
Bones are also dynamic organs that can modify their strength and thickness in response to changes in muscle strength or body weight. Thus, muscle attachment sites on bones will thicken if you begin a workout program that increases muscle strength. Similarly, the walls of weight-bearing bones will thicken if you gain body weight or begin pounding the pavement as part of a new running regimen. In contrast, a reduction in muscle strength or body weight will cause bones to become thinner. This may happen during a prolonged hospital stay, following limb immobilization in a cast, or going into the weightlessness of outer space. Even a change in diet, such as eating only soft food due to the loss of teeth, will result in a noticeable decrease in the size and thickness of the jaw bones.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?