| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
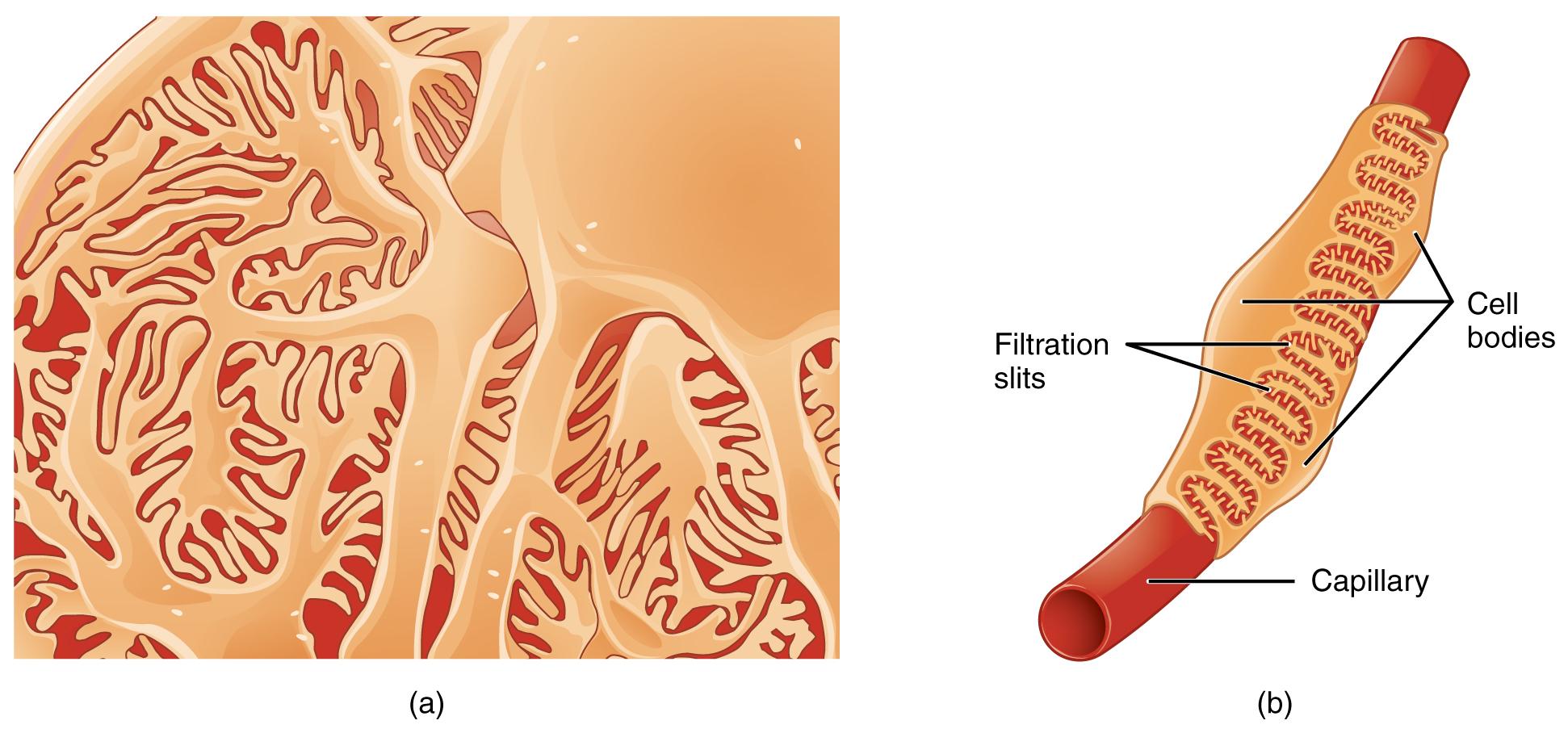
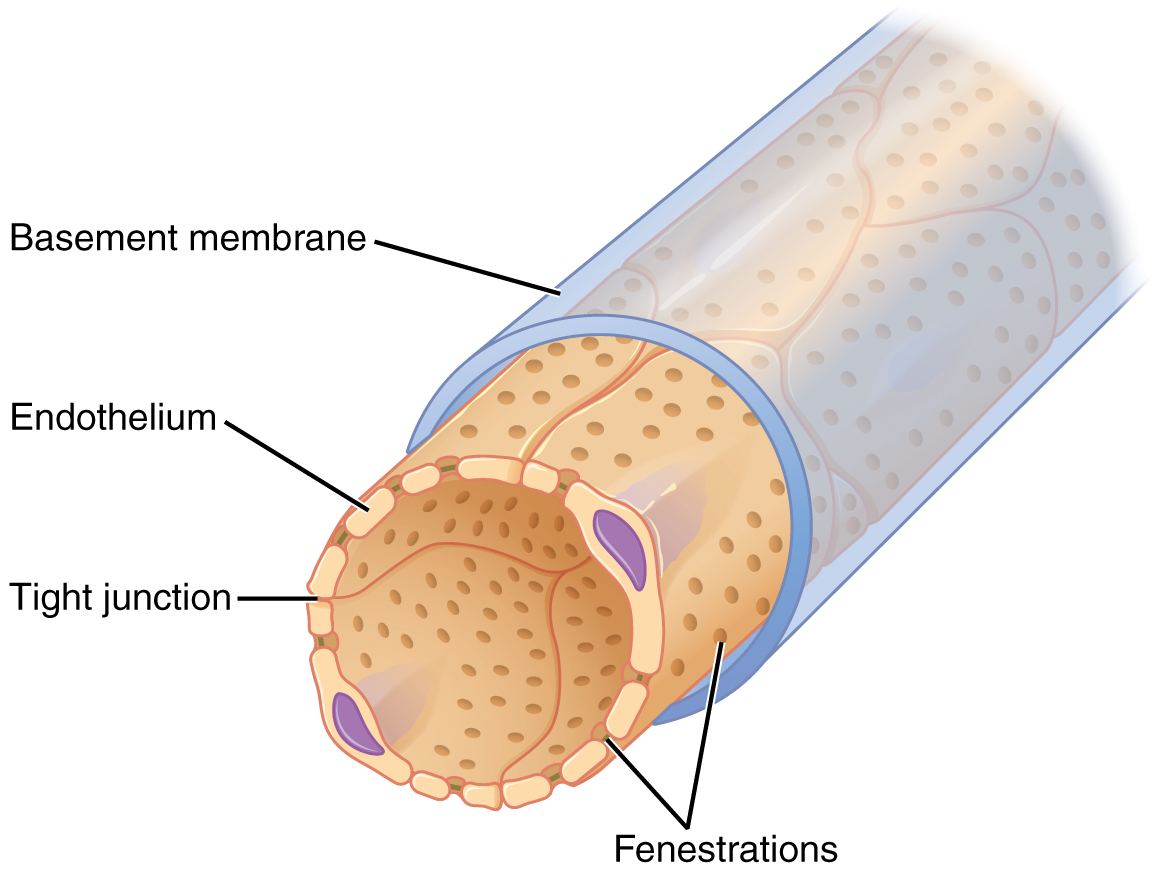
The fenestrations prevent filtration of blood cells or large proteins, but allow most other constituents through. These substances cross readily if they are less than 4 nm in size and most pass freely up to 8 nm in size. An additional factor affecting the ability of substances to cross this barrier is their electric charge. The proteins associated with these pores are negatively charged, so they tend to repel negatively charged substances and allow positively charged substances to pass more readily. The basement membrane prevents filtration of medium-to-large proteins such as globulins. There are also mesangial cells in the filtration membrane that can contract to help regulate the rate of filtration of the glomerulus. Overall, filtration is regulated by fenestrations in capillary endothelial cells, podocytes with filtration slits, membrane charge, and the basement membrane between capillary cells. The result is the creation of a filtrate that does not contain cells or large proteins, and has a slight predominance of positively charged substances.
Lying just outside Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus is the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) ( [link] ). At the juncture where the afferent and efferent arterioles enter and leave Bowman’s capsule, the initial part of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) comes into direct contact with the arterioles. The wall of the DCT at that point forms a part of the JGA known as the macula densa . This cluster of cuboidal epithelial cells monitors the fluid composition of fluid flowing through the DCT. In response to the concentration of Na + in the fluid flowing past them, these cells release paracrine signals. They also have a single, nonmotile cilium that responds to the rate of fluid movement in the tubule. The paracrine signals released in response to changes in flow rate and Na + concentration are adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine.
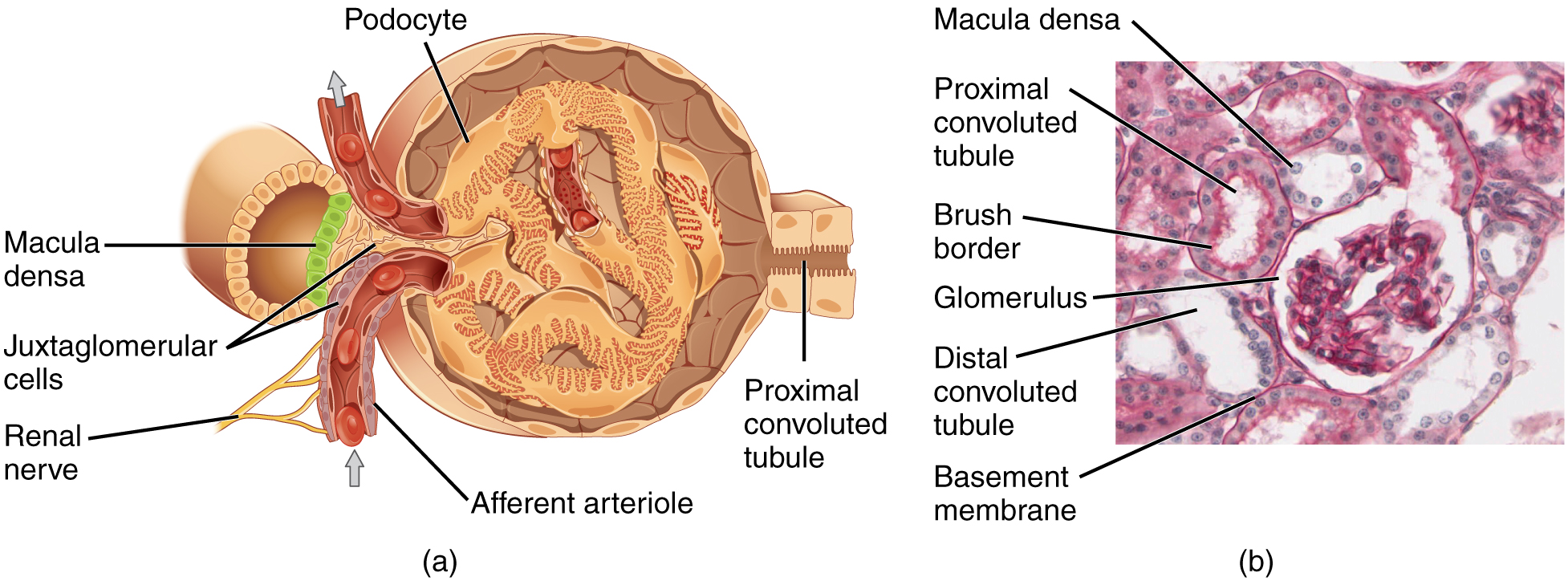
A second cell type in this apparatus is the juxtaglomerular cell . This is a modified, smooth muscle cell lining the afferent arteriole that can contract or relax in response to ATP or adenosine released by the macula densa. Such contraction and relaxation regulate blood flow to the glomerulus. If the osmolarity of the filtrate is too high (hyperosmotic), the juxtaglomerular cells will contract, decreasing the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) so less plasma is filtered, leading to less urine formation and greater retention of fluid. This will ultimately decrease blood osmolarity toward the physiologic norm. If the osmolarity of the filtrate is too low, the juxtaglomerular cells will relax, increasing the GFR and enhancing the loss of water to the urine, causing blood osmolarity to rise. In other words, when osmolarity goes up, filtration and urine formation decrease and water is retained. When osmolarity goes down, filtration and urine formation increase and water is lost by way of the urine. The net result of these opposing actions is to keep the rate of filtration relatively constant. A second function of the macula densa cells is to regulate renin release from the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent arteriole ( [link] ). Active renin is a protein comprised of 304 amino acids that cleaves several amino acids from angiotensinogen to produce angiotensin I . Angiotensin I is not biologically active until converted to angiotensin II by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) from the lungs. Angiotensin II is a systemic vasoconstrictor that helps to regulate blood pressure by increasing it. Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of the steroid hormone aldosterone from the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone stimulates Na + reabsorption by the kidney, which also results in water retention and increased blood pressure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?