| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help to maintain acid-base balance. Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, speech production, and for straining, such as during childbirth or coughing ( [link] ).
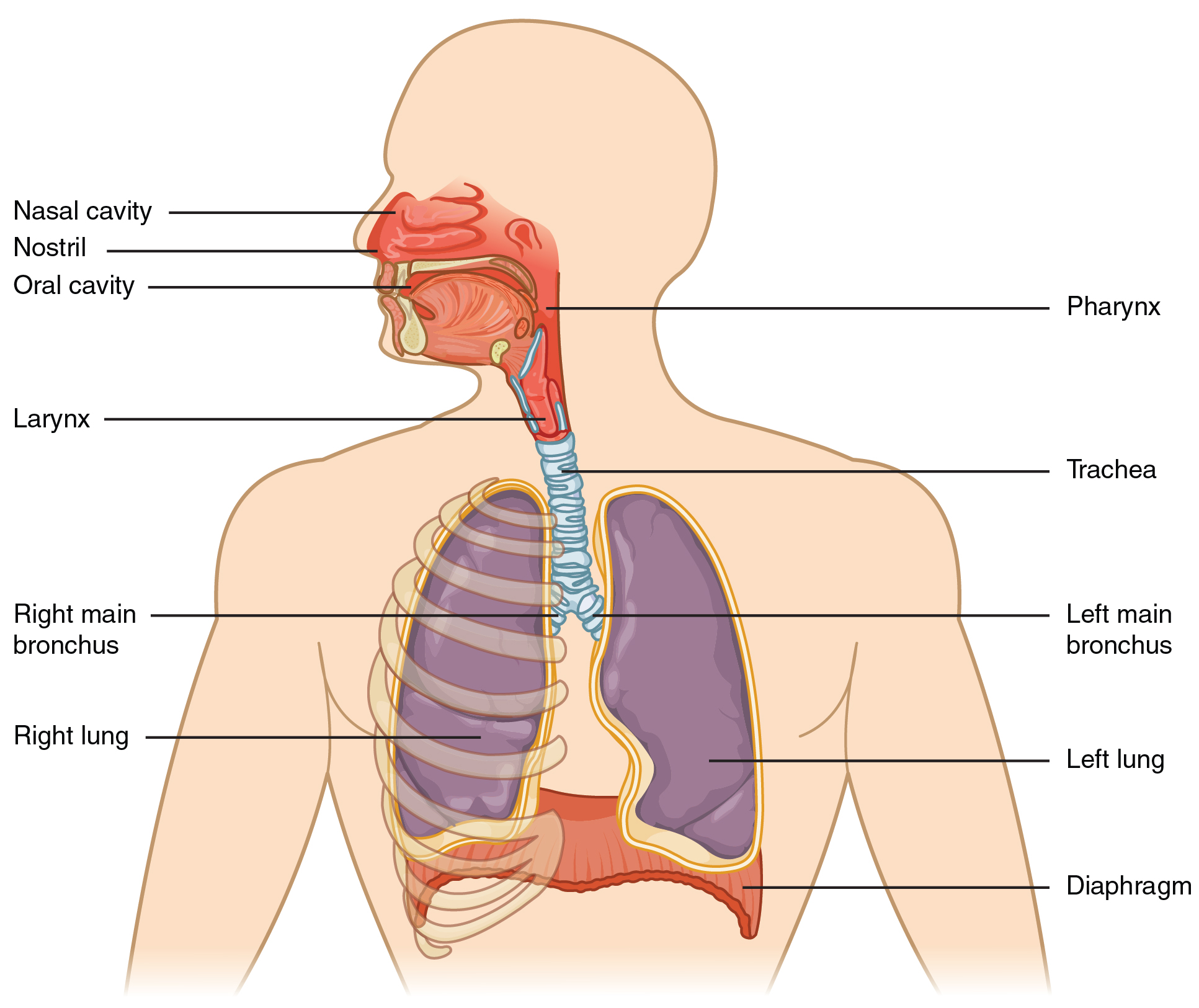
Functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. The conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange. The gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone .
The major functions of the conducting zone are to provide a route for incoming and outgoing air, remove debris and pathogens from the incoming air, and warm and humidify the incoming air. Several structures within the conducting zone perform other functions as well. The epithelium of the nasal passages, for example, is essential to sensing odors, and the bronchial epithelium that lines the lungs can metabolize some airborne carcinogens.
The major entrance and exit for the respiratory system is through the nose. When discussing the nose, it is helpful to divide it into two major sections: the external nose, and the nasal cavity or internal nose.
The external nose consists of the surface and skeletal structures that result in the outward appearance of the nose and contribute to its numerous functions ( [link] ). The root is the region of the nose located between the eyebrows. The bridge is the part of the nose that connects the root to the rest of the nose. The dorsum nasi is the length of the nose. The apex is the tip of the nose. On either side of the apex, the nostrils are formed by the alae (singular = ala). An ala is a cartilaginous structure that forms the lateral side of each naris (plural = nares), or nostril opening. The philtrum is the concave surface that connects the apex of the nose to the upper lip.
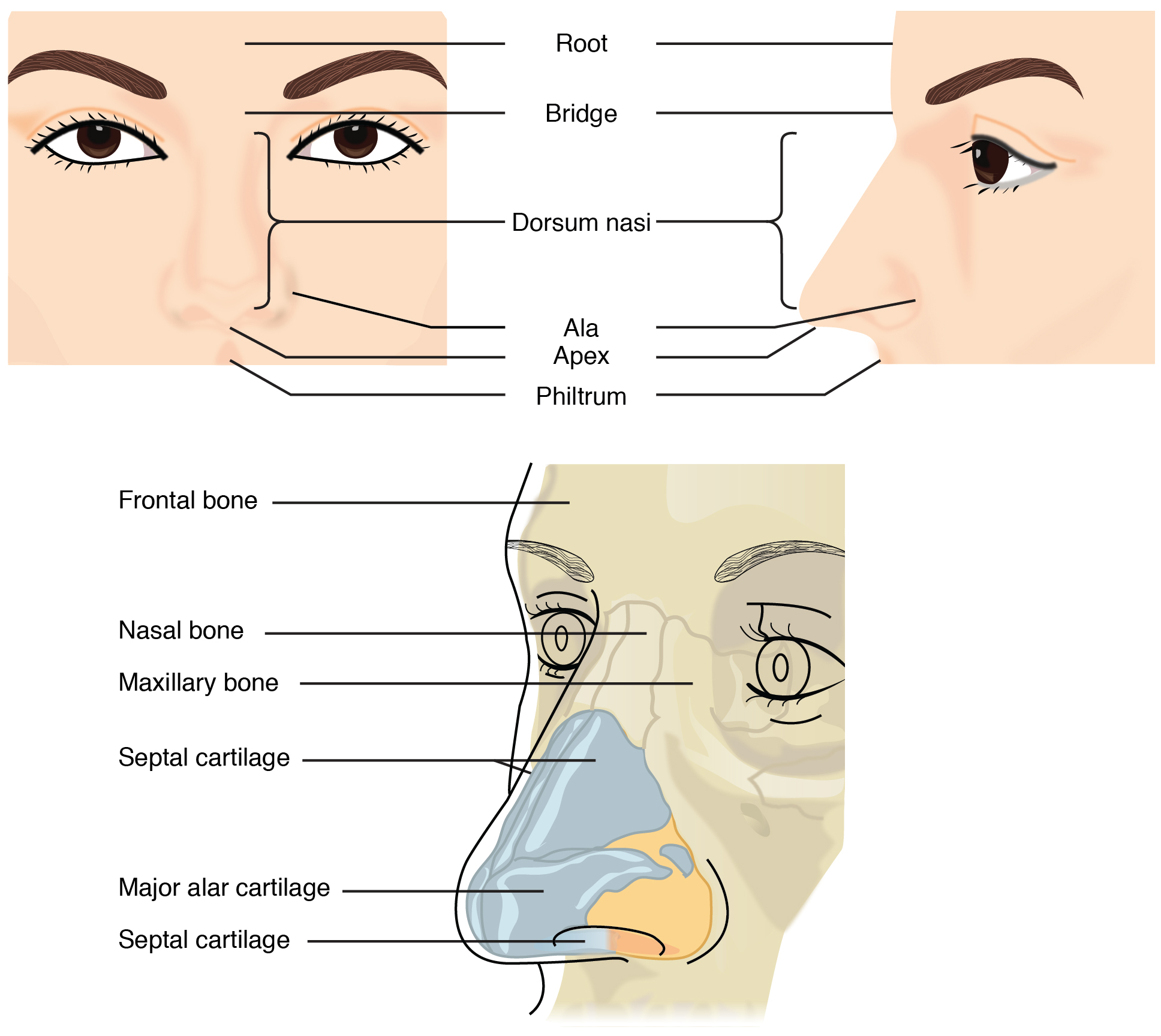
Underneath the thin skin of the nose are its skeletal features (see [link] , lower illustration). While the root and bridge of the nose consist of bone, the protruding portion of the nose is composed of cartilage. As a result, when looking at a skull, the nose is missing. The nasal bone is one of a pair of bones that lies under the root and bridge of the nose. The nasal bone articulates superiorly with the frontal bone and laterally with the maxillary bones. Septal cartilage is flexible hyaline cartilage connected to the nasal bone, forming the dorsum nasi. The alar cartilage consists of the apex of the nose; it surrounds the naris.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?