| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The autorhythmicity inherent in cardiac cells keeps the heart beating at a regular pace; however, the heart is regulated by and responds to outside influences as well. Neural and endocrine controls are vital to the regulation of cardiac function. In addition, the heart is sensitive to several environmental factors, including electrolytes.
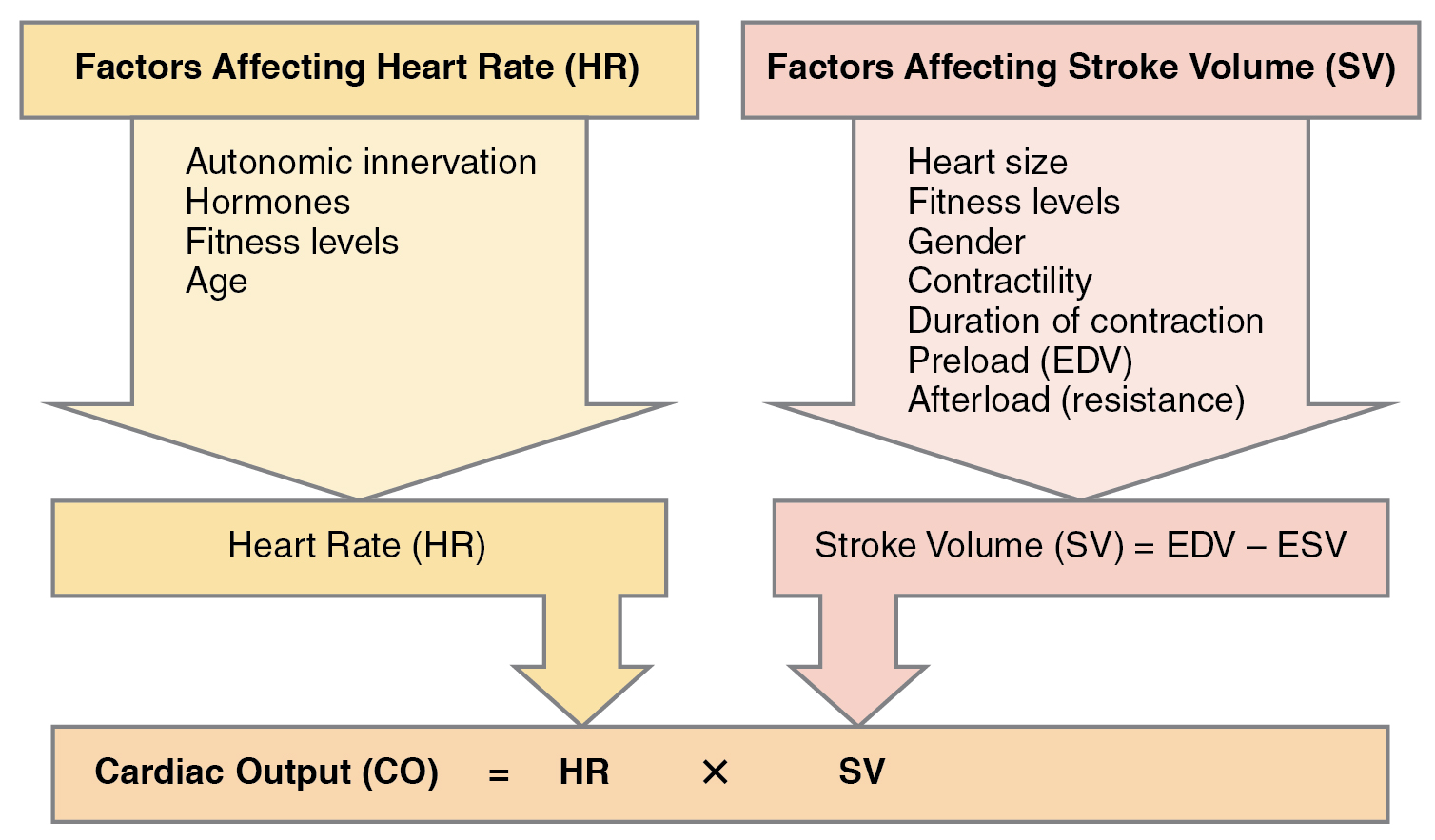
Cardiac output (CO) is a measurement of the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle in one minute. To calculate this value, multiply stroke volume (SV) , the amount of blood pumped by each ventricle, by heart rate (HR) , in contractions per minute (or beats per minute, bpm). It can be represented mathematically by the following equation:
CO = HR × SV
SV is normally measured using an echocardiogram to record EDV and ESV, and calculating the difference: SV = EDV – ESV. SV can also be measured using a specialized catheter, but this is an invasive procedure and far more dangerous to the patient. A mean SV for a resting 70-kg (150-lb) individual would be approximately 70 mL. There are several important variables, including size of the heart, physical and mental condition of the individual, sex, contractility, duration of contraction, preload or EDV, and afterload or resistance. Normal range for SV would be 55–100 mL. An average resting HR would be approximately 75 bpm but could range from 60–100 in some individuals.
Using these numbers, the mean CO is 5.25 L/min, with a range of 4.0–8.0 L/min. Remember, however, that these numbers refer to CO from each ventricle separately, not the total for the heart. Factors influencing CO are summarized in [link] .
SVs are also used to calculate ejection fraction , which is the portion of the blood that is pumped or ejected from the heart with each contraction. To calculate ejection fraction, SV is divided by EDV. Despite the name, the ejection fraction is normally expressed as a percentage. Ejection fractions range from approximately 55–70 percent, with a mean of 58 percent.
In healthy young individuals, HR may increase to 150 bpm during exercise. SV can also increase from 70 to approximately 130 mL due to increased strength of contraction. This would increase CO to approximately 19.5 L/min, 4–5 times the resting rate. Top cardiovascular athletes can achieve even higher levels. At their peak performance, they may increase resting CO by 7–8 times.
Since the heart is a muscle, exercising it increases its efficiency. The difference between maximum and resting CO is known as the cardiac reserve . It measures the residual capacity of the heart to pump blood.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?