| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The amino acid neurotransmitters, glutamate, glycine, and GABA, are almost exclusively associated with just one effect. Glutamate is considered an excitatory amino acid, but only because Glu receptors in the adult cause depolarization of the postsynaptic cell. Glycine and GABA are considered inhibitory amino acids, again because their receptors cause hyperpolarization.
The biogenic amines have mixed effects. For example, the dopamine receptors that are classified as D1 receptors are excitatory whereas D2-type receptors are inhibitory. Biogenic amine receptors and neuropeptide receptors can have even more complex effects because some may not directly affect the membrane potential, but rather have an effect on gene transcription or other metabolic processes in the neuron. The characteristics of the various neurotransmitter systems presented in this section are organized in [link] .
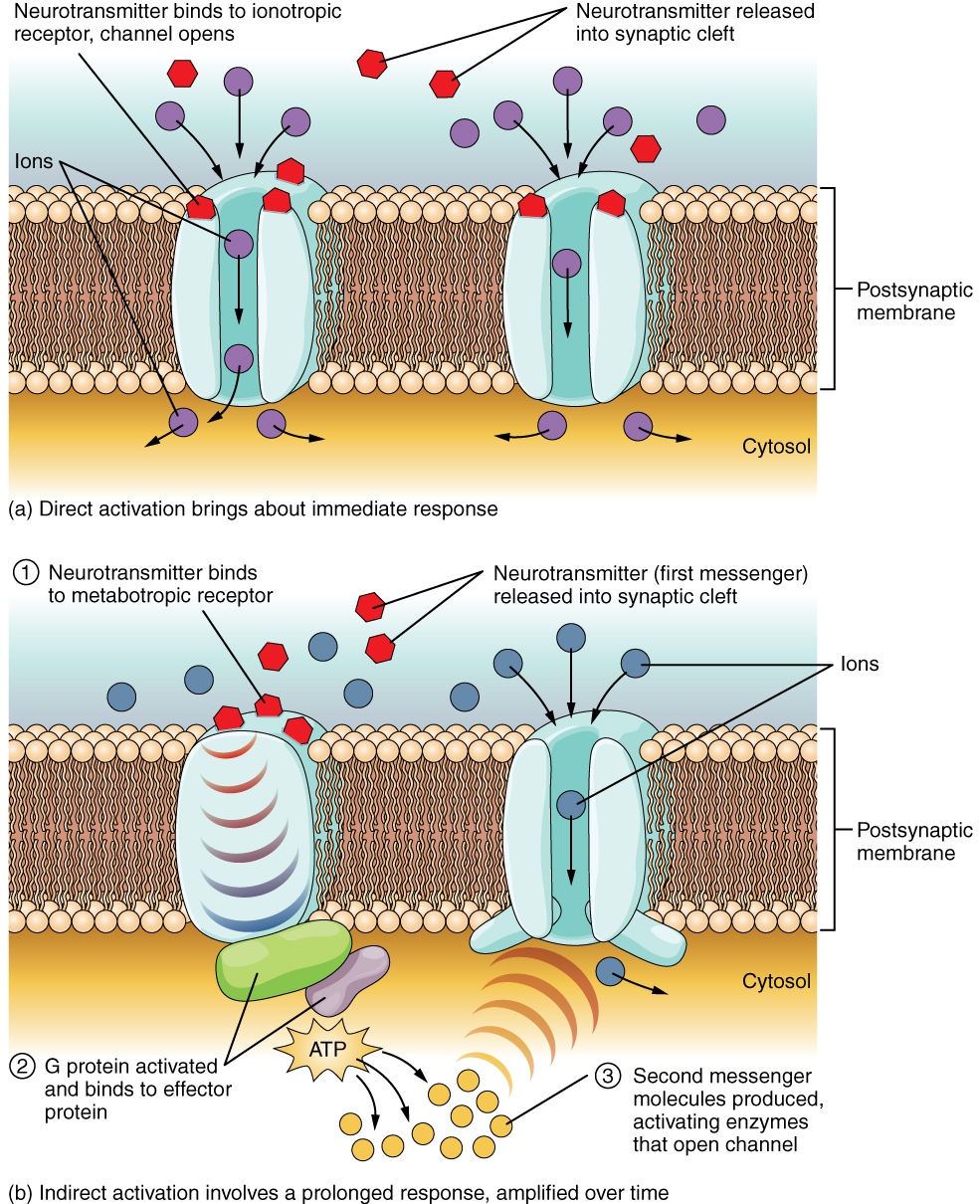
The important thing to remember about neurotransmitters, and signaling chemicals in general, is that the effect is entirely dependent on the receptor. Neurotransmitters bind to one of two classes of receptors at the cell surface, ionotropic or metabotropic ( [link] ). Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, such as the nicotinic receptor for acetylcholine or the glycine receptor. A metabotropic receptor involves a complex of proteins that result in metabolic changes within the cell. The receptor complex includes the transmembrane receptor protein, a G protein, and an effector protein. The neurotransmitter, referred to as the first messenger, binds to the receptor protein on the extracellular surface of the cell, and the intracellular side of the protein initiates activity of the G protein. The G protein is a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) hydrolase that physically moves from the receptor protein to the effector protein to activate the latter. An effector protein is an enzyme that catalyzes the generation of a new molecule, which acts as the intracellular mediator of the signal that binds to the receptor. This intracellular mediator is called the second messenger.
Different receptors use different second messengers. Two common examples of second messengers are cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and inositol triphosphate (IP 3 ). The enzyme adenylate cyclase (an example of an effector protein) makes cAMP, and phospholipase C is the enzyme that makes IP 3 . Second messengers, after they are produced by the effector protein, cause metabolic changes within the cell. These changes are most likely the activation of other enzymes in the cell. In neurons, they often modify ion channels, either opening or closing them. These enzymes can also cause changes in the cell, such as the activation of genes in the nucleus, and therefore the increased synthesis of proteins. In neurons, these kinds of changes are often the basis of stronger connections between cells at the synapse and may be the basis of learning and memory.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?