| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It is a complex job to balance the body on two feet and walk upright. The muscles of the vertebral column, thorax, and abdominal wall extend, flex, and stabilize different parts of the body’s trunk. The deep muscles of the core of the body help maintain posture as well as carry out other functions. The brain sends out electrical impulses to these various muscle groups to control posture by alternate contraction and relaxation. This is necessary so that no single muscle group becomes fatigued too quickly. If any one group fails to function, body posture will be compromised.
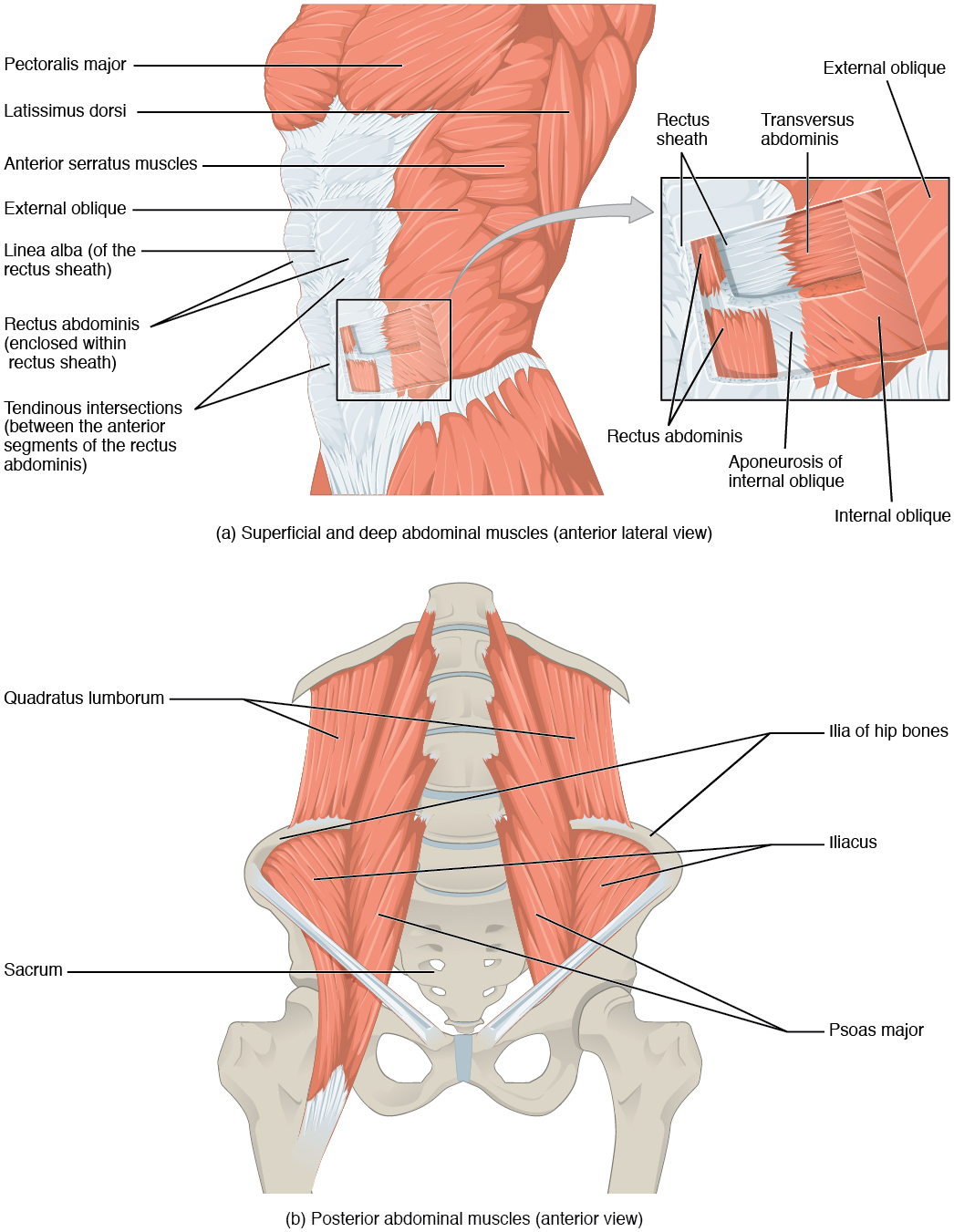
There are four pairs of abdominal muscles that cover the anterior and lateral abdominal region and meet at the anterior midline. These muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall can be divided into four groups: the external obliques, the internal obliques, the transversus abdominis, and the rectus abdominis ( [link] and [link] ).
| Muscles of the Abdomen | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Movement | Target | Target motion direction | Prime mover | Origin | Insertion |
| Twisting at waist; also bending to the side | Vertebral column | Supination; lateral flexion | External obliques; internal obliques | Ribs 5–12; ilium | Ribs 7–10; linea alba; ilium |
| Squeezing abdomen during forceful exhalations, defecation, urination, and childbirth | Abdominal cavity | Compression | Transversus abdominus | Ilium; ribs 5–10 | Sternum; linea alba; pubis |
| Sitting up | Vertebral column | Flexion | Rectus abdominis | Pubis | Sternum; ribs 5 and 7 |
| Bending to the side | Vertebral column | Lateral flexion | Quadratus lumborum | Ilium; ribs 5–10 | Rib 12; vertebrae L1–L4 |
There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero-lateral wall of the abdomen. The external oblique , closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. Perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique , extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs usually go when the other fingers are in the pants pocket. The deep muscle, the transversus abdominis , is arranged transversely around the abdomen, similar to the front of a belt on a pair of pants. This arrangement of three bands of muscles in different orientations allows various movements and rotations of the trunk. The three layers of muscle also help to protect the internal abdominal organs in an area where there is no bone.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?