| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
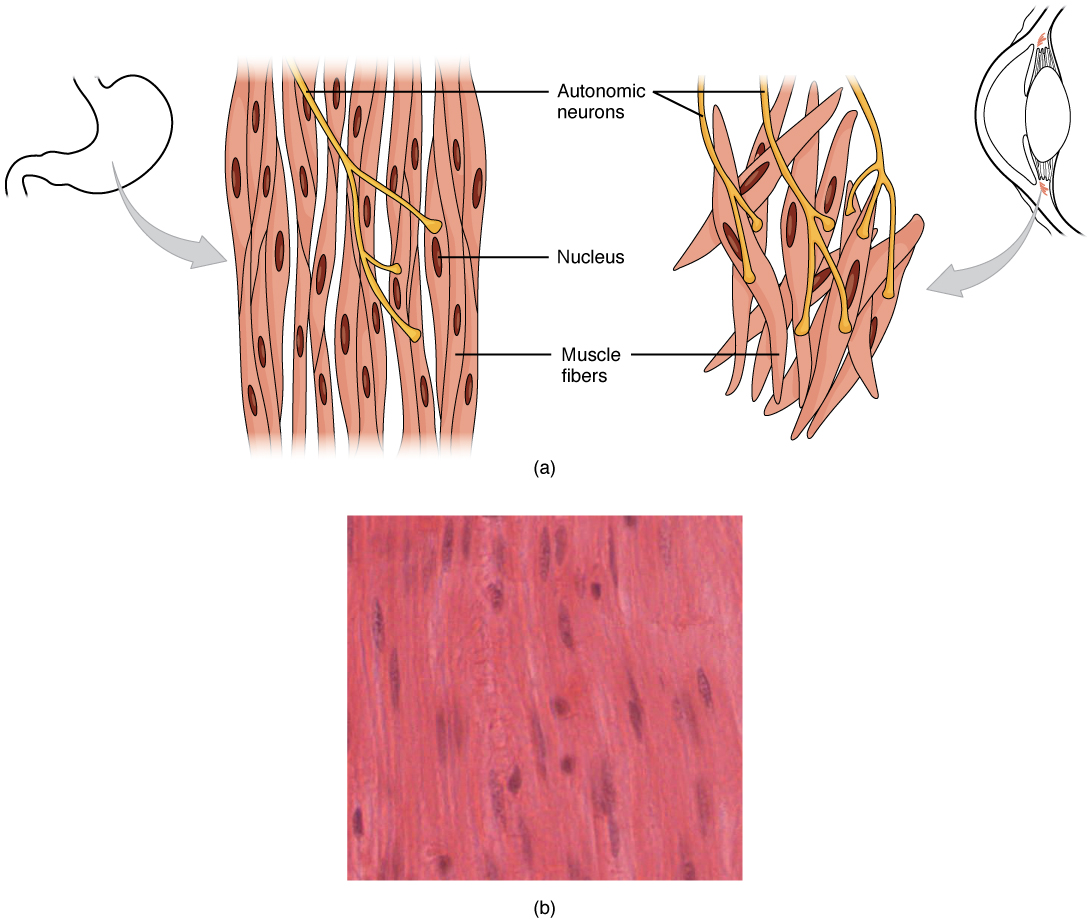
Smooth muscle (so-named because the cells do not have striations) is present in the walls of hollow organs like the urinary bladder, uterus, stomach, intestines, and in the walls of passageways, such as the arteries and veins of the circulatory system, and the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems ( [link] ab ). Smooth muscle is also present in the eyes, where it functions to change the size of the iris and alter the shape of the lens; and in the skin where it causes hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear.
View the University of Michigan WebScope at (External Link) to explore the tissue sample in greater detail.
Smooth muscle fibers are spindle-shaped (wide in the middle and tapered at both ends, somewhat like a football) and have a single nucleus; they range from about 30 to 200 μ m (thousands of times shorter than skeletal muscle fibers), and they produce their own connective tissue, endomysium. Although they do not have striations and sarcomeres, smooth muscle fibers do have actin and myosin contractile proteins, and thick and thin filaments. These thin filaments are anchored by dense bodies. A dense body is analogous to the Z-discs of skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers and is fastened to the sarcolemma. Calcium ions are supplied by the SR in the fibers and by sequestration from the extracellular fluid through membrane indentations called calveoli.
Because smooth muscle cells do not contain troponin, cross-bridge formation is not regulated by the troponin-tropomyosin complex but instead by the regulatory protein calmodulin . In a smooth muscle fiber, external Ca ++ ions passing through opened calcium channels in the sarcolemma, and additional Ca ++ released from SR, bind to calmodulin. The Ca ++ -calmodulin complex then activates an enzyme called myosin (light chain) kinase, which, in turn, activates the myosin heads by phosphorylating them (converting ATP to ADP and P i , with the P i attaching to the head). The heads can then attach to actin-binding sites and pull on the thin filaments. The thin filaments also are anchored to the dense bodies; the structures invested in the inner membrane of the sarcolemma (at adherens junctions) that also have cord-like intermediate filaments attached to them. When the thin filaments slide past the thick filaments, they pull on the dense bodies, structures tethered to the sarcolemma, which then pull on the intermediate filaments networks throughout the sarcoplasm. This arrangement causes the entire muscle fiber to contract in a manner whereby the ends are pulled toward the center, causing the midsection to bulge in a corkscrew motion ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?