| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A used-car company has just offered their best candidate, Nicole, a position in sales. The position offers 16% commission on her sales. Her earnings depend on the amount of her sales. For instance, if she sells a vehicle for $4,600, she will earn $736. She wants to evaluate the offer, but she is not sure how. In this section, we will look at relationships, such as this one, between earnings, sales, and commission rate.
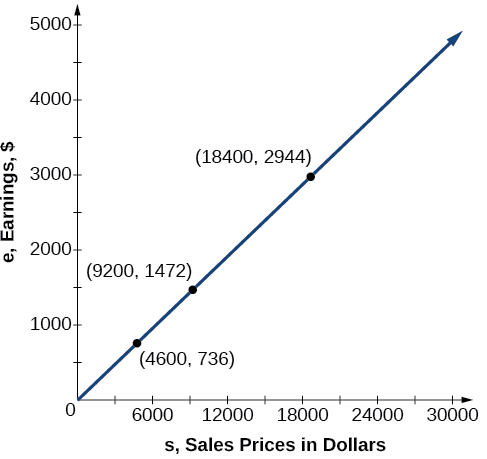
In the example above, Nicole’s earnings can be found by multiplying her sales by her commission. The formula tells us her earnings, come from the product of 0.16, her commission, and the sale price of the vehicle. If we create a table, we observe that as the sales price increases, the earnings increase as well, which should be intuitive. See [link] .
| , sales price | Interpretation | |
|---|---|---|
| $4,600 | A sale of a $4,600 vehicle results in $736 earnings. | |
| $9,200 | A sale of a $9,200 vehicle results in $1472 earnings. | |
| $18,400 | A sale of a $18,400 vehicle results in $2944 earnings. |
Notice that earnings are a multiple of sales. As sales increase, earnings increase in a predictable way. Double the sales of the vehicle from $4,600 to $9,200, and we double the earnings from $736 to $1,472. As the input increases, the output increases as a multiple of the input. A relationship in which one quantity is a constant multiplied by another quantity is called direct variation . Each variable in this type of relationship varies directly with the other.
[link] represents the data for Nicole’s potential earnings. We say that earnings vary directly with the sales price of the car. The formula is used for direct variation. The value is a nonzero constant greater than zero and is called the constant of variation . In this case, and We saw functions like this one when we discussed power functions.
If are related by an equation of the form
then we say that the relationship is direct variation and varies directly with, or is proportional to, the power of In direct variation relationships, there is a nonzero constant ratio where is called the constant of variation , which help defines the relationship between the variables.
Given a description of a direct variation problem, solve for an unknown.
The quantity varies directly with the cube of If when find when is 6.
The general formula for direct variation with a cube is The constant can be found by dividing by the cube of
Now use the constant to write an equation that represents this relationship.
Substitute and solve for

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?