| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Given a polynomial function use the Rational Zero Theorem to find rational zeros.
List all possible rational zeros of
The only possible rational zeros of are the quotients of the factors of the last term, –4, and the factors of the leading coefficient, 2.
The constant term is –4; the factors of –4 are
The leading coefficient is 2; the factors of 2 are
If any of the four real zeros are rational zeros, then they will be of one of the following factors of –4 divided by one of the factors of 2.
Note that and which have already been listed. So we can shorten our list.
Use the Rational Zero Theorem to find the rational zeros of
The Rational Zero Theorem tells us that if is a zero of then is a factor of 1 and is a factor of 2.
The factors of 1 are and the factors of 2 are and The possible values for are and These are the possible rational zeros for the function. We can determine which of the possible zeros are actual zeros by substituting these values for in
Of those, are not zeros of 1 is the only rational zero of
Use the Rational Zero Theorem to find the rational zeros of
There are no rational zeros.
The Rational Zero Theorem helps us to narrow down the list of possible rational zeros for a polynomial function. Once we have done this, we can use synthetic division repeatedly to determine all of the zeros of a polynomial function.
Given a polynomial function use synthetic division to find its zeros.
Find the zeros of
The Rational Zero Theorem tells us that if is a zero of then is a factor of –1 and is a factor of 4.
The factors of are and the factors of are and The possible values for are and These are the possible rational zeros for the function. We will use synthetic division to evaluate each possible zero until we find one that gives a remainder of 0. Let’s begin with 1.
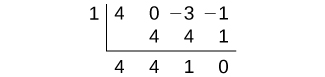
Dividing by gives a remainder of 0, so 1 is a zero of the function. The polynomial can be written as
The quadratic is a perfect square. can be written as
We already know that 1 is a zero. The other zero will have a multiplicity of 2 because the factor is squared. To find the other zero, we can set the factor equal to 0.
The zeros of the function are 1 and with multiplicity 2.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?