| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Most of us are familiar with orbital motion, such as the motion of a planet around the sun or an electron around an atomic nucleus. Within the planetary system, orbits of planets, asteroids, and comets around a larger celestial body are often elliptical. Comets, however, may take on a parabolic or hyperbolic orbit instead. And, in reality, the characteristics of the planets’ orbits may vary over time. Each orbit is tied to the location of the celestial body being orbited and the distance and direction of the planet or other object from that body. As a result, we tend to use polar coordinates to represent these orbits.
In an elliptical orbit, the periapsis is the point at which the two objects are closest, and the apoapsis is the point at which they are farthest apart. Generally, the velocity of the orbiting body tends to increase as it approaches the periapsis and decrease as it approaches the apoapsis. Some objects reach an escape velocity, which results in an infinite orbit. These bodies exhibit either a parabolic or a hyperbolic orbit about a body; the orbiting body breaks free of the celestial body’s gravitational pull and fires off into space. Each of these orbits can be modeled by a conic section in the polar coordinate system.
Any conic may be determined by three characteristics: a single focus , a fixed line called the directrix , and the ratio of the distances of each to a point on the graph. Consider the parabola shown in [link] .
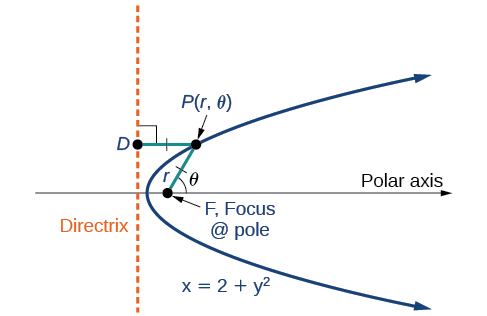
In The Parabola , we learned how a parabola is defined by the focus (a fixed point) and the directrix (a fixed line). In this section, we will learn how to define any conic in the polar coordinate system in terms of a fixed point, the focus at the pole, and a line, the directrix, which is perpendicular to the polar axis.
If is a fixed point, the focus, and is a fixed line, the directrix, then we can let be a fixed positive number, called the eccentricity , which we can define as the ratio of the distances from a point on the graph to the focus and the point on the graph to the directrix. Then the set of all points such that is a conic. In other words, we can define a conic as the set of all points with the property that the ratio of the distance from to to the distance from to is equal to the constant
For a conic with eccentricity
With this definition, we may now define a conic in terms of the directrix, the eccentricity and the angle Thus, each conic may be written as a polar equation , an equation written in terms of and
For a conic with a focus at the origin, if the directrix is where is a positive real number, and the eccentricity is a positive real number the conic has a polar equation
For a conic with a focus at the origin, if the directrix is where is a positive real number, and the eccentricity is a positive real number the conic has a polar equation

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?