| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Other theorists, however, doubted that the physiological arousal that occurs with different types of emotions is distinct enough to result in the wide variety of emotions that we experience. Thus, the Cannon-Bard theory of emotion was developed. According to this view, physiological arousal and emotional experience occur simultaneously, yet independently (Lang, 1994). So, when you see the venomous snake, you feel fear at exactly the same time that your body mounts its fight or flight response. This emotional reaction would be separate and independent of the physiological arousal, even though they co-occur.
The James-Lange and Cannon-Bard theories have each garnered some empirical support in various research paradigms. For instance, Chwalisz, Diener, and Gallagher (1988) conducted a study of the emotional experiences of people who had spinal cord injuries. They reported that individuals who were incapable of receiving autonomic feedback because of their injuries still experienced emotion; however, there was a tendency for people with less awareness of autonomic arousal to experience less intense emotions. More recently, research investigating the facial feedback hypothesis suggested that suppression of facial expression of emotion lowered the intensity of some emotions experienced by participants (Davis, Senghas,&Ochsner, 2009). In both of these examples, neither theory is fully supported because physiological arousal does not seem to be necessary for the emotional experience, but this arousal does appear to be involved in enhancing the intensity of the emotional experience.
The Schachter-Singer two-factor theory of emotion is another variation on theories of emotions that takes into account both physiological arousal and the emotional experience. According to this theory, emotions are composed of two factors: physiological and cognitive. In other words, physiological arousal is interpreted in context to produce the emotional experience. In revisiting our example involving the venomous snake in your backyard, the two-factor theory maintains that the snake elicits sympathetic nervous system activation that is labeled as fear given the context, and our experience is that of fear.
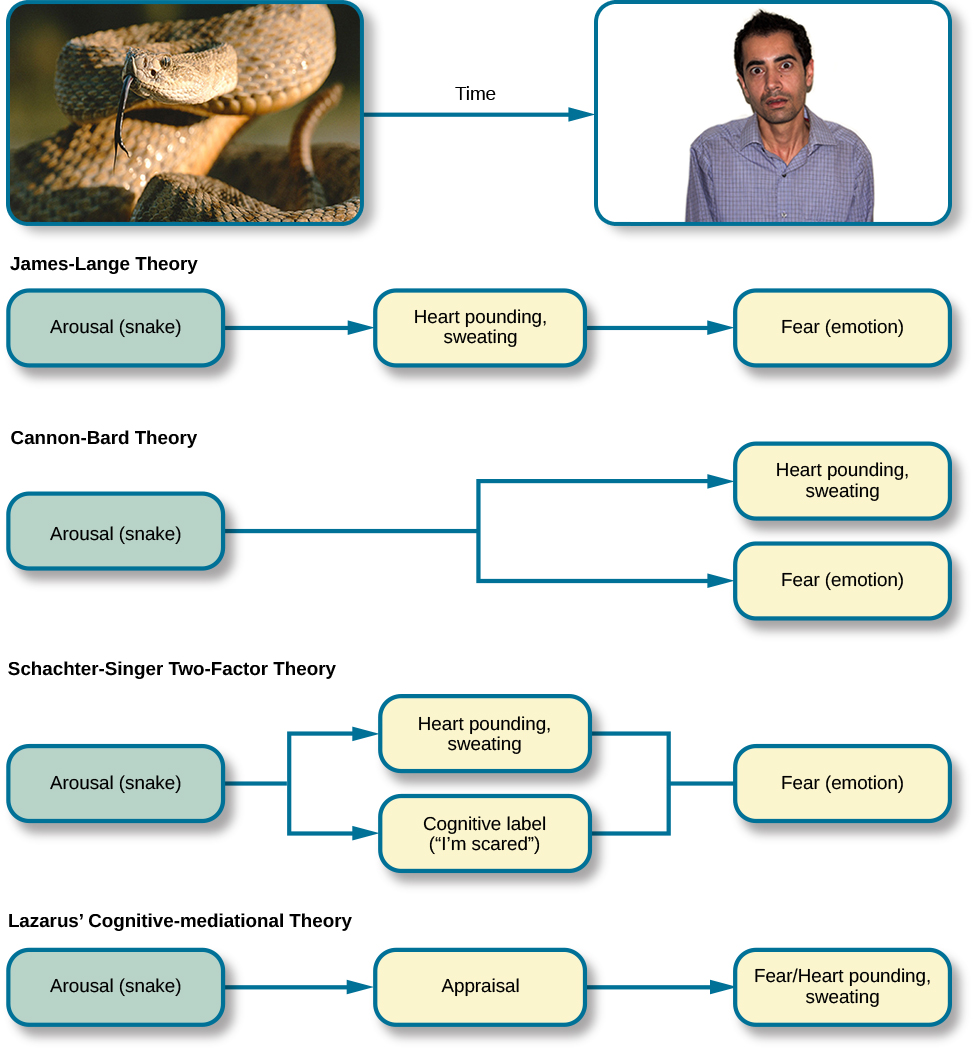
It is important to point out that Schachter and Singer believed that physiological arousal is very similar across the different types of emotions that we experience, and therefore, the cognitive appraisal of the situation is critical to the actual emotion experienced. In fact, it might be possible to misattribute arousal to an emotional experience if the circumstances were right (Schachter&Singer, 1962).
To test their idea, Schachter and Singer performed a clever experiment. Male participants were randomly assigned to one of several groups. Some of the participants received injections of epinephrine that caused bodily changes that mimicked the fight-or-flight response of the sympathetic nervous system; however, only some of these men were told to expect these reactions as side effects of the injection. The other men that received injections of epinephrine were told either that the injection would have no side effects or that it would result in a side effect unrelated to a sympathetic response, such as itching feet or headache. After receiving these injections, participants waited in a room with someone else they thought was another subject in the research project. In reality, the other person was a confederate of the researcher. The confederate engaged in scripted displays of euphoric or angry behavior (Schachter&Singer, 1962).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?