| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
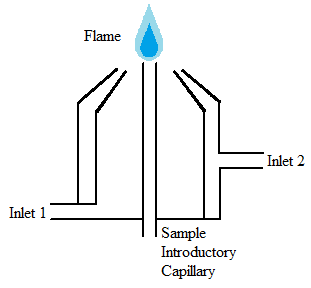
Flame atomizers [link] are widely used for a multitude of reasons including their simplicity, low cost, and long length of time that they have been utilized. Flame atomizers accept an aerosol from a nebulizer into a flame that has enough energy to both volatilize and atomize the sample ( [link] ). When this happens, the sample is dried, vaporized, atomized, and ionized. Within this category of atomizers, there are many subcategories determined by the chemical composition of the flame. The composition of the flame is often determined based on the sample being analyzed. The flame itself should meet several requirements including sufficient energy, a long length, non-turbulent, and safe.
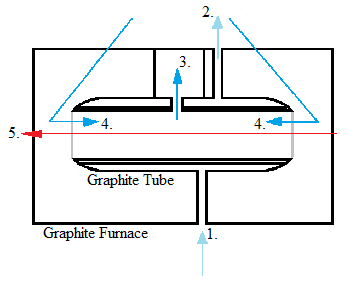
Although electrothermal atomizers were developed before flame atomizers, they did not become popular until more recently due to improvements made to the detection level. They employ graphite tubes that increase temperature in a stepwise manner ( [link] ). Electrothermal atomization first dries the sample and evaporates much of the solvent and impurities, then atomizes the sample, and then rises it to an extremely high temperature to clean the graphite tube. Some requirements for this form of atomization are the ability to maintain a constant temperature during atomization, have rapid atomization, hold a large volume of solution, and emit minimal radiation. Electrothermal atomization is much less harsh than the method of flame atomization.
The radiation source then irradiates the atomized sample. The sample absorbs some of the radiation, and the rest passes through the spectrometer to a detector. Radiation sources can be separated into two broad categories: line sources and continuum sources. Line sources excite the analyte and thus emit its own line spectrum. Hollow cathode lamps and electrodeless discharge lamps are the most commonly used examples of line sources. On the other hand, continuum sources have radiation that spreads out over a wider range of wavelengths. These sources are typically only used for background correction. Deuterium lamps and halogen lamps are often used for this purpose.
Spectrometers are used to separate the different wavelengths of light before they pass to the detector. The spectrometer used in AAS can be either single-beam or double-beam. Single-beam spectrometers only require radiation that passes directly through the atomized sample, while double-beam spectrometers [link] , as implied by the name, require two beams of light; one that passes directly through the sample, and one that does not pass through the sample at all. (Insert diagrams) The single-beam spectrometers have less optical components and therefore suffer less radiation loss. Double-beam monochromators have more optical components, but they are also more stable over time because they can compensate for changes more readily.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?