| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In situations with a polyatomic eluent, three models are used to account for the multiple anions in the eluent. The first is the dominant equilibrium model, in which one anion is so dominant in concentration; the other eluent anions are ignored. The dominant equilibrium model works best for multivalence analytes. The second is the effective charge model, where an effective charge of the eluent anions is found, and a relationship similar to EQ is found with the effective charge. The effective charge models works best with monovalent analytes. The third is the multiple eluent species model, where [link] describes the retention factor:
C 3 is a constant that includes the phase volume ratio between stationary, the equilibrium constant, and mobile and the exchange capacity. C p is the total concentration of the eluent species. X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , correspond to the shares of a particular eluent anion in the retention of the analyte.
For eluents with a single cation and analytes that are alkaline earth metals, heavy metals or transition metals, a complexing agent is used to bind with the metal during chromatography. This introduces the quantity A(m) to the retention rate calculations, where A(m) is the ratio of free metal ion to the total concentration of metal. Following a similar derivation to the single anion case, [link] is found.
Solving for the retention coefficient, [link] is found.
From this expression, the retention rate of the cation can be determined from eluent concentration and the ratio of free metal ions to the total concentration of the metal, which itself is depended on the equilibrium of the metal ion with the complexing agent.
The solid phase packing material used in the chromatography column is important to the exchange capacity of the anion or cation. There are many types of packing material, but all share a functional group that can bind either the anion or the cation complex. The functional group is mounted on a polymer surface or sphere, allowing large surface area for interaction.
The primary functional group used for anion chromatography is the ammonium group. Amine groups are mounted on the polymer surface, and the pH is lowered to produce ammonium groups. As such, the exchange capacity is depended on the pH of the eluent. To reduce the pH dependency, the protons on the ammonium are successively replaced with alkyl groups until the all the protons are replaced and the functional group is still positively charged, but pH independent. The two packing materials used in almost all anion chromatography are trimethylamine (NMe 3 , [link] ) and dimethylanolamine ( [link] ).

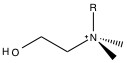
Cation chromatography allows for the use of both organic polymer based and silica gel based packing material. In the silica gel based packing material, the most common packing material is a polymer-coated silica gel. The silicate is coated in polymer, which is held together by cross-linking of the polymer. Polybutadiene maleic acid ( [link] ) is then used to create a weakly acidic material, allowing the analyte to diffuse through the polymer and exchange. Silica gel based packing material is limited by the pH dependent solubility of the silica gel and the pH dependent linking of the silica gel and the functionalized polymer. However, silica gel based packing material is suitable for separation of alkali metals and alkali earth metals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?