| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
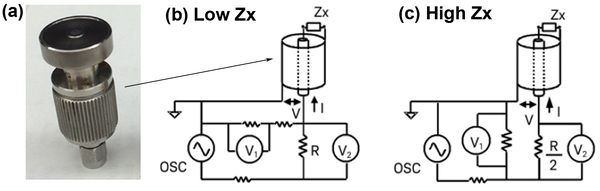
As can be seen in Figure 3, the RF I-V method, which incorporates the use of a dielectric probe, essentially measures variations in voltage and current when a sample is placed on the dielectric probe. For the low-impedance case, the impedance of the sample (Zx) is given by [link] , for a high-impedance sample, the impedance of the sample (Zx) is given by [link] .
The instrumentation and methods described herein consist of an Agilent E4991A impedance analyzer connected to an Agilent 85070E dielectric probe kit. The impedance analyzer directly measures the complex impedance of the sample under test by measuring either the frequency-dependent voltage or current across the sample. These values are then converted to permittivity values using the system software.
In order to acquire the electrical permittivity of aqueous solutions the impedance analyzer and dielectric probe must first be calibrated. In the first instance, the impedance analyzer unit is calibrated under open-circuit, short-circuit, 50 ohm load, and low loss capacitance conditions by attaching the relevant probes shown in [link] . The dielectric probe is then attached to the system and re-calibrated in open-air, with an attached short circuit probe, and finally with 500 μl of highly purified deionized water (with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ/cm at 25 °C) ( [link] ). The water is then removed and the system is ready for acquiring data.
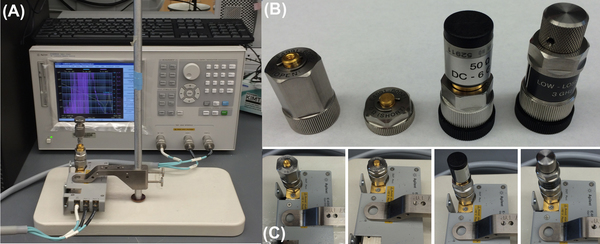

In order to maintain accurate calibration only the purest deionized water with a resistivity of 18.2 MΩ/cm at 25 °C should be used. To perform an analysis simply load the dielectric probe with 500 μl of the sample and click on the ‘acquire data’ tab in the software. The system will perform a scan across the frequency range 200 MHz – 3 GHz and acquire the real and imaginary parts of the complex permittivity. The period with which a data point is taken as well as the scale (i.e. log or linear) can also be altered in the software if necessary. To analyze another sample, remove the liquid and gently dry the dielectric probe with a paper towel. An open air refresh calibration should then be performed (by pressing the relevant button in the software) as this prevents errors and instrument drift from sample to sample. To analyze a normal saline (0.9 % NaCl w/v) solution, dissolve 8.99 g of NaCl in 1 litre of DI water (18.2 MΩ/cm at 25 °C) to create a 154 mM NaCl solution (equivalent to a 0.9 % NaCl w/v solution). Load 500 μl of the sample on the dielectric probe and acquire a new data set as mentioned previously.
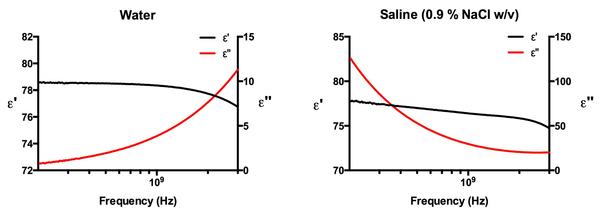
The data files extracted from the impedance analyzer and dielectric probe setup previously described can be opened using any standard data processing software such as Microsoft Excel. The data will appear in three columns, which will be labeled frequency (Hz), ε', and ε" (representing the real and imaginary components of the permittivity, respectively). Any graphing software can be used to create simple graphs of the complex permittivity versus frequency. In the example below ( [link] ) we have used Prism to graph the real and complex permittivity’s versus frequency (200 MHz – 3 GHz) for the water and saline samples. For this frequency range no error correction is needed. For the analysis of frequencies below 200 MHz down to 10 MHz, which can be achieved using the impedance analyzer and dielectric probe configuration, error correction algorithms are needed to take into account electrode polarization effects that skew and distort the data. Gach et al . cover these necessary algorithms that can be used if needed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?