| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
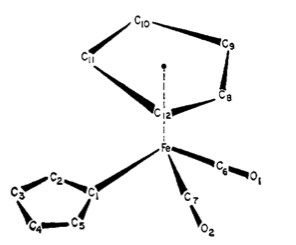
Sample preparation is essentially the same for routine NMR. The compound of interest will need to be dissolved in an NMR compatible solvent (CDCl 3 is a common example) and transferred into an NMR tube. Approximately 600 μL of solution is needed with only micrograms of compound. Compounds should be at least 99 % pure in order to ease peak assignments and analysis. Because each spectrometer has its own protocol for shimming and optimization, having the supervision of a trained specialist is strongly advised. Additionally, using an NMR with temperature control is essential. The basic goal of this experiment is to find three temperatures: slow interchange, fast interchange, and coalescence. Thus many spectra will be needed to be obtained at different temperatures in order to determine the energetics of the fluctuation.
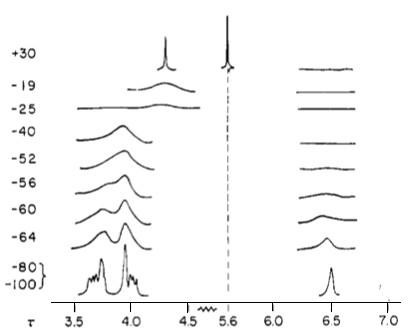
The process will be much swifter if the lower temperature range (in which the fluctuation is much slower than the spectrometer timescale) is known. A spectra should be taken in this range. Spectra at higher temperatures should be taken, preferably in regular increments (for instance, 10 K), until the peaks of interest condense into a sharp single at higher temperature. A spectrum at the coalescence temperature should also be taken in case of publishing a manuscript. This procedure should then be repeated in reverse; that is, spectra should be taken from high temperature to low temperature. This ensures that no thermal reaction has taken place and that no hysteresis is observed. With the data (spectra) in hand, the energetics can now be determined.
For intramolecular processes that exchange two chemically equivalent nuclei, the function of the difference in their resonance frequencies (Δ v ) and rate of exchange (k) is the NMR spectrum. Slow interchange occurs when Δ v >>k, and two separate peaks are observed. When Δ v <<k, fast interchange is said to occur, and one sharp peak is observed. At intermediate temperatures, the peaks are broadened and overlap one another. When they completely merge into one peak, the coalescence temperature, T c is said to be reached. In the case of coalescence of an equal doublet (for instance, one proton exchanging with one proton), coalescences occurs when Δv 0 t = 1.4142/(2π), where Δv 0 is the difference in chemical shift at low interchange and where t is defined by [link] , where t a and t b are the respective lifetimes of species a and b. This condition only occurs when t a = t b , and as a result, k = ½ t.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?