| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The working principle of a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) module is the utilization of the resonance properties of some piezoelectric of materials. A piezoelectric material is a material that exhibits an electrical field when a mechanical strain is applied. This phenomenon is also observed in the contrary where an applied electrical field produce a mechanical strain in the material. The material used is α-SiO 2 that produces a very stable and constant frequency. The direction and magnitude of the mechanical strain is directly dependent of the direction of the applied electrical field and the inherent physical properties of the crystal.
A special crystal cut is used, called AT-cut, which is obtain as wafers of the crystal of about 0.1 to 0.3 mm in width and 1 cm in diameter. The AT-cut is obtained when the wafer is cut at 35.25° of the main crystallographic axis of SiO 2 . This special cut allows only one vibration mode, the shear mode, to be accessed and thus exploited for analytical purposes. When a electrical field is applied to the crystal wafer via metal electrodes, that are vapor-deposited in the surface, a mechanical shear is produced and maintained as long as the electrical field is applied. Since this electric field can be controlled by opening and closing an electrical circuit, a resonance within the crystal is formed ( [link] ).
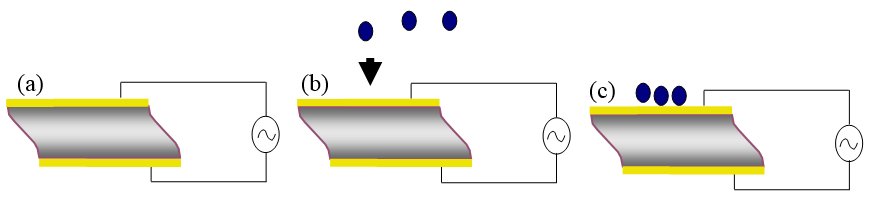
Since the frequency of the resonance is dependent of the characteristics of the crystal, an increase of mass, for example when the sample is loaded into the sensor would change the frequency change. This relation [link] was obtained by Sauerbrey in 1959, where Δm (ng.cm -2 ) is the areal mass, C (17.7 ngcm -2 Hz -1 ) is the vibrational constant (shear, effective area, etc.), n in Hz is the resonant overtone, and Δf is the change in frequency. The dependence of the change in the frequency can be related directly to the change in mass deposited in the sensor only when three conditions are met and assumed:
An important incorporation in recent equipment is the use of the dissipation factor. The inclusion of the dissipation faster takes into account the weakening of the frequency as it travels along the newly deposited mass. In a rigid layer the frequency is usually constant and travels through the newly formed mass without interruption, thus, the dissipation is not important. On the other hand, when the deposited material has a soft consistency the dissipation of the frequency is increased. This effect can be monitored and related directly to the nature of the mass deposited.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?