| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

An additional type of nuclear decay is that of gamma radiation (denoted as γ), a process in which the excited nucleus emits high-energy gamma ray photons. There is no change in either neutron number N or atomic number Z, yet the nucleus undergoes a nuclear transformation involving the loss of energy. In order to distinguish the higher energy parent nucleus (prior to gamma decay) from the lower energy daughter nucleus (after gamma decay), the mass number of the parent nucleus is labeled with the letter m , which means “metastable.” An example of gamma radiation with the element technetium is provided in [link] .
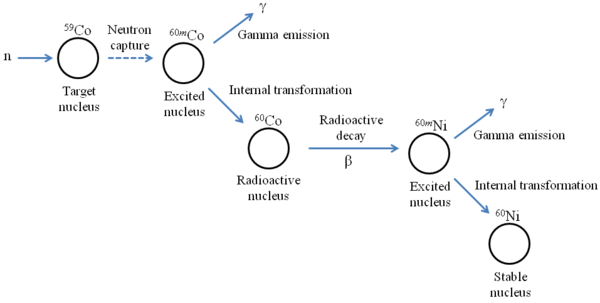
In NAA, the radioactive nuclei in the sample undergo both gamma and particle nuclear decay. [link] below presents a schematic example of nuclear decay. After capturing a free neutron, the excited 60m Co nucleus undergoes an internal transformation by emitting gamma rays. The lower-energy daughter nucleus 60 Co, which is still radioactive, then emits a beta particle. This results in a high-energy 60 Ni nucleus, which once again undergoes an internal transformation by emitting gamma rays. The nucleus then reaches the stable 60 Ni state.
Although alpha and beta particle detectors do exist, most detectors used in NAA are designed to detect the gamma rays that are emitted from the excited nuclei following neutron capture. Each element has a unique radioactive emission and decay path that is scientifically known. Thus, based on the path and the spectrum produced by the instrument, NAA can determine the identity and concentration of the element.
As mentioned above, there are many different neutron sources that can be used in modern-day NAA. A chart comparing three common sources is shown in [link] .
| Source type | Description | Example(s) | Typical output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isotopic neutron sources | Certain isotopes undergo spontaneous fission and release neutrons as they decay. | 226 Ra(Be), 124 Sb(Be), 241 Am(Be), 252 Cf | 10 5 -10 7 s -1 GBq -1 or 2.2 10 12 s -1 g -1 for 252 Cf |
| Particle accelerators or neutron generators | Particle accelerators produce neutrons by colliding hydrogen, deuterium, and tritium with target nuclei such as deuterium, tritium, lithium, and beryllium. | Acceleration of deuterium ions toward a target containing deuterium or tritium, resulting in the reactions 2 H( 2 H,n) 3 He and 3 H( 2 H,n) 4 He | 10 8 -10 10 s -1 for the first deuterium on deuterium reactions and 10 9 -10 11 s -1 for deuterium on tritium reactions |
| Nuclear research reactors | Within nuclear reactors, large atomic nuclei absorbs neutrons and undergo nuclear fission. The nuclei split into lighter nuclei, which releases energy, radiation, and free neutrons. | 235 U and 239 Pu | 10 15 -10 18 m -2 s -1 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?