| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
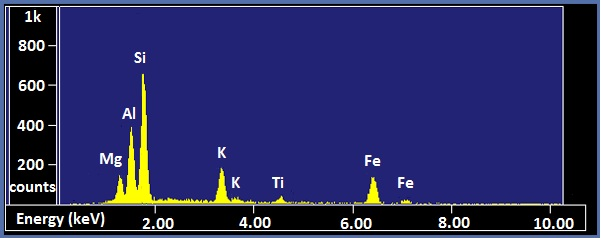
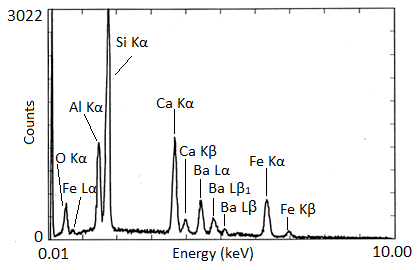
X-ray spectra are presented with energy in keV on the x-axis and the number of counts on the y-axis. The EDX spectra of biotite and NIST glass K309 are shown as examples ( [link] and [link] , respectively). Biotite is a mineral similar to mica which has the approximate chemical formula K(Mg,Fe) 3 AlSi 3 O 10 (F,OH) 2 . Strong peaks for manganese, aluminum, silicon, potassium, and iron can be seen in the spectrum. The lack of visible hydrogen is expected, and the absence of oxygen and fluorine peaks suggests the instrument had a beryllium window. The titanium peak is small and unexpected, so it may only be present in trace amounts. K309 is a mix of glass developed by the National Institute for Standards and Technology. The spectrum shows that it contains significant amounts of silicon, aluminum, calcium, oxygen, iron, and barium. The large peak at the far left is the carbon signal from the carbon substrate the glass was placed on.
As has just been discussed, X-ray spectroscopy is incapable of seeing elements lighter than boron. This is a problem given the abundance of hydrogen in natural and man-made materials. The related techniques X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Auger spectroscopy are able to detect Li and Be, but are likewise unable to measure hydrogen.
X-ray spectroscopy relies heavily on standards for peak identification. Because a combination of elements can have noticeably different properties from the individual constituent elements in terms of X-ray fluorescence or absorption, it is important to use a standard as compositionally similar to the sample as possible. Naturally, this is more difficult to accomplish when examining new materials, and there is always a risk of the structure of the sample being appreciably different than expected.
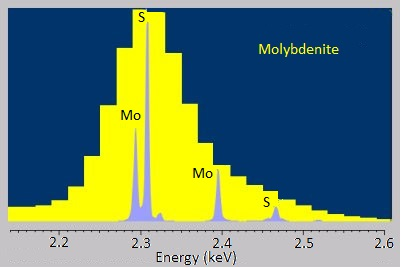
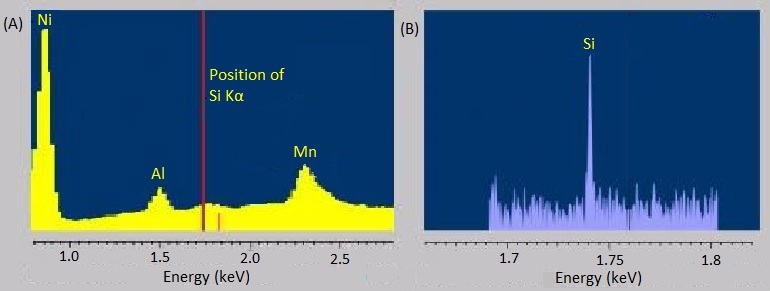
The energy-dispersive variants of X-ray spectroscopy sometimes have a hard time distinguishing between emissions that are very near each other in energy or distinguishing peaks from trace elements from background noise. Fortunately, the wavelength-dispersive variants are much better at both of these. The rough, stepwise curve in [link] represents the EDS spectrum of molybdenite, a mineral with the chemical formula MoS 2 . Broadened peaks make it difficult to distinguish the molybdenum signals from the sulfur ones. Because WDS can select specific wavelengths, it has much better resolution and can pinpoint the separate peaks more accurately. Similarly, the trace silicon signal in the EDS spectrum of the nickel-aluminum-manganese alloy in [link] A is barely distinguishable as a bump in the baseline, but the WDS spectrum in [link] B clearly picks it up.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?