| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The predicted abundances of the elements in the universe provide a stringent test of the Big Bang and the Big Bang nucleosynthesis. Recent experimental estimates of the matter density from the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) agree with model predictions. This agreement provides convincing evidence of the Big Bang model.
According to cosmological models, the Big Bang event should have left behind thermal radiation called the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR). The intensity of this radiation should follow the blackbody radiation curve ( Photons and Matter Waves ). Wien’s law states that the wavelength of the radiation at peak intensity is
where T is temperature in kelvins. Scientists expected the expansion of the universe to “stretch the light,” and the temperature to be very low, so cosmic background radiation should be long-wavelength and low energy.
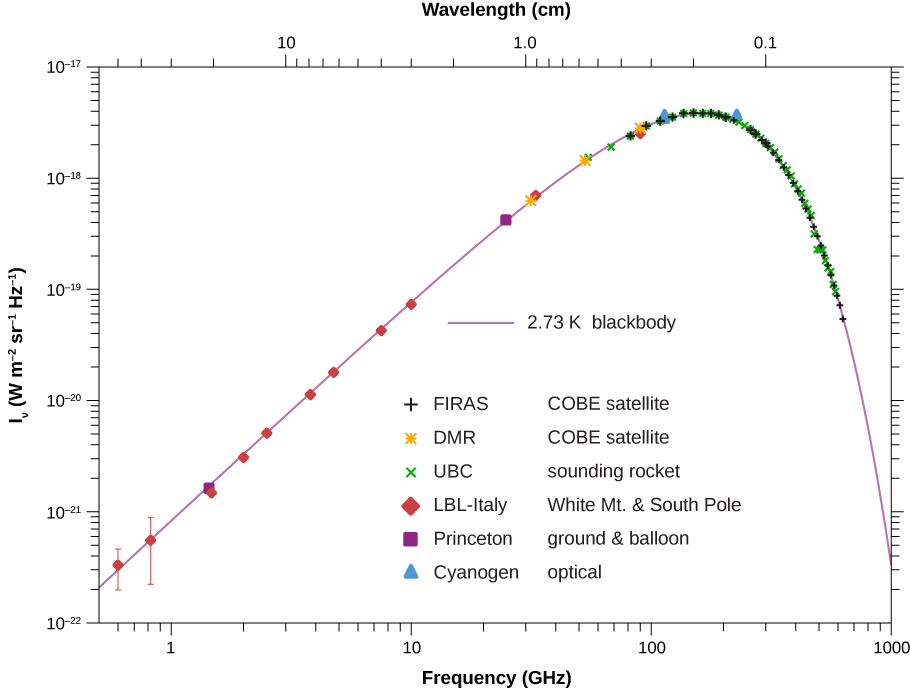
In the 1960s, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson of Bell Laboratories noticed that no matter what they did, they could not get rid of a faint background noise in their satellite communication system. The noise was due to radiation with wavelengths in the centimeter range (the microwave region). Later, this noise was associated with the cosmic background radiation. An intensity map of the cosmic background radiation appears in [link] . The thermal spectrum is modeled well by a blackbody curve that corresponds to a temperature ( [link] ).

The formation of atoms in the early universe makes these atoms less likely to interact with light. Therefore, photons that belong to the cosmic background radiation must have separated from matter at a temperature T associated with 1 eV (the approximate ionization energy of an atom) . The temperature of the universe at this point was
According to cosmological models, the time when photons last scattered off charged particles was approximately 380,000 years after the Big Bang. Before that time, matter in the universe was in the plasma form and the photons were “thermalized.”
We know from direct observation that antimatter is rare. Earth and the solar system are nearly pure matter, and most of the universe also seems dominated by matter. This is proven by the lack of annihilation radiation coming to us from space, particularly the relative absence of 0.511-MeV rays created by the mutual annihilation of electrons and positrons. (Antimatter in nature is created in particle collisions and in decays, but only in small amounts that quickly annihilate, leaving almost pure matter surviving.)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?