| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Coordinate system types determine position of a point with measurements of distance or angle or combination of them. A spatial point requires three measurements in each of these coordinate types. It must, however, be noted that the descriptions of a point in any of these systems are equivalent. Different coordinate types are mere convenience of appropriateness for a given situation. Three major coordinate systems used in the study of physics are :
Rectangular (Cartesian) coordinate system is the most convenient as it is easy to visualize and associate with our perception of motion in daily life. Spherical and cylindrical systems are specifically designed to describe motions, which follow spherical or cylindrical curvatures.
The measurements of distances along three mutually perpendicular directions, designated as x,y and z, completely define a point A (x,y,z).
A point in rectangular coordinate system
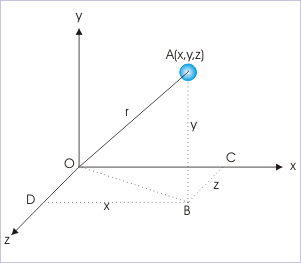
From geometric consideration of triangle OAB,
From geometric consideration of triangle OBD,
Combining above two relations, we have :
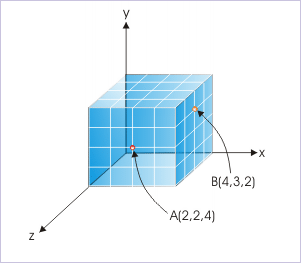
The numbers are assigned to a point in the sequence x, y, z as shown for the points A and B.
Specifying points in rectangular coordinate system
Rectangular coordinate system can also be viewed as volume composed of three rectangular surfaces. The three surfaces are designated as a pair of axial designations like “xy” plane. We may infer that the “xy” plane is defined by two lines (x and y axes) at right angle. Thus, there are “xy”, “yz” and “zx” rectangular planes that make up the space (volumetric extent) of the coordinate system (See figure).
Planes in rectangular coordinate system
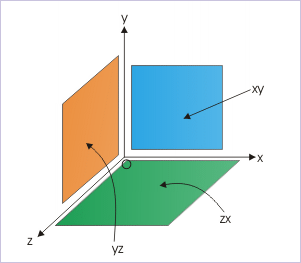
The motion need not be extended in all three directions, but may be limited to two or one dimensions. A circular motion, for example, can be represented in any of the three planes, whereby only two axes with an origin will be required to describe motion. A linear motion, on the other hand, will require representation in one dimension only.
A three dimensional point “A” in spherical coordinate system is considered to be located on a sphere of a radius “r”. The point lies on a particular cross section (or plane) containing origin of the coordinate system. This cross section makes an angle “θ” from the “zx” plane (also known as longitude angle). Once the plane is identified, the angle, φ, that the line joining origin O to the point A, makes with “z” axis, uniquely defines the point A (r, θ, φ).
Spherical coordinate system
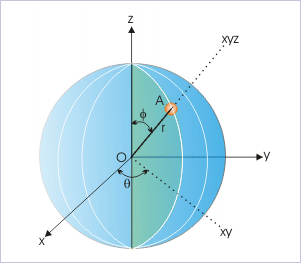
It must be realized here that we need to designate three values r, θ and φ to uniquely define the point A. If we do not specify θ, the point could then lie any of the infinite numbers of possible cross section through the sphere like A'(See Figure below).
Spherical coordinate system
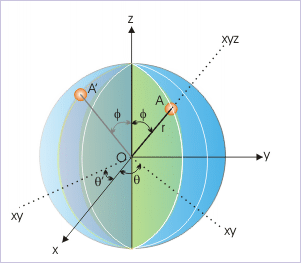
From geometric consideration of spherical coordinate system :
These relations can be easily obtained, if we know to determine projection of a directional quantity like position vector. For example, the projection of "r" in "xy" plane is "r sinφ". In turn, projection of "r sinφ" along x-axis is ""r sinφ cosθ". Hence,
In the similar fashion, we can determine other relations.
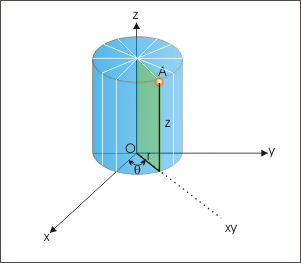
A three dimensional point “A” in cylindrical coordinate system is considered to be located on a cylinder of a radius “r”. The point lies on a particular cross section (or plane) containing origin of the coordinate system. This cross section makes an angle “θ” from the “zx” plane. Once the plane is identified, the height, z, parallel to vertical axis “z” uniquely defines the point A(r, θ, z)
Cylindrical coordinate system

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?