| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section we investigate double integrals and show how we can use them to find the volume of a solid over a rectangular region in the -plane. Many of the properties of double integrals are similar to those we have already discussed for single integrals.
We begin by considering the space above a rectangular region R . Consider a continuous function of two variables defined on the closed rectangle R :
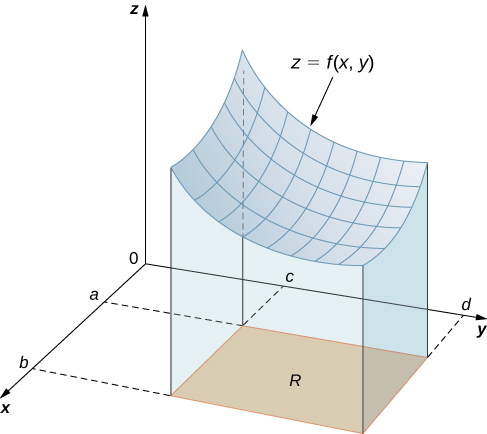
Here denotes the Cartesian product of the two closed intervals and It consists of rectangular pairs such that and The graph of represents a surface above the -plane with equation where is the height of the surface at the point Let be the solid that lies above and under the graph of ( [link] ). The base of the solid is the rectangle in the -plane. We want to find the volume of the solid
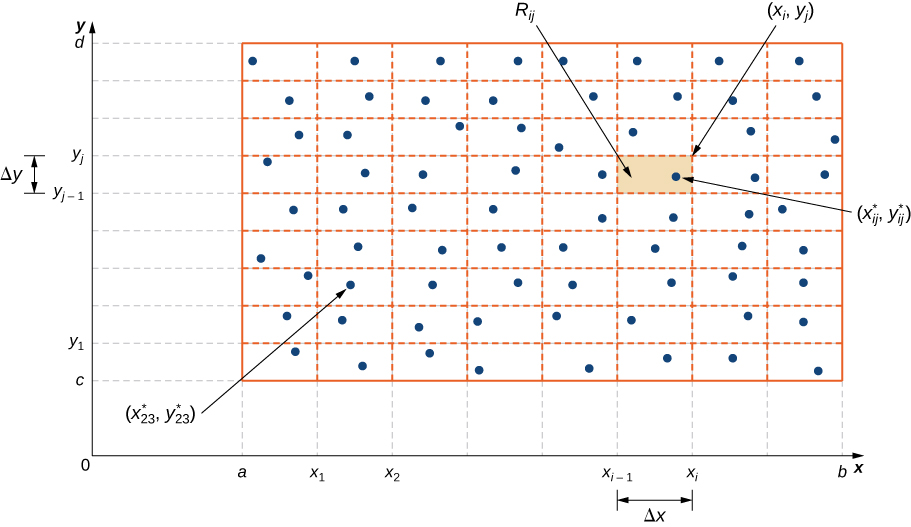
We divide the region into small rectangles each with area and with sides and ( [link] ). We do this by dividing the interval into subintervals and dividing the interval into subintervals. Hence and
The volume of a thin rectangular box above is where is an arbitrary sample point in each as shown in the following figure.
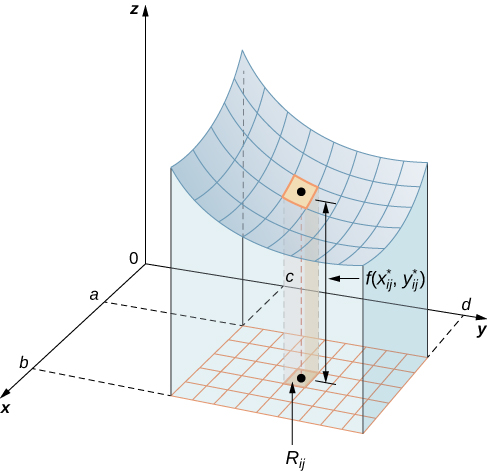
Using the same idea for all the subrectangles, we obtain an approximate volume of the solid as This sum is known as a double Riemann sum and can be used to approximate the value of the volume of the solid. Here the double sum means that for each subrectangle we evaluate the function at the chosen point, multiply by the area of each rectangle, and then add all the results.
As we have seen in the single-variable case, we obtain a better approximation to the actual volume if m and n become larger.
Note that the sum approaches a limit in either case and the limit is the volume of the solid with the base R . Now we are ready to define the double integral.
The double integral of the function over the rectangular region in the -plane is defined as
If then the volume V of the solid S , which lies above in the -plane and under the graph of f , is the double integral of the function over the rectangle If the function is ever negative, then the double integral can be considered a “signed” volume in a manner similar to the way we defined net signed area in The Definite Integral .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?