| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Spontaneous fission can occur, but this is usually not the most common decay mode for a given nuclide. For example, can spontaneously fission, but it decays mostly by emission. Neutron-induced fission is crucial as seen in [link] . Being chargeless, even low-energy neutrons can strike a nucleus and be absorbed once they feel the attractive nuclear force. Large nuclei are described by a liquid drop model with surface tension and oscillation modes, because the large number of nucleons act like atoms in a drop. The neutron is attracted and thus, deposits energy, causing the nucleus to deform as a liquid drop. If stretched enough, the nucleus narrows in the middle. The number of nucleons in contact and the strength of the nuclear force binding the nucleus together are reduced. Coulomb repulsion between the two ends then succeeds in fissioning the nucleus, which pops like a water drop into two large pieces and a few neutrons. Neutron-induced fission can be written as
where and are the two daughter nuclei, called fission fragments , and is the number of neutrons produced. Most often, the masses of the fission fragments are not the same. Most of the released energy goes into the kinetic energy of the fission fragments, with the remainder going into the neutrons and excited states of the fragments. Since neutrons can induce fission, a self-sustaining chain reaction is possible, provided more than one neutron is produced on average — that is, if in . This can also be seen in [link] .
An example of a typical neutron-induced fission reaction is
Note that in this equation, the total charge remains the same (is conserved): . Also, as far as whole numbers are concerned, the mass is constant: . This is not true when we consider the masses out to 6 or 7 significant places, as in the previous example.
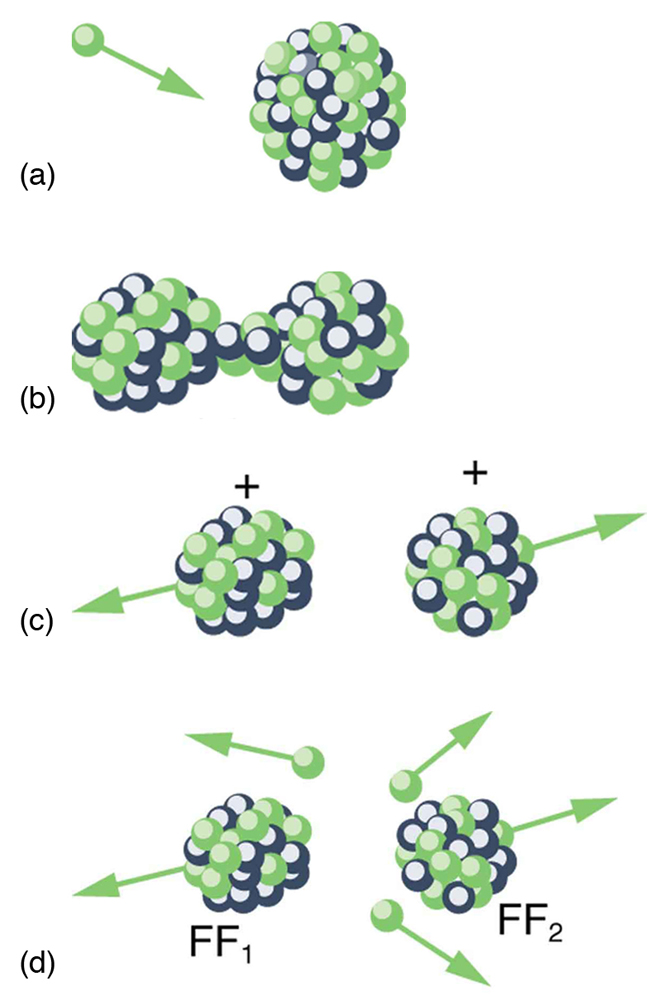
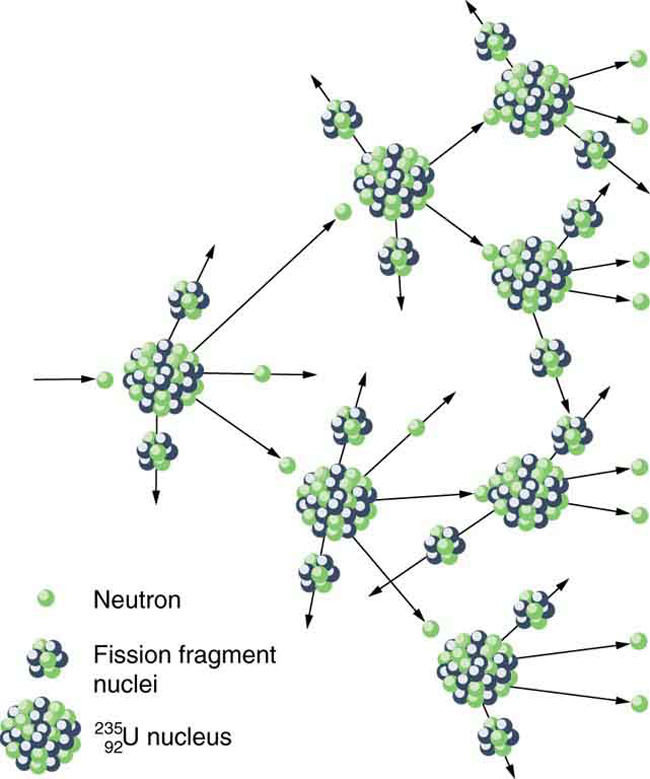
Not every neutron produced by fission induces fission. Some neutrons escape the fissionable material, while others interact with a nucleus without making it fission. We can enhance the number of fissions produced by neutrons by having a large amount of fissionable material. The minimum amount necessary for self-sustained fission of a given nuclide is called its critical mass . Some nuclides, such as , produce more neutrons per fission than others, such as . Additionally, some nuclides are easier to make fission than others. In particular, and are easier to fission than the much more abundant . Both factors affect critical mass, which is smallest for .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics -- hlca 1104' conversation and receive update notifications?