| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| LO 1.3 |
1. Licky was sad because ……………………………………………………........
2. Willy wanted to help Licky because …………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………..........3. The children could not find Licky’s tail because ................................................
……………………………………………………………………………………..........
4. They had to stop the search for Licky’s tail because …………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………..........
5. When someone is sad I ……………………………………………………........
6. Willy and Licky were laughing and shouting for joy because ……………........
……………………………………………………………………………………..........
7. Willy went to ask Wise Old Owl’s advice because …………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………..........
8. Wise Old Owl knew Licky would grow another tail because ………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………..........
| LO 1.3.6 | LO 4.5.1 | LO 5.2.1 |
Licky’s tail will grow again,
Hooray! Hooray! Hooray!
It will grow and grow and grow again
He’ll have a new one soon they say.
The sun is shining warm and bright
So come let’s sing and play,
We needn’t worry any more
We’ll smile and cheer, hooray! hooray!
G.J.M.
| LO 2.3 | LO 3.4.1 |
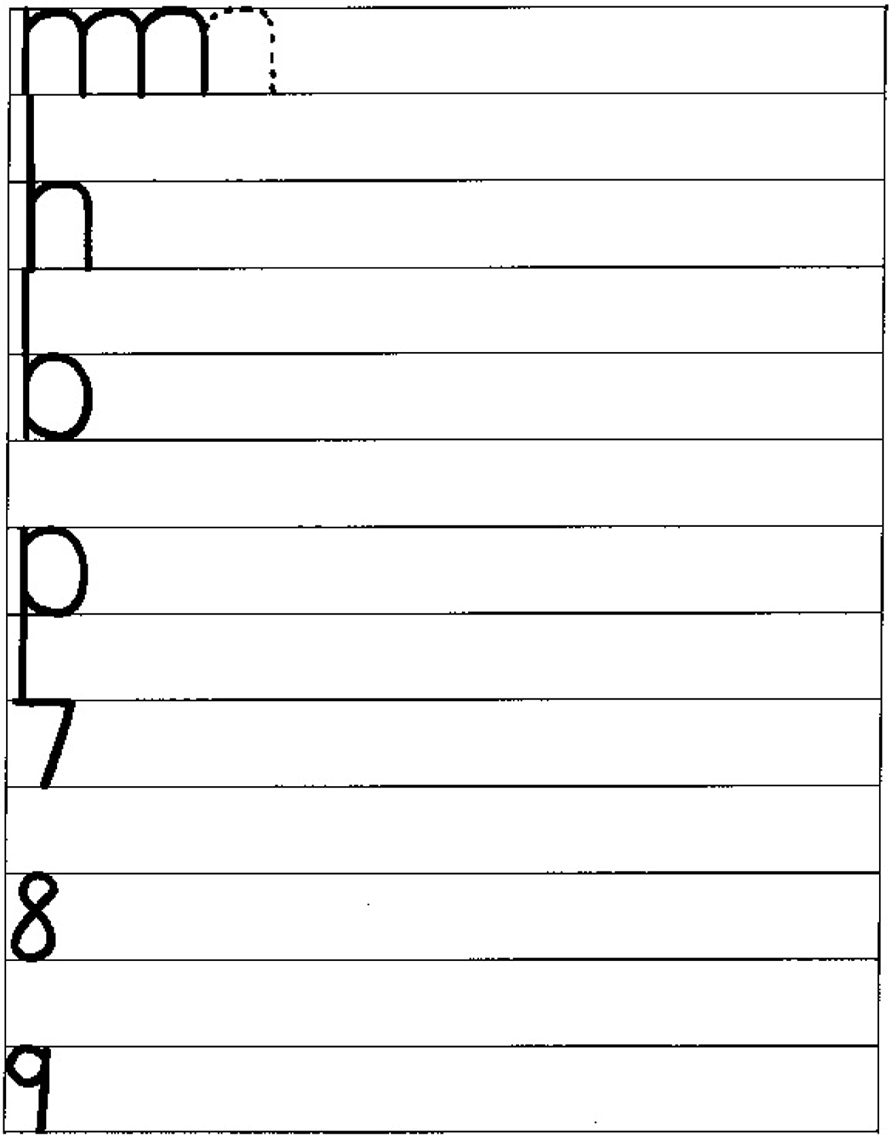

| LO 4.1.2 | LO 4.1.3 |
1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . lost his tail.
2. He lost it in the . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . caught Licky by the tail.
4. The children looked under the . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5. Licky was very . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6. Wise old Owl was sleeping in the . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Willy
Licky
tree
forest
leaves
sad
| LO 4.5.1 | LO 5.3.4 |
We’re h-a-p-p-y
We’re h-a-p-p-y
Licky’s found his tail again
Now he will not cry again
We’re h-a-p-p-y
We’ll jump up high
And bend down low
And clap our hands
All in a row,
We’ll turn and turn
And turn around,
We’ll touch the sky
And then the ground
We’re h-a-p-p-y!
G.J.M.
| LO 2.3 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING: The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to short stories, rhymes, poems and songs from a variety of cultures, and shows understanding:
1.3.6 answers open questions about the story.
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.3: We know this when the learner sings, recites, acts out and mimes songs, poems and rhymes.
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner recognises letters and words and makes meaning of written text:
3.4.1 reads simple written materials (labels, stories, ect.) for different purposes;
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.1: We know this when the learner writes with increasing legibility:
4.1.2 develops letter formation and handwriting skills, drawing patterns, tracing and copying word);
4.1.3 forms letters of the alphabet successfully.
Assessment Standard 4.5: We know this when the learner writes so that others can understand, using writing conventions:
4.5.1 uses letters to form single words and short sentences;
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.2: We know this when the learner uses language to think and reason:
5.2.1 understands and uses language for logic and reasoning, such as cause and effect;
Assessment Standard 5.3: We know this when the learner uses language to investigate and explore:
5.3.4 solves picture and word puzzles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?