| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
ACTIVITY 1
To understand how equations can be represented on a graph
[LO 2.2, 2.5, 2.6]
E x ample : The equation y = 3 x + 2 tells one how the values of x and y are connected – it shows the relationship between two variables, x and y .
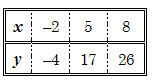
The point of making a table is that it gives us coordinates, which we can plot on a set of axes. From these we can draw a graph, which is a picture of the relationship between x and y.
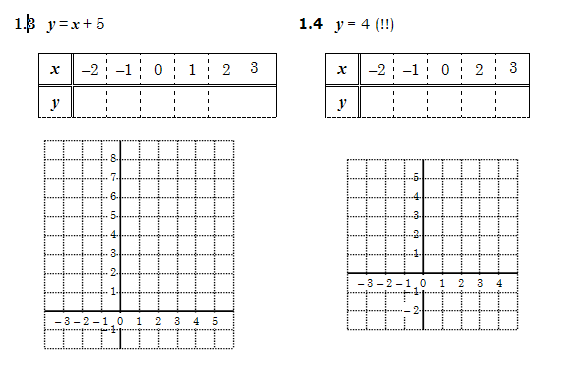
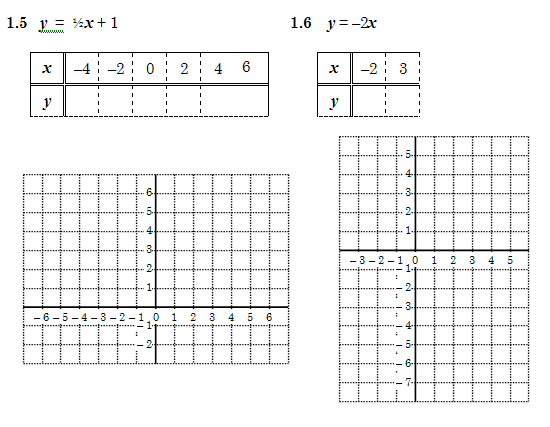
1 In a group of 4 or 5 learners, complete the tables from the equations below. Each one should do a different table, and then discuss the answers and copy the others’ tables into your book. Below each table is a set of axes on which to draw the graph. All of these graphs will be straight lines, so you may connect the points you plot from each table.

2 In your group, discuss what you see in your graphs. Compare the graph with the equation. Here are a few suggestions for you to investigate:
2.1 What does the coefficient of x in the equation do to the graph? What happens when the coefficient is negative?
2.2 In 1.6 the table has only two columns. Is it necessary to have more than two columns if you know that the graph will be a straight line?
2.3 Compare 1.1 and 1.5 to see if you can find out what the constant does to the graph.
| Equation: | x | y |
| Equation: | Independent variable | Dependent variable |
| Flow diagram:: | Input value | Output value |
| Table: | First row | Second row |
| Coordinates: | 1st coordinate | 2nd coordinate |
| Graph: | x – axis | y – axis |
| Graph: | Horizontal axis | Vertical axis |
ACTIVITY 2
To understand and apply all the characteristics of the straight-line graph
[LO 2.5]
1 In the previous activity you used equations to make tables from which graphs were drawn. One can also draw a graph from an equation without making a table. As we saw in graph 1.6 above, if we know that we have to draw a straight line, then two points on the graph paper are sufficient to enable us to draw the line. We don’t need a table if we have the equation of the straight line.
y = mx + c is the standard form of the equation:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?