This module is from Elementary Algebra by Denny Burzynski and Wade Ellis, Jr.
The symbols, notations, and properties of numbers that form the basis of algebra, as well as exponents and the rules of exponents, are introduced in this chapter. Each property of real numbers and the rules of exponents are expressed both symbolically and literally. Literal explanations are included because symbolic explanations alone may be difficult for a student to interpret.Objectives of this module: be familiar with the real number line and the real numbers, understand the ordering of the real numbers.
Overview
- The Real Number Line
- The Real Numbers
- Ordering the Real Numbers
The real number line
Real number line
In our study of algebra, we will use several collections of numbers. The
real number line allows us to
visually display the numbers in which we are interested.
A line is composed of infinitely many points. To each point we can associate a unique number, and with each number we can associate a particular point.
Coordinate
The number associated with a point on the number line is called the
coordinate of the point.
Graph
The point on a line that is associated with a particular number is called the
graph of that number.
We construct the real number line as follows:
Construction of the real number line
- Draw a horizontal line.

- Choose any point on the line and label it 0. This point is called the
origin .

- Choose a convenient length. This length is called "1 unit." Starting at 0, mark this length off in both directions, being careful to have the lengths look like they are about the same.

We now define a real number.
Real number
A
real number is any number that is the coordinate of a point on the real number line.
Positive and negative real numbers
The collection of these infinitely many numbers is called the
collection of real numbers . The real numbers whose graphs are to the right of 0 are called the
positive real numbers . The real numbers whose graphs appear to the left of 0 are called the
negative real numbers .
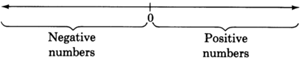
The number 0 is neither positive nor negative.
The real numbers
The collection of real numbers has many subcollections. The subcollections that are of most interest to us are listed below along with their notations and graphs.
Natural numbers
The
natural numbers
:
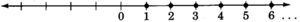
Whole numbers
The
whole numbers
:
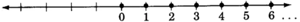
Notice that every natural number is a whole number.
Integers
The
integers
:

Notice that every whole number is an integer.
Rational numbers
The
rational numbers
: Rational numbers are real numbers that can be written in the form
, where
and
are integers, and
.
Fractions
Rational numbers are commonly called
fractions.
Division by 1
Since
can equal 1, every integer is a rational number:
.
Division by 0
Recall that
since
. However, if
, then
. But
, not 10. This suggests that no quotient exists.
Now consider
. If
, then
. But this means that
could be any number, that is,
since
, or
since
. This suggests that the quotient is indeterminant.

