| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
5. Where do you think Baby Wop is?
6. How will they find her?
| LO 3.1.1 | LO 1.3 | 5.3.2 |
Is she playing with Tiny?
Is she playing with Tuck?
Where is she?

Is she dancing with Tiny?
Is she dancing with Tuck?
Where is she?

Is she catching yellow butterflies?
Is she catching
white butterflies?
Where is she?

Is she talking to a little frog?
Is she talking to Tiny and Tuck?

| LO 2.8.1 | LO 3.4.1 | ||
| LO 3.3.1 | LO 3.4.3 |
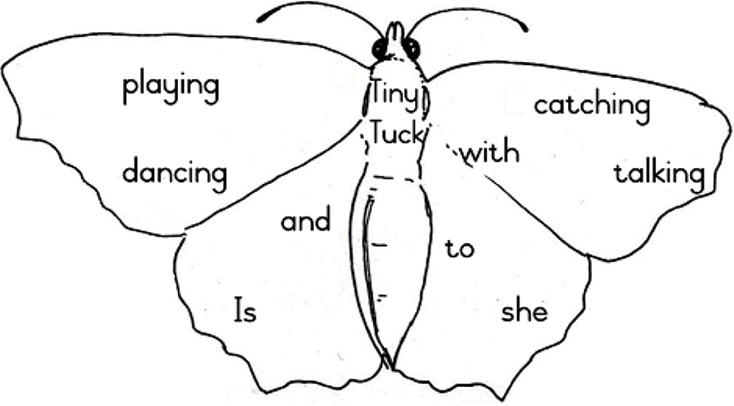
Is she……………………………………...
…………………………………………….
…………………………………………….
…………………………………………….
…………………………………………….
| LO 3.4.2 | LO 4.5.1 | LO 4.5.2 | LO 6.3.1 |
Learning Outcome 1: LISTENING: The learner is able to listen for information and enjoyment and respond appropriately and critically in a wider range of situations.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner listens with enjoyment to short stories, rhymes, poems and songs form a variety of cultures, and shows understanding;
Learning Outcome 2: SPEAKING : The learner is able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.
Assessment Standard 2.8: We know this when the learner contributes to class and group discussions:
2.8.1 by taking turns, asking questions and showing sensitivity to the rights and feelings of others,
Learning Outcome 3: READING AND VIEWING : The learner is able to read and view for information and enjoyment and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.
Assessment Standard 3.1: We know this when the learner uses visual clues to make meaning:
3.1.1 predicts from the cover of a book what the story is about;
Assessment Standard 3.3: We know this when the learner makes meaning of written text:
3.3.1 reads a story with the teacher and discusses the main idea;
Assessment Standard 3.4: We know this when the learner recognises letters and words and makes meaning of written text:
3.4.1 reads simple written materials (labels, stories, etc.) for different purposes;
3.4.2 reads own writing and the writing of classmates;
3.4.3 uses phonic and word recognition skills to decode new or unfamiliar words in context (e.g. visual cues like shape of word and letter patterns, picture clues, context clues, and letter-sound relationships);
Learning Outcome 4: WRITING : The learner is able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.
Assessment Standard 4.5: We know this when the learner writes so that others can understand, using writing conventions:
4.5.1 uses letters to form single words and short sentences;
4.5.2 leaves spaces between words;
Learning Outcome 5: THINKING AND REASONING : The learner is able to use language to think and reason, and access, process and use information for learning.
Assessment Standard 5.3: We know this when the learner uses language to investigate and explore:
5.3.2 offers explanations and solutions;
Learning Outcome 6: LANGUAGE STRUCTURE AND USE : The learner will know and be able to use the sounds, words and grammar of the language to create and interpret texts.
Assessment Standard 6.3: We know this when the learner works with sentences:
6.3.1 writes simple sentences.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'English home language grade 1' conversation and receive update notifications?