| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
to
where, in this case, is the pressure at the water works and is the resistance of the water main. During times of heavy use, the flow rate is large. This means that must also be large. Thus must decrease. It is correct to think of flow and resistance as causing the pressure to drop from to . is valid for both laminar and turbulent flows.
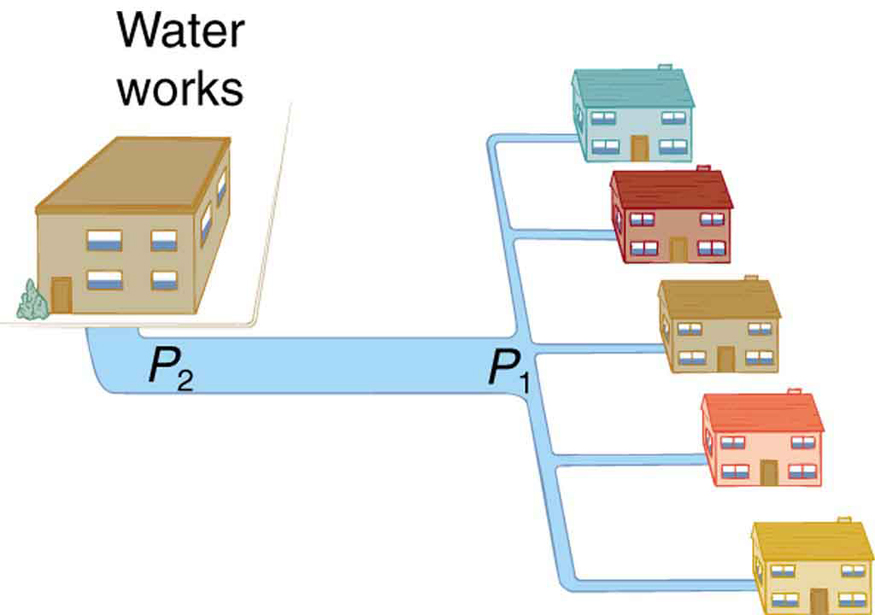
We can use to analyze pressure drops occurring in more complex systems in which the tube radius is not the same everywhere. Resistance will be much greater in narrow places, such as an obstructed coronary artery. For a given flow rate , the pressure drop will be greatest where the tube is most narrow. This is how water faucets control flow. Additionally, is greatly increased by turbulence, and a constriction that creates turbulence greatly reduces the pressure downstream. Plaque in an artery reduces pressure and hence flow, both by its resistance and by the turbulence it creates.
[link] is a schematic of the human circulatory system, showing average blood pressures in its major parts for an adult at rest. Pressure created by the heart’s two pumps, the right and left ventricles, is reduced by the resistance of the blood vessels as the blood flows through them. The left ventricle increases arterial blood pressure that drives the flow of blood through all parts of the body except the lungs. The right ventricle receives the lower pressure blood from two major veins and pumps it through the lungs for gas exchange with atmospheric gases – the disposal of carbon dioxide from the blood and the replenishment of oxygen. Only one major organ is shown schematically, with typical branching of arteries to ever smaller vessels, the smallest of which are the capillaries, and rejoining of small veins into larger ones. Similar branching takes place in a variety of organs in the body, and the circulatory system has considerable flexibility in flow regulation to these organs by the dilation and constriction of the arteries leading to them and the capillaries within them. The sensitivity of flow to tube radius makes this flexibility possible over a large range of flow rates.
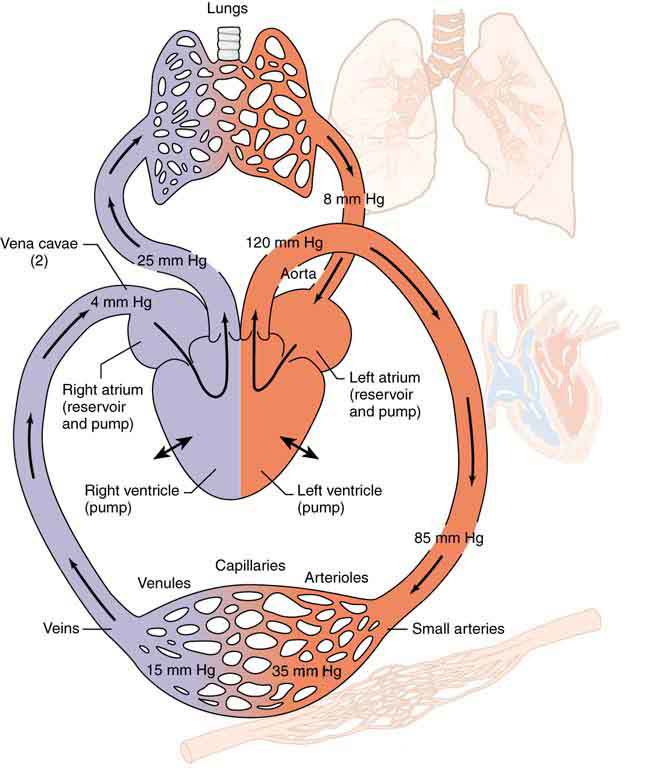
Each branching of larger vessels into smaller vessels increases the total cross-sectional area of the tubes through which the blood flows. For example, an artery with a cross section of may branch into 20 smaller arteries, each with cross sections of , with a total of . In that manner, the resistance of the branchings is reduced so that pressure is not entirely lost. Moreover, because and increases through branching, the average velocity of the blood in the smaller vessels is reduced. The blood velocity in the aorta ( ) is about 25 cm/s, while in the capillaries ( in diameter) the velocity is about 1 mm/s. This reduced velocity allows the blood to exchange substances with the cells in the capillaries and alveoli in particular.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics ii' conversation and receive update notifications?