| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
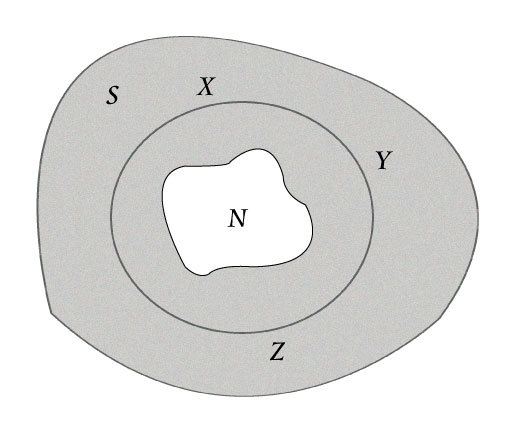
In the closed path XYZ encircling the non-superconducting region there will be a phase difference of the electron-pair wave between any two points, such as X and Y, on the curve due to the field and the circulating current.
If the superelectrons are represented by a single wave then at any point on XYZX it can only have one value of phase and amplitude. Due to the long range coherence the phase is single valued also called quantized meaning around the circumference of the ring Δφ must equal 2πn where n is any integer. Due to the wave only having a single value the fluxoid can only exist in quantized units. This quantum is termed the fluxon, φ 0 , given by
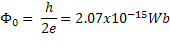
If two superconducting regions are kept totally isolated from each other the phases of the electron-pairs in the two regions will be unrelated. If the two regions are brought together then as they come close electron-pairs will be able to tunnel across the gap and the two electron-pair waves will become coupled. As the separation decreases, the strength of the coupling increases. The tunneling of the electron-pairs across the gap carries with it a superconducting current as predicted by B.D. Josephson and is called "Josephson tunneling" with the junction between the two superconductors called a "Josephson junction" ( [link] ).
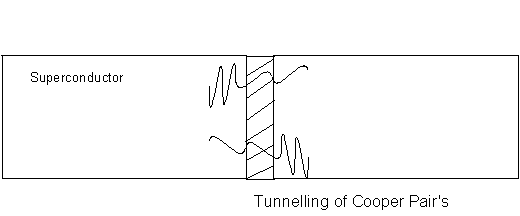
The Josephson tunneling junction is a special case of a more general type of weak link between two superconductors. Other forms include constrictions and point contacts but the general form is of a region between two superconductors which has a much lower critical current and through which a magnetic field can penetrate.
A superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) uses the properties of electron-pair wave coherence and Josephson Junctions to detect very small magnetic fields. The central element of a SQUID is a ring of superconducting material with one or more weak links called Josephesons Junctions. An example is shown in the below. With weak-links at points W and X whose critical current, i c , is much less than the critical current of the main ring. This produces a very low current density making the momentum of the electron-pairs small. The wavelength of the electron-pairs is thus very long leading to little difference in phase between any parts of the ring.
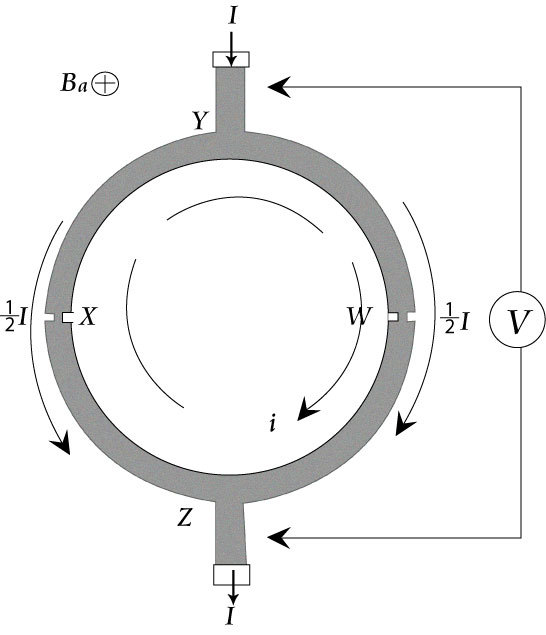
If a magnetic field, B a , is applied perpendicular to the plane of the ring ( [link] ), a phase difference is produced in the electron-pair wave along the path XYW and WZX. One of the features of a superconducting loop is that the magnetic flux, Φ, passing through it which is the product of the magnetic field and the area of the loop and is quantized in units of Φ 0 = h / (2 e ), where h is Planck’s constant, 2 e is the charge of the Cooper pair of electrons, and Φ 0 has a value of 2 × 10 –15 tesla m 2 . If there are no obstacles in the loop, then the superconducting current will compensate for the presence of an arbitrary magnetic field so that the total flux through the loop (due to the external field plus the field generated by the current) is a multiple of Φ 0 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?