| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For substrates that are diamagnetic, under zero applied field, this means it has no effect on the measurement of magnetization. Under applied fields its contribution is linear and temperature independent. The diamagnetic contribution can be calculated from knowledge of the volume and properties of the substrate and subtracted as a constant linear term to produce the signal from the sample alone. The diamagnetic background can also be seen clearly at high fields where the sample has reached saturation: the sample saturates but the linear background from the substrate continues to increase with field. The gradient of this background can be recorded and subtracted from the readings if the substrate properties are not known accurately.
When a material exhibits hysteresis, it means that the material responds to a force and has a history of that force contained within it. Consider if you press on something until it depresses. When you release that pressure, if the material remains depressed and doesn’t spring back then it is said to exhibit some type of hysteresis. It remembers a history of what happened to it, and may exhibit that history in some way. Consider a piece of iron that is brought into a magnetic field, it retains some magnetization, even after the external magnetic field is removed. Once magnetized, the iron will stay magnetized indefinitely. To demagnetize the iron, it is necessary to apply a magnetic field in the opposite direction. This is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive.
The response of a material to an applied field and its magnetic hysteresis is an essential tool of magnetometry. Paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials can easily be recognized, soft and hard ferromagnetic materials give different types of hysteresis curves and from these curves values such as saturation magnetization, remnant magnetization and coercivity are readily observed. More detailed curves can give indications of the type of magnetic interactions within the sample.
The intensity of magnetization depends upon both the magnetic moments in the sample and the way that they are oriented with respect to each other, known as the magnetic ordering.
Diamagnetic materials, which have no atomic magnetic moments, have no magnetization in zero field. When a field is applied a small, negative moment is induced on the diamagnetic atoms proportional to the applied field strength. As the field is reduced the induced moment is reduced.
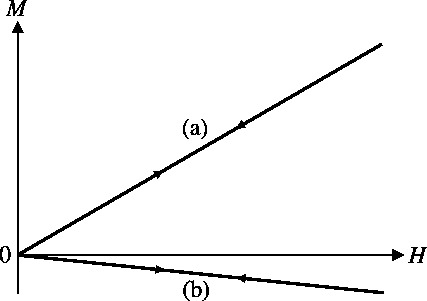
In a paramagnet the atoms have a net magnetic moment but are oriented randomly throughout the sample due to thermal agitation, giving zero magnetization. As a field is applied the moments tend towards alignment along the field, giving a net magnetization which increases with applied field as the moments become more ordered. As the field is reduced the moments become disordered again by their thermal agitation. The figure shows the linear response M v H where μH<<kT.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?