| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nanoparticles are dynamic; their properties can change when exposed to new chemical environments, leading to a new set of applications. It is the dynamics of nanoparticles that makes them so useful and is one of the reasons why scientists strive to understand their properties. However, it is this dynamic ability that makes analysis difficult to do properly. Nanoparticles are easily damaged and can change properties over time or with exposure to air, light or any other environment, chemical or otherwise. Surface analysis is often difficult because of the high rate of contamination. Once the particles are inserted into XPS, even more limitations appear.
There are often artifacts introduced from the simple mechanism of conducting the analysis. When XPS is used to analyze the relatively large surface of thin films, there is small change in temperature as energy is transferred. The thin films, however, are large enough that this small change in energy has to significant change to its properties. A nanoparticle is much smaller. Even a small amount of energy can drastically change the shape of particles, in turn changing the properties, giving a much different set of data than expected.
The electron beam itself can affect how the particles are supported on a substrate. Theoretically, nanoparticles would be considered separate from each other and any other chemical environments, such as solvents or substrates. This, however, is not possible, as the particles must be suspended in a solution or placed on a substrate when attempting analysis. The chemical environment around the particle will have some amount of interaction with the particle. This interaction will change characteristics of the nanoparticles, such as oxidation states or partial charges, which will then shift the peaks observed. If particles can be separated and suspended on a substrate, the supporting material will also be analyzed due to the fact that the X-ray beam is larger than the size of each individual particle. If the substrate is made of porous materials, it can adsorb gases and those will be detected along with the substrate and the particle, giving erroneous data.
Nanoparticles will often react, or at least interact, with their environments. If the particles are highly reactive, there will often be induced charges in the near environment of the particle. Gold nanoparticles have a well-documented ability to undergo plasmon interactions with each other. When XPS is performed on these particles, the charges will change the kinetic energy of the electrons, shifting the apparent binding energy. When working with nanoparticles that are well known for creating charges, it is often best to use an ion gun or a coating of gold. The purpose of the ion gun or gold coating is to try to move peaks back to their appropriate energies. If the peaks do not move, then the chance of there being no induced charge is high and thus the obtained data is fairly reliable.
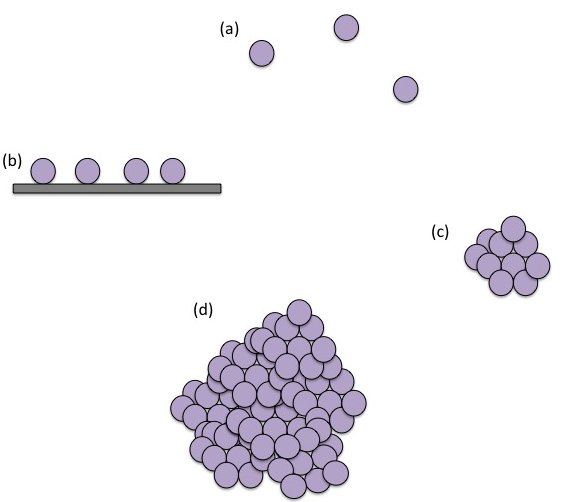
The proximity of the particles to each other will cause interactions between the particles. If there is a charge accumulation near one particle, and that particle is in close proximity with other particles, the charge will become enhanced as it spreads, affecting the signal strength and the binding energies of the electrons. While the knowledge of charge enhancement could be useful to potential applications, it is not beneficial if knowledge of the various properties of individual particles is sought.
Less isolated (i.e., less crowded) particles will have different properties as compared to more isolated particles. A good example of this is the plasmon effect in gold nanoparticles. The closer gold nanoparticles are to each other, the more likely they will induce the plasmon effect. This can change the properties of the particles, such as oxidation states and partial charges. These changes will then shift peaks seen in XPS spectra. These proximity effects are often introduced in the sample preparation. This, of course, shows why it is important to prepare samples correctly to get desired results.
Unfortunately there is no good general procedure for all nanoparticles samples. There are too many variables within each sample to create a basic procedure. A scientist wanting to use XPS to analyze nanoparticles must first understand the drawbacks and limitations of using their sample as well as how to counteract the artifacts that will be introduced in order to properly use XPS.
One must never make the assumption that nanoparticles are flat. This assumption will only lead to a misrepresentation of the particles. Once the curvature and stacking of the particles, as well as their interactions with each other are taken into account, XPS can be run.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?