| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Both AFM and STM are widely used in nano-science. According to the different working principles though, they have their own advantages and disadvantages when measuring specific properties of sample ( [link] ). STM requires an electric circuit including the tip and sample to let the tunneling current go through. That means, the sample for STM must be conducting. In case of AFM however, it just measures the deflection of the cantilever caused by the van der Waals forces between the tip and sample. Thus, in general any kind of sample can be used for AFM. But, because of the exponential relation of the tunneling current and distance, STM has a better resolution than AFM. In STM image one can actually “see” an individual atom, while in AFM it’s almost impossible, and the quality of AFM image is largely depended on the shape and contact force of the tip. In some cases, the measured signal would be rather complicated to interpret into morphology or other properties of sample. On the other side, STM can give straight forward electric property of the sample surface.
| AFM | STM | |
| Sample requirement | - | Conducting |
| Work environment | Air, liquid | Vacuum |
| Lateral resolution | ~1 nm | ~0.1 nm |
| Vertical resolution | ~0.05 nm | ~0.05 nm |
| Working mode | Tapping, contact | Constant current, constant height |
STM provides a powerful method to detect the surface of conducting and semi-conducting materials. Recently STM can also be applied in the imaging of insulators, superlattice assemblies and even the manipulation of molecules on surface. More importantly, STM can provide the surface structure and electric property of surface at atomic resolution, a true breakthrough in the development of nano-science. In this sense, the data collected from STM could reflect the local properties even of single molecule and atom. With these valuable measurement data, one could give a deeper understanding of structure-property relations in nanomaterials.
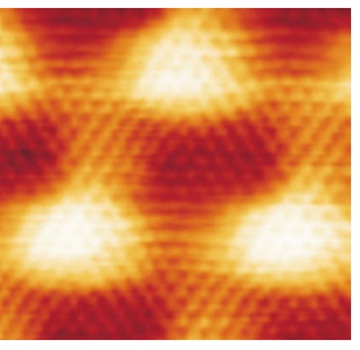
An excellent example is the STM imaging of graphene on Ru(0001), as shown in [link] . Clearly seen is the superstructure with a periodicity of ~30 Å , coming from the lattice mismatch of 12 unit cells of the graphene and 11 unit cells of the underneath Ru(0001) substrate. This so-called moiré structure can also be seen in other systems when the adsorbed layers have strong chemical bonds within the layer and weak interaction with the underlying surface. In this case, the periodic superstructure seen in graphene tells us that the formed graphene is well crystallized and expected to have high quality.
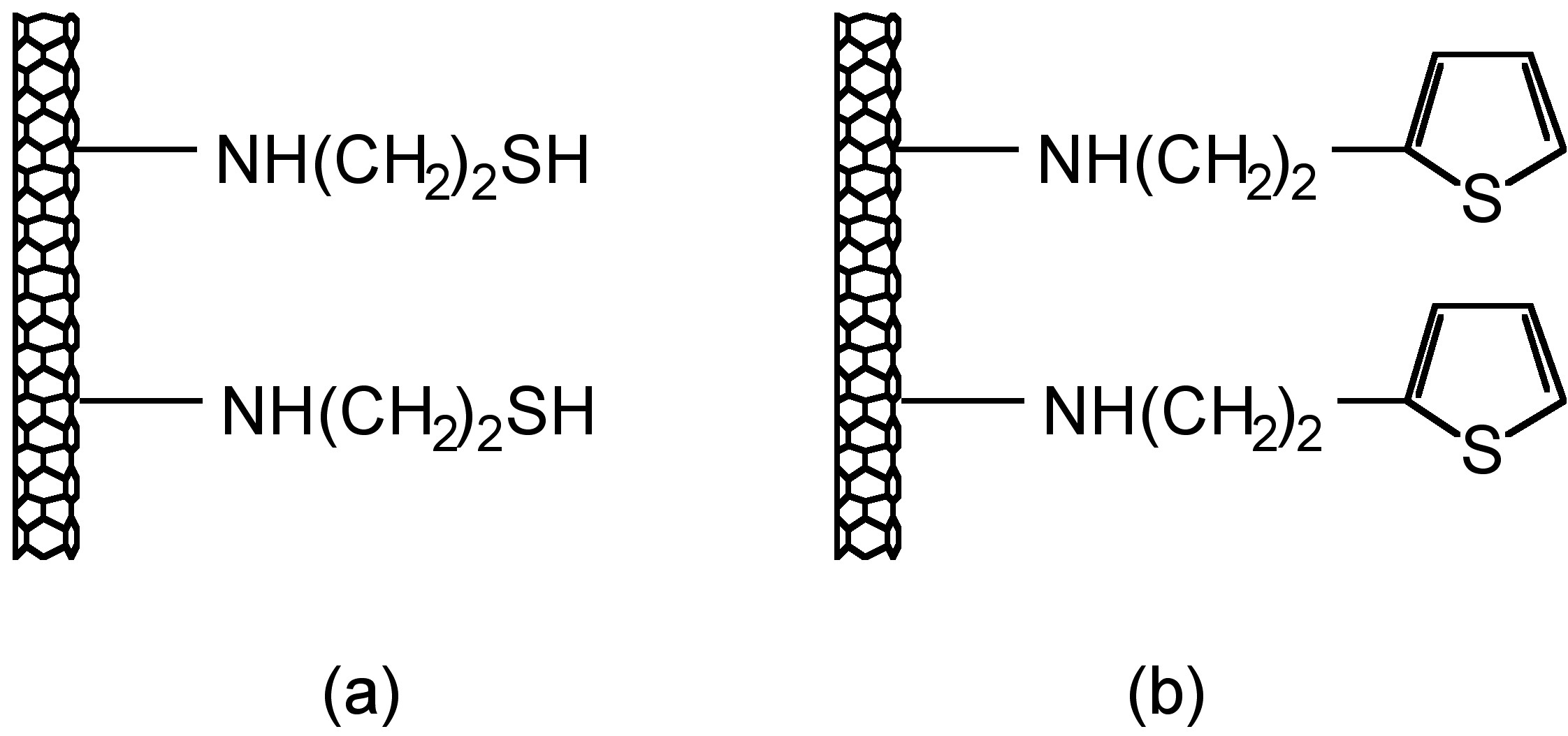
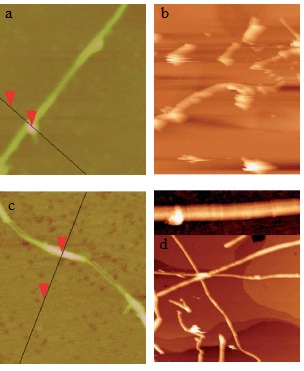
Another good example is shown to see that the measurement from STM could tell us the bonding information in single-molecular level. In thiol- and thiophene-functionalization of single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) ( [link] ), the use of Au nanoparticles as chemical markers for AFM gives misleading results, while STM imaging could give correct information of substituent location. From AFM image, Au-thiol-SWNT ( [link] a) shows that most of the sidewalls are unfunctionalized, while Au-thiophene-SWNT ( [link] c) shows long bands of continuous functionalized regions on SWNT. This could lead to the estimation that thiophene is better functionalized to SWNT than thiol. Yet, if we look up to the STM image ( [link] b and d), in thiol-SWNTs the multiple functional groups are tightly bonded in about 5 - 25 nm, while in thiophene-SWNTs the functionalization is spread out uniformly along the whole length of SWNT. This information indicates that actually the functionalization levels of thiol- and thiophene-SWNTs are comparable. The difference is that, in thiol-SWNTs, functional groups are grouped together and each group is bonded to a single gold nanoparticle, while in thiophene-SWNTs, every individual functional group is bonded to a nanoparticle.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?