| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Attenuated total reflectance-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) is a physical method of compositional analysis that builds upon traditional transmission FTIR spectroscopy to minimize sample preparation and optimize reproducibility. Condensed phase samples of relatively low refractive index are placed in close contact with a crystal of high refractive index and the infrared (IR) absorption spectrum of the sample can be collected. Based on total internal reflection, the absorption spectra of ATR resemble those of transmission FTIR. To learn more about transmission IR spectroscopy (FTIR) please refer to the module Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Metal Ligand Complexes .
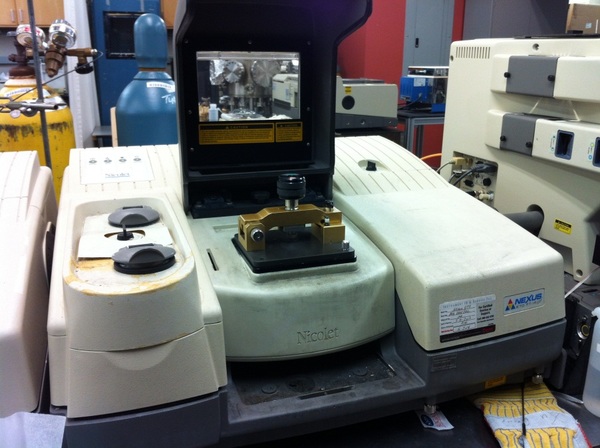
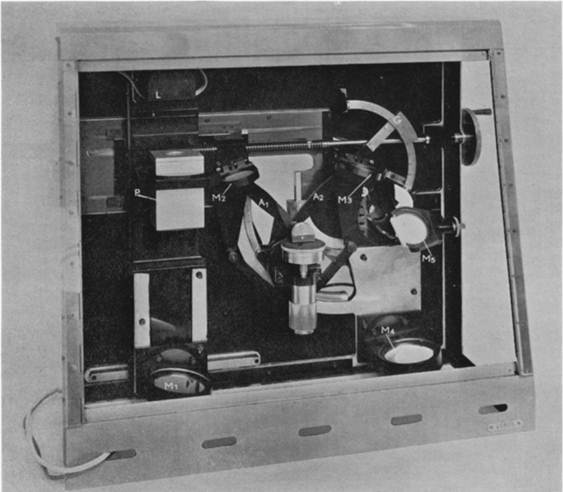
First publicly proposed in 1959 by Jacques Fahrenfort from the Royal Dutch Shell laboratories in Amsterdam, ATR IR spectroscopy was described as a technique to effectively measure weakly absorbing condensed phase materials. In Fahrenfort's first article describing the technique, published in 1961, he used a hemicylindrical ATR crystal (see Experimental Conditions) to produce single-reflection ATR ( [link] ). ATR IR spectroscopy was slow to become accepted as a method of characterization due to concerns about its quantitative effectiveness and reproducibility. The main concern being the sample and ATR crystal contact necessary to achieve decent spectral contrast. In the late 1980’s FTIR spectrometers began improving due to an increased dynamic range, signal to noise ratio, and faster computers. As a result ATR-FTIR also started gaining traction as an efficient spectroscopic technique. These days ATR accessories are often manufactured to work in conjunction with most FTIR spectrometers, as can be seen in [link] .

For additional information on light waves and their properties please refer to the module on Vertical Scanning Interferometry (VSI) .
When considering light propagating across an interface between two materials with different indices of refraction, the angle of refraction can be given by Snell’s law, [link] , where n 1 and n 2 refer to the refractive indices of the two materials.
When the incident medium has a higher refractive index than that of the transmitted medium, there will be a critical angle of incidence, [link] , where none of the incident light will be transmitted.
The reflectance of the interface is total and whenever light is incident from a higher refractive index medium onto a lower refractive index medium, the reflection is deemed internal (as opposed to external in the opposite scenario). Total internal reflectance experiences no losses, or no transmitted light ( [link] ).


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?