| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sample morphology has also seen to affect the RBMs. The same unfunctionalized sample in different aggregation states gives rise to different spectra. This is because the transition energy, E ii depends on the aggregation state of the SWNTs.
The tangential modes are the most intensive high-energy modes of SWNTs and form the so-called G-band, which is typically observed at around 1600 cm -1 . For this mode, the atomic displacements occur along the cicumferential direction ( [link] ). Spectra in this frequency can be used for SWNT characterization, independent of the RBM observation. This multi-peak feature can, for example, also be used for diameter characterization, although the information provided is less accurate than the RBM feature, and it gives information about the metallic character of the SWNTs in resonance with laser line.
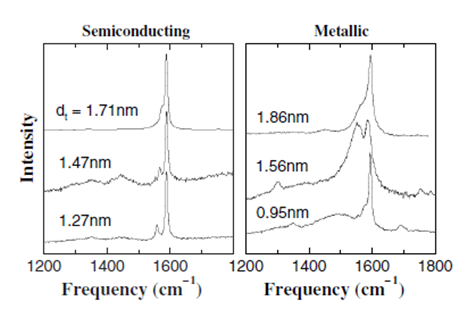
The tangential modes are useful in distinguishing semiconducting from metallic SWNTs. The difference is evident in the G- feature ( [link] and [link] ) which broadens and becomes asymmetric for metallic SWNTs in comparison with the Lorentzian lineshape for semiconducting tubes, and this broadening is related to the presence of free electrons in nanotubes with metallic character. This broadened G-feature is usually fit using a Breit-Wigner-Fano (BWF) line that accounts for the coupling of a discrete phonon with a continuum related to conduction electrons. This BWF line is observed in many graphite-like materials with metallic character, such as n-doped graphite intercalation compounds (GIC), n-doped fullerenes, as well as metallic SWNTs. The intensity of this G- mode depends on the size and number of metallic SWNTs in a bundle ( [link] ).

Chemical treatments are found to affect the line shape of the tangential line modes. Selective functionalization of SWNTs or a change in the ratio of metallic to semiconducting SWNTs due to selective etching is responsible for such a change. According to [link] , it can be seen that an increase or decrease of the BWF line shape is observed depending on the laser wavelength. At λ exc = 633 nm, the preferentially functionalized small diameter SWNTs are semiconducting, therefore the G-band shows a decrease in the BWG asymmetry. However, the situation is reversed at 514 nm, where small metallic tubes are probed. BWF resonance intensity of small bundles increases with bundle thickness, so care should be taken that the effect ascribed directly to functionalization of the SWNTs is not caused by the exfoliation of the previously bundles SWNT.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?