| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Various applications of nanotubes require different, specific modification to achieve desirable physical and chemical properties of nanotubes. In this regard, covalent functionalization provides a higher degree of fine-tuning the chemistry and physics of SWNTs than non-covalent functionalization. Until now, a variety of methods have been used to achieve the functionalization of nanotubes ( [link] ).
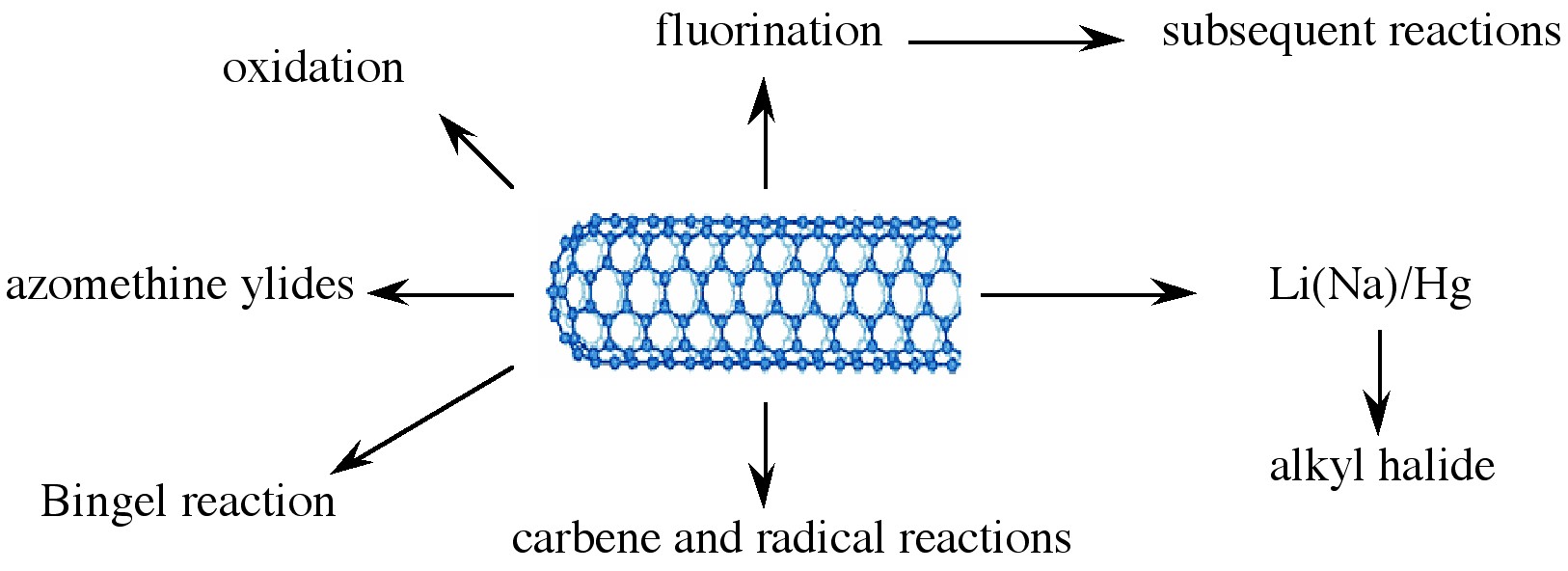
Taking chemistry developed for C 60 , SWNTs may be functionalized using 1,3 dipolar addition of azomethine ylides. The functionalized SWNTs are soluble in most common organic solvents. The azomethine ylide functionalization method was also used for the purification of SWNTs. Under electrochemical conditions, aryl diazonium salts react with SWNTs to achieve functionalized SWNTs, alternatively the diazonium ions may be generated in-situ from the corresponding aniline, while a solvent free reaction provides the best chance for large-scale functionalization this way. In each of these methods it is possible to control the amount of functionalization on the tube by varying reaction times and the reagents used; functionalization as high as 1 group per every 10 - 25 carbon atoms is possible.
Organic functionalization through the use of alkyl halides, a radical pathway, on tubes treated with lithium in liquid ammonia offers a simple and flexible route to a range of functional groups. In this reaction, functionalization occurs on every 17 carbons. Most success has been found when the tubes are dodecylated. These tubes are soluble in chloroform, DMF, and THF.
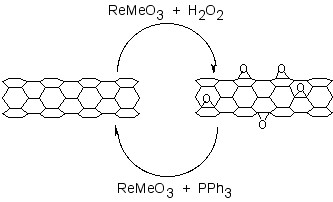
The addition of oxygen moieties to SWNT sidewalls can be achieved by treatment with acid or wet air oxidation, and ozonolysis. The direct epoxidation of SWNTs may be accomplished by the direct reaction with a peroxide reagent, or catalytically. Catalytic de-epoxidation ( [link] ) allows for the quantitative analysis of sidewall epoxide and led to the surprising result that previously assumed “pure” SWNTs actually contain ca . 1 oxygen per 250 carbon atoms.
One of the easiest functionalization routes, and a useful synthon for subsequent conversions, is the fluorination of SWNTs, using elemental fluorine. Importantly, a C:F ratios of up to 2:1 can be achieved without disruption of the tubular structure. The fluorinated SWNTs (F-SWNTs) proved to be much more soluble than pristine SWNTs in alcohols (1 mg/mL in iso -propanol), DMF and other selected organic solvents. Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) revealed that the fluorine formed bands of approximately 20 nm, while calculations using DFT revealed 1,2 addition is more energetically preferable than 1,4 addition, which has been confirmed by solid state 13 C NMR. F-SWNTs make highly flexible synthons and subsequent elaboration has been performed with organo lithium, Grignard reagents, and amines.
Functionalized nanotubes can be characterized by a variety of techniques, such as atomic force microscopy (AFM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV-vis spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy. Changes in the Raman spectrum of a nanotube sample can indicate if functionalization has occurred. Pristine tubes exhibit two distinct bands. They are the radial breathing mode (230 cm -1 ) and the tangential mode (1590 cm -1 ). When functionalized, a new band, called the disorder band, appears at ca. 1350 cm -1 . This band is attributed to sp 3 -hybridized carbons in the tube. Unfortunately, while the presence of a significant D mode is consistent with sidewall functionalization and the relative intensity of D (disorder) mode versus the tangential G mode (1550 – 1600 cm -1 ) is often used as a measure of the level of substitution. However, it has been shown that Raman is an unreliable method for determination of the extent of functionalization since the relative intensity of the D band is also a function of the substituents distribution as well as concentration. Recent studies suggest that solid state 13 C NMR are possibly the only definitive method of demonstrating covalent attachment of particular functional groups.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?