| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Due to the sensitivity of the equipment, it is important to rinse and clean the tubing before loading any sample or performing any experiments. To rinse the tubing and the chambers, use a solution of 2% of SDS. For this purpose, a cycle in the autosampler equipment is program with the steps shown in [link] .
| Step | Duration (min) | Speed (μL/min) | Volume (mL) |
| DI water (1:2) | 10 | 100 | 1 |
| SDS (1:1) | 20 | 300 | 6 |
| DI water (1:2) | 10 | 100 | 1 |
Once the equipment is cleaned, it is ready to perform an experiment, a second program in the autosampler is loaded with the parameters shown in [link] .
| Step | Duration (min) | Speed (μL/min) | Volume (mL) |
| Buffer (1:3) | 7 | 100 | 0.7 |
| Nanoparticles (1:4) | 30 | 100 | 3.0 |
The purpose of flowing the buffer in the beginning is to provide a background signal to take into account when running the samples. Usually a small quantity of the sample is loaded into the sensor at a very slow flow rate in order to let the deposition take place.
Example data obtained with the above parameters is shown in [link] . The blue squares depict the change in the frequency. As the experiment continues, the frequency decreases as more mass is deposited. On the other hand, shown as the red squares, the dissipation increases, describing the increase of both the height and certain loss of the rigidity in the layer from the top of the sensor. To illustrate the different steps of the experiment, each section has been color coded. The blue part of the data obtained corresponds to the flow of the buffer, while the yellow part corresponds to the deposition equilibrium of the nanoparticles onto the gold surface. After certain length of time equilibrium is reached and there is no further change. Once equilibrium indicates no change for about five minutes, it is safe to say the deposition will not change.
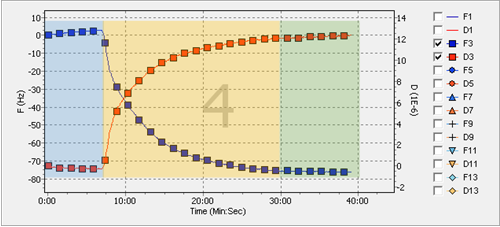
As a measure preventive care for the equipment, the same cleaning procedure should be followed as what was done before loading the sample. Use of a 2% solution of SDS helps to ensure the equipment remains as clean as possible.
Once the data has been obtained, QTools (software that is available in the software suit of the equipment) can be used to convert the change in the frequency to areal mass, via the Sauerbrey equation, [link] . The correspondent graph of areal mass is shown in [link] . From this graph we can observe how the mass is increasing as the nMag is deposited in the surface of the sensor. The blue section again illustrates the part of the experiment where only buffer was been flown to the chamber. The yellow part illustrates the deposition, while the green part shows no change in the mass after a period of time, which indicates the deposition is finished. The conversion from areal mass to mass is a simple process, as gold sensors come with a definite area of 1 cm 2 , but a more accurate measure should be taken when using functionalized sensors.
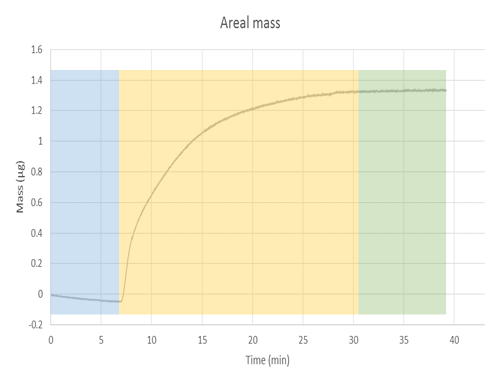
It is important to take into account the limitations of the Saubery equation, because the equation accounts for a uniform layer on top of the surface of the sensor. Deviations due to clusters of material deposited in one place or the formation of partial multilayers in the sensor cannot be calculated through this model. Further characterization of the surface should be done to have a more accurate model of the phenomena.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?