| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Typically the sample mass range should be between 0.1 to 10 mg and the heating rate should be 3 to 5 °C/min.
SWNTs are typically synthesized using metal catalysts. Those prepared using the HiPco method, contain residual Fe catalyst. The metal (i.e., Fe) is usually oxidized upon exposure to air to the appropriate oxide (i.e., Fe 2 O 3 ). While it is sometimes unimportant that traces of metal oxide are present during subsequent applications it is often necessary to quantify their presence. This is particularly true if the SWNTs are to be used for cell studies since it has been shown that the catalyst residue is often responsible for observed cellular toxicity.
In order to calculate the mass of catalyst residue the SWNTs are pyrolyzed under air or O 2 , and the residue is assumed to be the oxide of the metal catalyst. Water can be added to the raw SWNTs, which enhances the low-temperature catalytic oxidation of carbon. A typical TGA plot of a sample of raw HiPco SWNTs is shown in [link] .
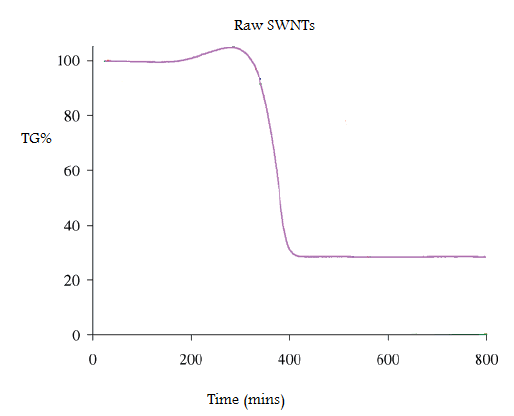
The weight gain (of ca. 5%) at 300 °C is due to the formation of metal oxide from the incompletely oxidized catalyst. To determine the mass of iron catalyst impurity in the SWNT, the residual mass must be calculated. The residual mass is the mass that is left in the sample pan at the end of the experiment. From this TGA diagram, it is seen that 70% of the total mass is lost at 400 °C. This mass loss is attributed to the removal of carbon. The residual mass is 30%. Given that this is due to both oxide and oxidized metal, the original total mass of residual catalyst in raw HiPCO SWNTs is ca. 25%.
The limitation of using SWNTs in any practical applications is their solubility; for example SWNTs have little to no solubility in most solvents due to aggregation of the tubes. Aggregation/roping of nanotubes occurs as a result of the high van der Waals binding energy of ca. 500 eV per μm of tube contact. The van der Waals force between the tubes is so great, that it take tremendous energy to pry them apart, making it very difficult to make combination of nanotubes with other materials such as in composite applications. The functionalization of nanotubes, i.e., the attachment of “chemical functional groups”, provides the path to overcome these barriers. Functionalization can improve solubility as well as processability, and has been used to align the properties of nanotubes to those of other materials. In this regard, covalent functionalization provides a higher degree of fine-tuning for the chemical and physical properties of SWNTs than non-covalent functionalization.
Functionalized nanotubes can be characterized by a variety of techniques, such as atomic force microscopy (AFM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), UV-vis spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy, however, the quantification of the extent of functionalization is important and can be determined using TGA. Because any sample of functionalized-SWNTs will have individual tubes of different lengths (and diameters) it is impossible to determine the number of substituents per SWNT. Instead the extent of functionalization is expressed as number of substituents per SWNT carbon atom (C SWNT ), or more often as C SWNT /substituent, since this is then represented as a number greater than 1.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Nanomaterials and nanotechnology' conversation and receive update notifications?