| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
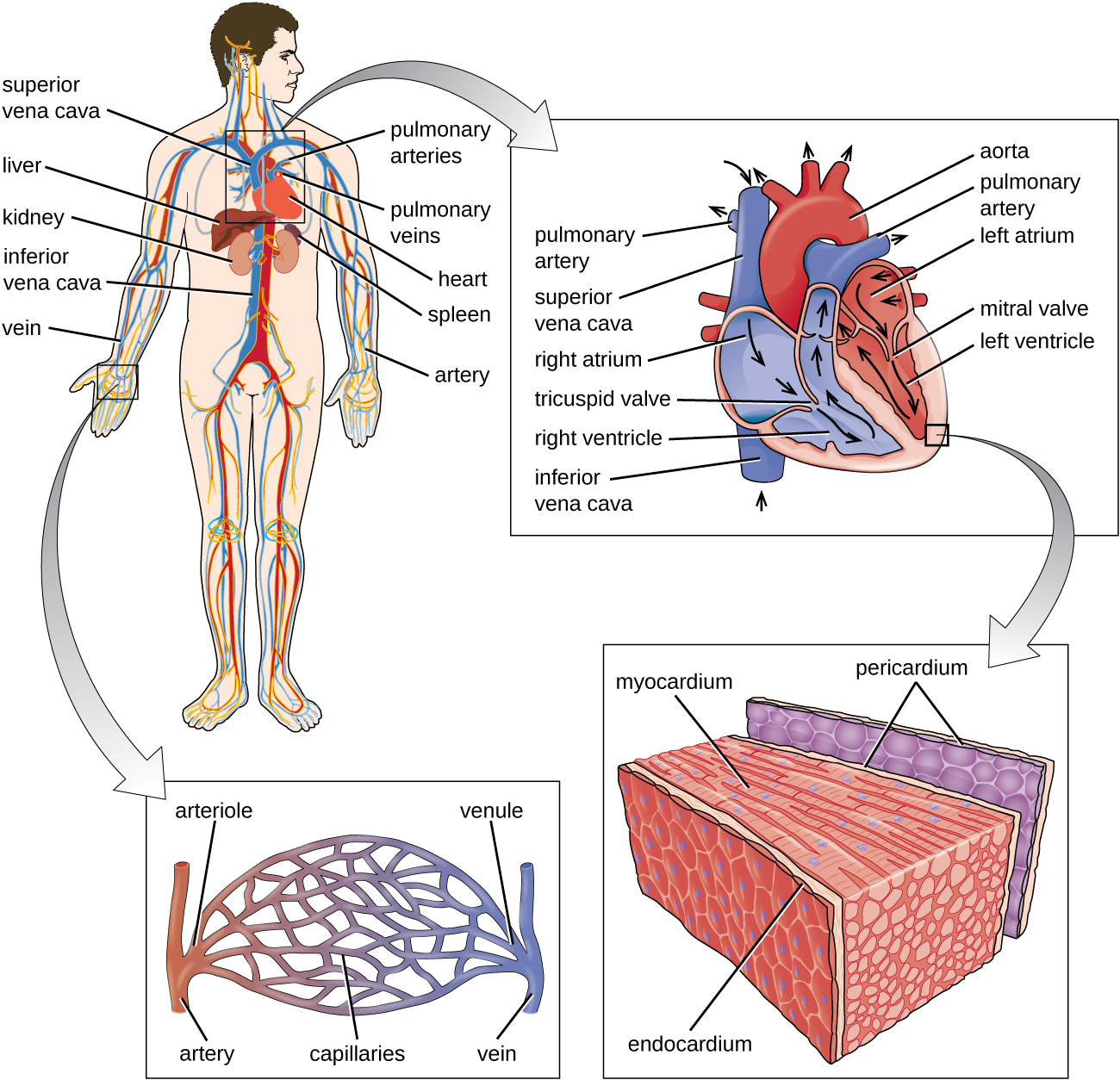
Other organs play important roles in the circulatory system as well. The kidneys filter the blood, removing waste products and eliminating them in the urine. The liver also filters the blood and removes damaged or defective red blood cells. The spleen filters and stores blood, removes damaged red blood cells, and is a reservoir for immune factors. All of these filtering structures serve as sites for entrapment of microorganisms and help maintain an environment free of microorganisms in the blood.
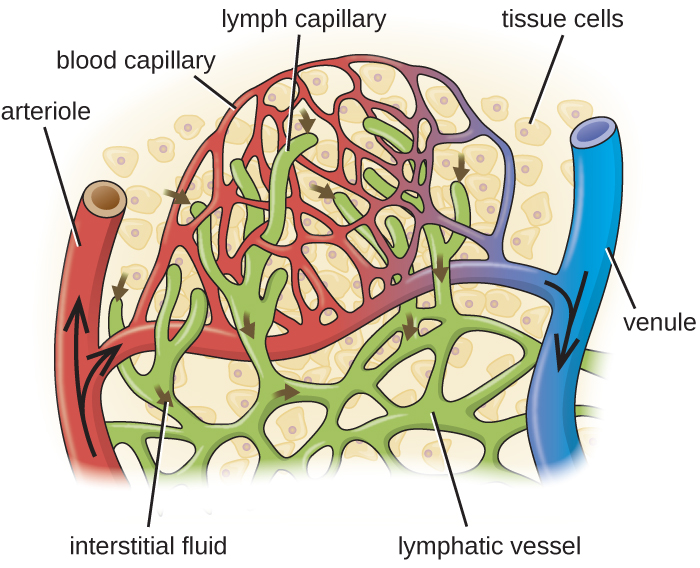
The lymphatic system is also a network of vessels that run throughout the body ( [link] ). However, these vessels do not form a full circulating system and are not pressurized by the heart. Rather, the lymphatic system is an open system with the fluid moving in one direction from the extremities toward two drainage points into veins just above the heart. Lymphatic fluids move more slowly than blood because they are not pressurized. Small lymph capillaries interact with blood capillaries in the interstitial spaces in tissues. Fluids from the tissues enter the lymph capillaries and are drained away ( [link] ). These fluids, termed lymph , also contain large numbers of white blood cells.
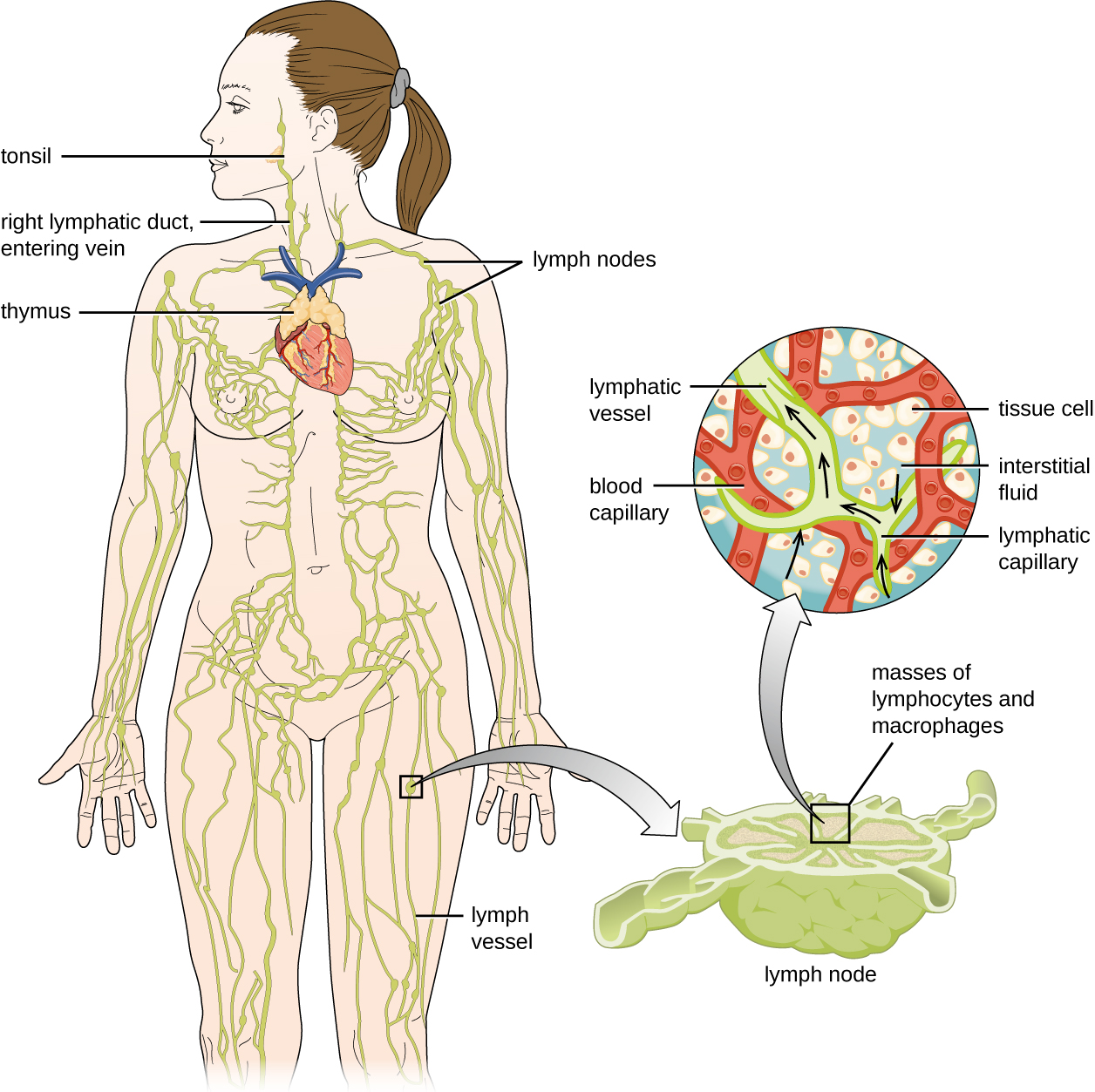
The lymphatic system contains two types of lymphoid tissues. The primary lymphoid tissue includes bone marrow and the thymus. Bone marrow contains the hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) that differentiate and mature into the various types of blood cells and lymphocytes (see [link] ). The secondary lymphoid tissue s include the spleen, lymph nodes, and several areas of diffuse lymphoid tissues underlying epithelial membranes. The spleen , an encapsulated structure, filters blood and captures pathogens and antigens that pass into it ( [link] ). The spleen contains specialized macrophages and dendritic cells that are crucial for antigen presentation, a mechanism critical for activation of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes (see Major Histocompatibility Complexes and Antigen-Presenting Cells ). Lymph nodes are bean-shaped organs situated throughout the body. These structures contain areas called germinal centers that are rich in B and T lymphocytes. The lymph nodes also contain macrophages and dendritic cells for antigen presentation. Lymph from nearby tissues enters the lymph node through afferent lymphatic vessels and encounters these lymphocytes as it passes through; the lymph exits the lymph node through the efferent lymphatic vessels ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?