| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Flagella (singular: flagellum) are tail-like cellular structures used for locomotion by some bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. Because they are so thin, flagella typically cannot be seen under a light microscope without a specialized flagella staining technique. Flagella staining thickens the flagella by first applying mordant (generally tannic acid, but sometimes potassium alum), which coats the flagella; then the specimen is stained with pararosaniline (most commonly) or basic fuchsin ( [link] ).
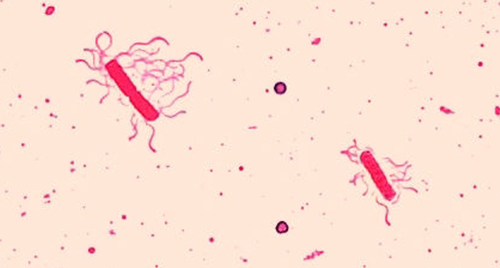
Though flagella staining is uncommon in clinical settings, the technique is commonly used by microbiologists, since the location and number of flagella can be useful in classifying and identifying bacteria in a sample. When using this technique, it is important to handle the specimen with great care; flagella are delicate structures that can easily be damaged or pulled off, compromising attempts to accurately locate and count the number of flagella.
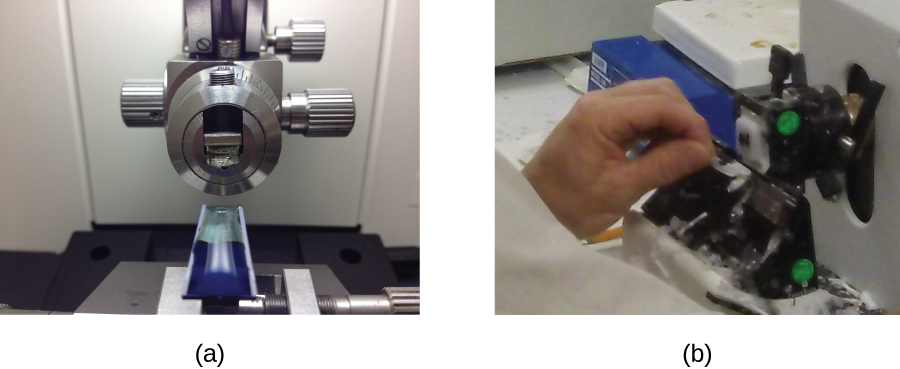
Samples to be analyzed using a TEM must have very thin sections. But cells are too soft to cut thinly, even with diamond knives. To cut cells without damage, the cells must be embedded in plastic resin and then dehydrated through a series of soaks in ethanol solutions (50%, 60%, 70%, and so on). The ethanol replaces the water in the cells, and the resin dissolves in ethanol and enters the cell, where it solidifies. Next, thin sections are cut using a specialized device called an ultramicrotome ( [link] ). Finally, samples are fixed to fine copper wire or carbon-fiber grids and stained—not with colored dyes, but with substances like uranyl acetate or osmium tetroxide, which contain electron-dense heavy metal atoms.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?