| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
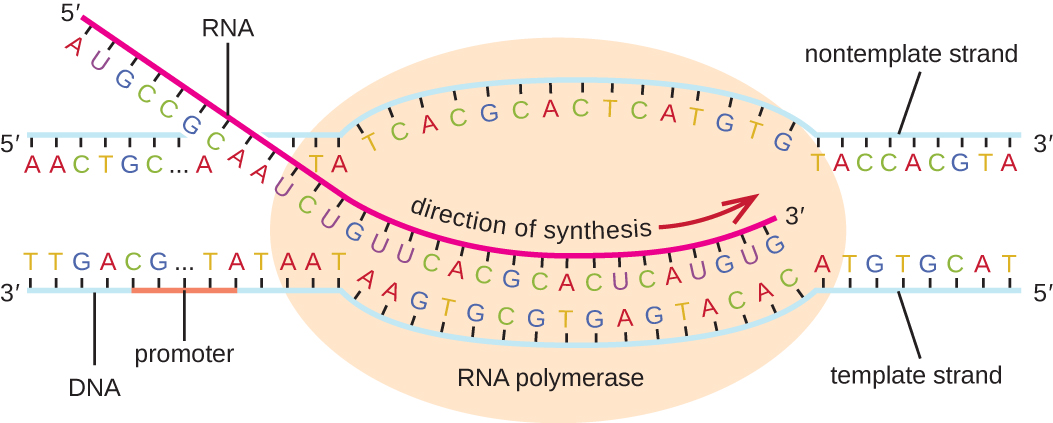
The elongation in transcription phase begins when the σ subunit dissociates from the polymerase, allowing the core enzyme to synthesize RNA complementary to the DNA template in a 5’ to 3’ direction at a rate of approximately 40 nucleotides per second. As elongation proceeds, the DNA is continuously unwound ahead of the core enzyme and rewound behind it ( [link] ).
Once a gene is transcribed, the bacterial polymerase must dissociate from the DNA template and liberate the newly made RNA. This is referred to as termination of transcription . The DNA template includes repeated nucleotide sequences that act as termination signals, causing RNA polymerase to stall and release from the DNA template, freeing the RNA transcript.
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process of transcription, with a few significant differences (see [link] ). Eukaryotes use three different polymerases, RNA polymerases I, II, and III, all structurally distinct from the bacterial RNA polymerase . Each transcribes a different subset of genes. Interestingly, archaea contain a single RNA polymerase that is more closely related to eukaryotic RNA polymerase II than to its bacterial counterpart. Eukaryotic mRNAs are also usually monocistronic, meaning that they each encode only a single polypeptide, whereas prokaryotic mRNAs of bacteria and archaea are commonly polycistronic , meaning that they encode multiple polypeptides.
The most important difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the latter’s membrane-bound nucleus, which influences the ease of use of RNA molecules for protein synthesis. With the genes bound in a nucleus, the eukaryotic cell must transport protein-encoding RNA molecules to the cytoplasm to be translated. Protein-encoding primary transcript s, the RNA molecules directly synthesized by RNA polymerase, must undergo several processing steps to protect these RNA molecules from degradation during the time they are transferred from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and translated into a protein. For example, eukaryotic mRNAs may last for several hours, whereas the typical prokaryotic mRNA lasts no more than 5 seconds.
The primary transcript (also called pre-mRNA) is first coated with RNA-stabilizing proteins to protect it from degradation while it is processed and exported out of the nucleus. The first type of processing begins while the primary transcript is still being synthesized; a special 7-methylguanosine nucleotide, called the 5’ cap , is added to the 5’ end of the growing transcript. In addition to preventing degradation, factors involved in subsequent protein synthesis recognize the cap, which helps initiate translation by ribosomes. Once elongation is complete, another processing enzyme then adds a string of approximately 200 adenine nucleotides to the 3’ end, called the poly-A tail . This modification further protects the pre-mRNA from degradation and signals to cellular factors that the transcript needs to be exported to the cytoplasm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?