| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |


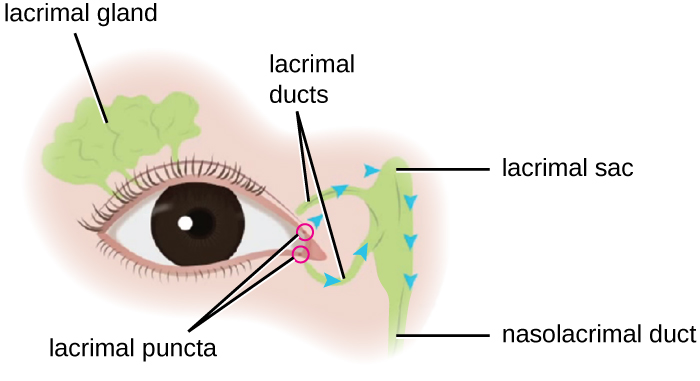
Although the eye and skin have distinct anatomy, they are both in direct contact with the external environment. An important component of the eye is the nasolacrimal drainage system, which serves as a conduit for the fluid of the eye, called tears . Tears flow from the external eye to the nasal cavity by the lacrimal apparatus, which is composed of the structures involved in tear production ( [link] ). The lacrimal gland , above the eye, secretes tears to keep the eye moist. There are two small openings, one on the inside edge of the upper eyelid and one on the inside edge of the lower eyelid, near the nose. Each of these openings is called a lacrimal punctum . Together, these lacrimal puncta collect tears from the eye that are then conveyed through lacrimal ducts to a reservoir for tears called the lacrimal sac , also known as the dacrocyst or tear sac .
From the sac, tear fluid flows via a nasolacrimal duct to the inner nose. Each nasolacrimal duct is located underneath the skin and passes through the bones of the face into the nose. Chemicals in tears, such as defensins , lactoferrin , and lysozyme , help to prevent colonization by pathogens. In addition, mucins facilitate removal of microbes from the surface of the eye.
The surfaces of the eyeball and inner eyelid are mucous membranes called conjunctiva . The normal conjunctival microbiota has not been well characterized, but does exist. One small study (part of the Ocular Microbiome project) found twelve genera that were consistently present in the conjunctiva. Abelson, M.B., Lane, K., and Slocum, C.. “The Secrets of Ocular Microbiomes.” Review of Ophthalmology June 8, 2015. http://www.reviewofophthalmology.com/content/t/ocular_disease/c/55178. Accessed Sept 14, 2016. These microbes are thought to help defend the membranes against pathogens. However, it is still unclear which microbes may be transient and which may form a stable microbiota. Shaikh-Lesko, R. “Visualizing the Ocular Microbiome.” The Scientist May 12, 2014. http://www.the-scientist.com/?articles.view/articleNo/39945/title/Visualizing-the-Ocular-Microbiome. Accessed Sept 14, 2016.
Use of contact lenses can cause changes in the normal microbiota of the conjunctiva by introducing another surface into the natural anatomy of the eye. Research is currently underway to better understand how contact lenses may impact the normal microbiota and contribute to eye disease.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?